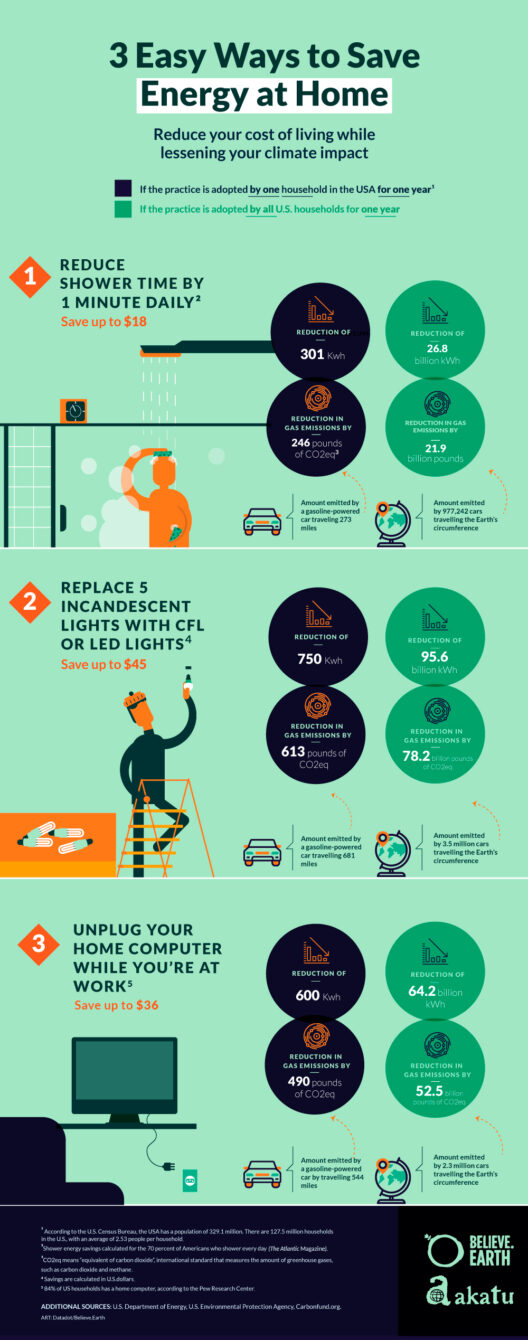
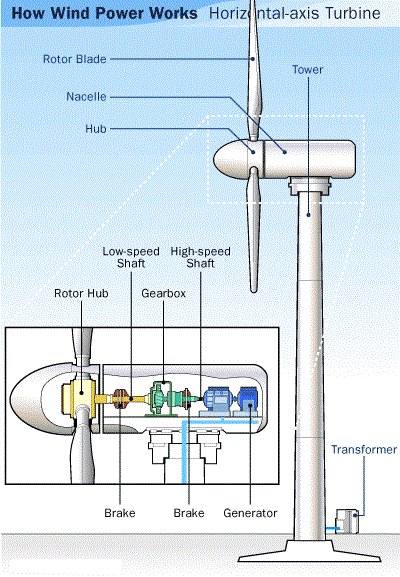
In contemporary discourse surrounding environmental issues, a persistent conflation between the terms “global warming” and “climate change” often emerges. This misunderstanding is not merely semantic; it reflects a broader confusion about the complex mechanisms governing our planet’s climate systems. To untangle this intricate web, it is essential to dissect both terms, drawing upon expert opinions to elucidate the distinctions and interconnections.
The Crucial Distinction: Global Warming vs. Climate Change
Global warming refers specifically to the long-term rise in Earth’s average surface temperature, primarily attributed to the increased concentrations of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. This phenomenon is largely the result of human activities, notably the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, which release these gases into the atmosphere. The implications of global warming are profound, leading to altered weather patterns, melting polar ice, and rising sea levels.
On the other hand, climate change encompasses a broader spectrum of alterations occurring in the Earth’s climate system, which may include global warming as a component. Climate change refers not only to temperature increases but also to shifts in precipitation patterns, the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, and changes in ecosystems and wildlife populations. Experts assert that while global warming is a significant driver of climate change, it is only one facet of a multifaceted issue.
Understanding the Parameters of the Issue
The nuances of climate change highlight the necessity of examining various indicators beyond temperature. For example, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports emphasize that while global temperatures are rising, other critical factors such as ocean acidification, glacial retreat, and changes in biodiversity must also be scrutinized to gain a comprehensive understanding of climate dynamics. This reveals a more complex narrative: one where the increase in temperature is merely the tip of the iceberg—a phenomenon enfolded within a larger story of ecological transformation.
The Interplay of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors
Further complicating the distinction between global warming and climate change is the interplay between natural variability and human-induced alterations. Experts acknowledge that Earth’s climate is inherently subject to natural fluctuations resulting from solar radiation variations, volcanic activity, and oceanic currents. However, the current trajectory of climate change is unprecedented in its rapidity and intensity, leading many scientists to classify it as anthropogenic in origin. In this context, understanding the interplay between natural and human factors becomes critical for effective policy formulation and public awareness.
Societal Implications: Why the Distinction Matters
The confusion between these two terms directly impacts how societies respond to environmental challenges. Misunderstandings may lead to inadequate policy measures or a lack of cohesive action against climate threats. For instance, individuals who perceive global warming merely as a radical increase in temperature may be less inclined to consider the broader consequences of climate change, such as food security issues, water shortages, and public health crises. Thus, it is imperative that clear communication from leaders and educators delineates the nuances between global warming and climate change to facilitate informed dialogue and inspire action.
Engaging Narratives: How Global Warming and Climate Change Resonate with Public Consciousness
There is an inherent fascination with both terms, which often stems from their portrayal in media, literature, and even art. Global warming, with its stark imagery of melting glaciers and rising seas, evokes visceral emotional responses. In contrast, climate change, with its broader implications, invites more profound reflection on societal structures, environmental ethics, and our collective future. This dual fascination reveals a deeper connection to humanity’s role in shaping the environment and raises existential questions about our responsibility toward future generations.
The Role of Scientists and Activists in Shaping Understanding
In the pursuit of clarity, scientists play a vital role in educating the public. They use rigorous research and empirical evidence to disentangle misconceptions and articulate the implications of both global warming and climate change. Environmental activists, on the other hand, amplify these messages through advocacy and awareness campaigns, seeking to inspire collective action. The collaboration between scientists and activists serves as a powerful nexus for enacting change, ensuring that the imperative of addressing climate issues transcends personal misunderstandings and becomes a collective priority.
Conclusion: Embracing Complexity in the Pursuit of Environmental Solutions
Ultimately, acknowledging the distinction between global warming and climate change is fundamental to addressing the environmental crises plaguing the planet. While global warming constitutes a critical piece of the puzzle, it is by no means the entirety of the picture. As the global community grapples with these interconnected challenges, fostering a nuanced understanding—paired with strategic action—will be vital for cultivating a sustainable future. Combating climate change requires informed discourse that embraces complexity, encouraging societies to engage with the magnitude of these issues rather than reductively simplifying them into catchy phrases. Only through this lens can humanity hope to navigate the currents of climate transformation and emerge resilient in the face of impending challenges.