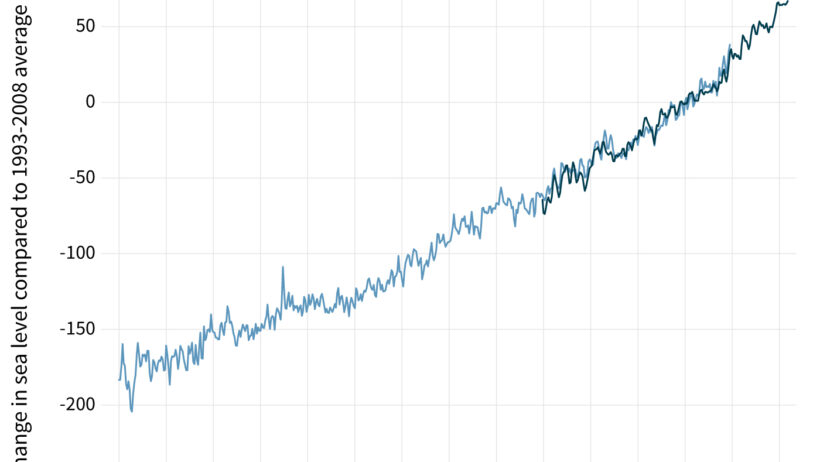
Rising sea levels are one of the most palpable effects of climate change that humanity is facing today. Understanding the intricacies of this phenomenon reveals a complex interplay between various factors, including melting ice caps, thermal expansion, and human intervention. This article delves into the science behind sea-level rise, explores its implications, and examines the necessary responses to mitigate its impact.
As global temperatures rise, the oceans expand and absorb more water, contributing to an increase in sea levels. This critical issue necessitates a deep dive into the underlying mechanisms driving these changes. Through the lens of scientific research, we can decipher how human activity accelerates these natural processes.
The Interconnected Factors of Sea-Level Rise
A variety of elements contribute to the intricate puzzle of rising sea levels. Two primary drivers stand out: thermal expansion and the melting of ice masses. When water warms, it expands—a concept known as thermal expansion. As greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, seawater warms and occupies more space, resulting in elevated sea levels.
Equally pivotal is the melting of glaciers and polar ice caps. Ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica hold vast volumes of water, and their accelerated melting adds substantial amounts to ocean levels. Studies indicate that these regions are losing ice at an alarming rate, primarily due to increased temperatures, which further compounds the issue.
A comprehensive understanding of these phenomena outlines the multifaceted relationships at play. For example, while thermal expansion is a direct consequence of heat retention in the atmosphere, glacial melting can also prompt thermal feedbacks that accelerate warming further. Increasing meltwater from glaciers can dilute ocean salinity, which may also affect ocean currents and weather patterns, elucidating the complexities of sea-level dynamics.
The Global Impact of Rising Sea Levels
The ramifications of rising sea levels are staggering and omnipresent across the globe. Coastal communities, already vulnerable, face increasing risks of flooding, erosion, and habitat loss. Major cities such as Miami, New York, and New Orleans are grappling with the reality of encroaching seawater, necessitating innovative adaptation strategies.
Moreover, the effects don’t limit themselves to geographic shores; they extend to economic systems, agriculture, and biodiversity. Saltwater intrusion can compromise freshwater reserves, impacting agriculture and drinking water supplies. This disruption creates a ripple effect, affecting food security and economic stability, particularly in developing nations that may lack the resources to respond adequately.
The biodiversity crisis is another major concern stemming from rising sea levels. Coastal ecosystems, such as mangroves and marshes, provide vital habitats for myriad species. As ocean levels rise, these areas face inundation, leading to decreased biodiversity and threatening the ecosystems’ natural services, such as carbon sequestration and natural habitat stabilization.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
A recognition of the underlying challenges posed by rising sea levels compels action. Strategies to mitigate the effects and adapt to the changes are critical components of addressing climate change. Governments, communities, and individuals are faced with the task of implementing effective solutions.
Firstly, reducing greenhouse gas emissions remains paramount. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and fostering sustainable transportation can significantly reduce our carbon footprint. Legislative measures aimed at limiting emissions can also drive collective efforts to combat climate change.
Secondly, coastal cities must invest in adaptive infrastructure. This includes implementing sea walls, restoration of wetlands, and improving drainage systems. For example, New York City has taken significant strides since Hurricane Sandy to enhance its coastal resilience through green infrastructure and community planning initiatives.
Lastly, fostering community awareness and preparedness is essential. Educating the public about the risks associated with rising sea levels can empower individuals to participate in local initiatives and advocate for policy changes. Grassroots movements have demonstrated that informed and engaged communities can affect substantial shifts in government policy, particularly around climate action.
The Path Forward: An Urgent Call to Action
As sea levels continue to rise, the inexorable link between climate change and this phenomenon becomes increasingly clear. The changes that lead to higher ocean levels are driven primarily by human activities, rendering it our responsibility to address the crisis. Through a holistic understanding of the factors at play, acknowledging the profound implications on ecosystems and human societies, and implementing robust mitigation and adaptation strategies, we can pave the way for a resilient future.
Ultimately, while the science can appear daunting, it is imperative to remember that actions taken today can shape the trajectory of our planet. Every effort counts in reversing the trend of climate change and its ensuing consequences, including rising sea levels. We must act collectively and decisively as stewards of the Earth to ensure a sustainable and livable planet for future generations.