The greenhouse effect, often maligned as a primary culprit of climate change, is an intricate phenomenon that warrants a comprehensive exploration. While the prevailing narrative tends to paint greenhouse gases as unequivocally harmful, a more nuanced perspective reveals that they play a pivotal role in sustaining life on Earth. This article delves into the complexities of the greenhouse effect, elucidating its pros and cons to foster a deeper understanding of this ecological paradigm.
In an era where climate change dominates discourse, the necessity to disentangle fact from fear is paramount. What if, rather than presenting a binary choice of good versus evil, we could appreciate the multifaceted nature of greenhouse gases? This exploration not only promises to shift our perspective but also ignites curiosity into the delicate balance our environment maintains.
Let us embark on a journey to explore the dual nature of greenhouse gases, tracing their role from atmospheric protectants to climate disruptors.
Understanding the Greenhouse Effect
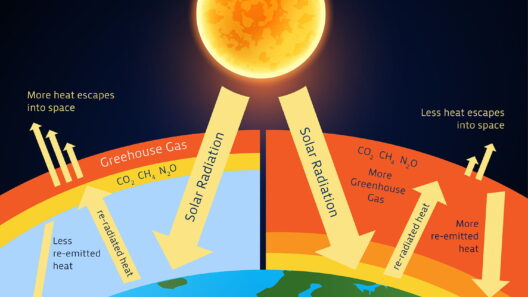
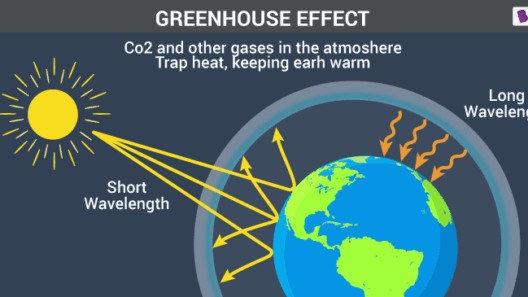
To grasp the ramifications of the greenhouse effect, one must first understand its fundamental mechanics. Simply put, the greenhouse effect occurs when certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere trap heat from the Sun. This heat retention is crucial for maintaining the planet’s temperature—without it, Earth would be a frozen wasteland.
Key players in this atmospheric orchestra include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). Each of these greenhouse gases possesses unique properties, varying in their heat-trapping capacity and duration within the atmosphere. For instance, methane is significantly more effective at trapping heat than carbon dioxide, albeit for a shorter duration. This variance complicates the conversation around which gases should be minimized in emissions strategies.
The Natural Balance: Benefits of Greenhouse Gases
The most salient benefit of the greenhouse effect is its essential role in creating a habitable planet. The natural greenhouse effect maintains Earth’s average temperature at around 59°F (15°C). In absence of this effect, temperatures would plummet to an inhospitable average of −0°F (−18°C), rendering life as we know it virtually impossible.
Moreover, greenhouse gases help regulate weather patterns and seasons. They foster the precipitation cycles that nourish crops and replenish freshwater sources. The interplay of these gases facilitates ecosystems, enabling biodiversity to flourish. From the tiniest microorganisms in the soil to the tallest trees in the rainforest, life is intricately woven into this climatic framework.
In essence, greenhouse gases have provided the bedrock of agricultural evolution. The agricultural practices that enable food security across the globe have thrived under the umbrella of this thermoregulated environment. To dismiss the benefits entirely overlooks the foundational role that these gases play in our biological systems.
However, the situation becomes intricate when human activities—namely fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes—unleash excess greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
The Dark Side: Harmful Impacts of Excessive Greenhouse Gases
While greenhouse gases are indispensable to life, their overabundance leads to detrimental consequences. Human-induced activities have escalated concentrations of CO2 and methane to unprecedented levels, driving global temperatures higher and disrupting ecosystems. This phenomenon is known as anthropogenic climate change, and its impacts are far-reaching.
As temperatures rise, we witness extreme weather events becoming more common—intensified hurricanes, prolonged droughts, and rising sea levels threaten not only natural habitats but also human livelihoods. Species extinction rates are accelerating, as organisms struggle to adapt to the rapid climate changes. Coral reefs, which are vital to marine biodiversity, are particularly vulnerable to temperature fluctuations and ocean acidification.
Additionally, the feedback loops created by climate change exacerbate the problem. Melting ice caps reduce the Earth’s albedo effect—the ability to reflect solar radiation—further warming the planet. Thawing permafrost releases copious amounts of methane, causing an amplification of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, perpetuating a vicious cycle.
Finding the Balance: Sustainable Solutions and Perspectives
Amidst the looming threat of climate change, the conversation must shift toward sustainability and balance. Understanding that greenhouse gases are not strictly adversarial allows for the formulation of innovative solutions that harness their benefits while curbing their excesses.
Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power can significantly reduce carbon emissions while ensuring the continued generation of electricity. Adoption of regenerative agricultural practices can enhance soil health, sequester carbon, and mitigate the release of greenhouse gases. By embracing a circular economy, we can reduce waste and minimize our environmental footprint.
Moreover, investing in technology for carbon capture and storage (CCS) presents a promising avenue for mitigating the impacts of greenhouse gases. These innovations can facilitate the removal of CO2 from industrial processes, offering an additional layer of safeguarding the atmosphere.
Educating and engaging local communities on environmental stewardship can empower citizens to take an active role in combating climate change. Advocacy for policy changes and sustainable practices can create a ripple effect, amplifying efforts to balance atmospheric gases.
In conclusion, the greenhouse effect is a double-edged sword— integral to life on Earth while also capable of precipitating catastrophic climate changes when subjected to human excesses. By nurturing a comprehensive understanding of its implications, society can approach environmental challenges with informed strategies that protect our planet. A balanced view of greenhouse gases enables us to appreciate their essential roles while maintaining vigilant stewardship over our Earth’s delicate climatic equilibrium.