In our quest for sustainable energy alternatives, the allure of wind power stands out as one of the most fascinating aspects of renewable energy. The winds—ever-changing and dynamic—have captured humanity’s imagination and substance for centuries. However, the pivotal question remains: Is wind truly renewable energy? This inquiry transcends mere semantics; it delves into the very fabric of our energy systems and their impact on the planet. In this exploration, we will dissect the essence of wind as an inexhaustible power source, elucidate its aesthetic appeal, and glean the nuances that underscore its viability in a sustainable future.
Understanding Wind as a Natural Phenomenon
To appreciate wind power, we must first understand the elemental forces that create wind itself. Wind arises from the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface by the sun. This phenomenon creates variations in air pressure, leading to the movement of air from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. The Earth’s rotation further influences atmospheric patterns, resulting in complex wind currents that traverse vast distances.
The distinction between renewable and non-renewable energy hinges on the sustainability of the energy source’s availability. In this regard, wind is categorized as renewable. The inexhaustible nature of wind energy stems from its ongoing regeneration through natural climatic processes. While some argue that local geographical constraints and changing weather patterns might impact wind availability, the overarching principle remains steadfast: as long as the sun shines and the Earth rotates, wind will be within our grasp. This ceaseless vitality makes wind an invigorating player in our renewable energy arsenal.
The Aesthetic Appeal of Wind Power
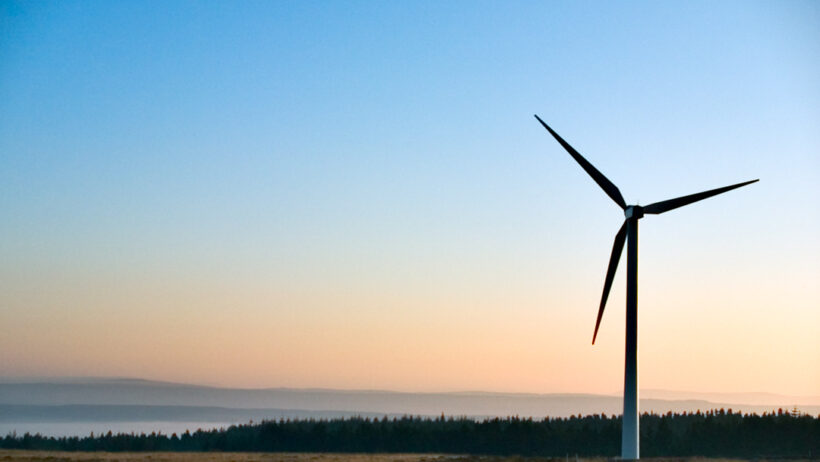
Aesthetics and environmental consciousness often intertwine, especially in the realm of renewable energy. Wind turbines, with their towering structures and gracefully sweeping blades, add a striking silhouette to the landscapes they inhabit. Whether perched atop rolling hills or standing sentinel by open seas, these elegant machines harmonize with nature in a way that fossil fuel infrastructures simply cannot.
For many, wind farms symbolize hope and progress—a tangible manifestation of our collective effort to transition towards cleaner energy sources. The sight of turbines dancing in the breeze can evoke feelings of serenity and optimism. Indeed, the picturesque vistas that accompany these installations serve as reminders of the delicate balance between modern energy demands and environmental stewardship. Wind energy is not just about functionality; it’s also about embracing a legacy of sustainable beauty.
The Ecological Impact of Wind Power
Wind energy’s classification as renewable is further reinforced by its relatively low ecological footprint. Unlike fossil fuels, which emit copious amounts of greenhouse gases and other pollutants when burned, wind turbines generate electricity without producing direct emissions. This characteristic plays a critical role in combating climate change and mitigating environmental degradation.
Moreover, once installed, wind farms occupy minimal ground space compared to traditional energy facilities, allowing for agricultural and recreational uses to continue beneath and around the turbines. This multifaceted approach to land use can enhance local economies while preserving the natural landscape. Wind energy, therefore, exemplifies a harmonious coexistence of industry and nature, striking a compelling balance that benefits both human society and the ecological web that sustains it.
Challenges and Criticisms: A Balanced Perspective
No discussion of wind energy is complete without addressing its associated challenges. Critics often cite issues such as noise pollution, threats to wildlife, and the intermittent nature of wind as obstacles to widespread adoption. Indeed, the relationship between wind turbines and avian populations has sparked considerable debate, compelling engineers and environmentalists alike to devise innovative solutions to mitigate risks to birds and bats. Mesh screening and advanced sound-dampening technology are some of the advancements being harnessed to address these concerns.
Moreover, the sporadic availability of wind raises questions about reliability. However, advancements in energy storage technology and grid integration are continually breaking down barriers that once impeded the effectiveness of wind power as a consistent energy source. As these technologies evolve, the potential of wind energy as a steadfast component of our energy mix becomes increasingly attainable.
Wind Energy: A Future Built on Possibilities
The tantalizing potential of wind energy stretches far beyond current applications. As we stand on the precipice of a global energy transition, investing in wind power unlocks a plethora of opportunities. The innovation within this field invites collaboration across interdisciplinary boundaries, forging partnerships among scientists, engineers, and local communities.
Moreover, wind energy has the potential to revolutionize economic models surrounding energy production. By decentralizing energy generation through small-scale wind projects, communities can reclaim their energy futures, fostering resilience against market fluctuations and energy insecurity.
Conclusion: Embracing the Winds of Change
In summation, wind power inherently embodies the principles of renewable energy—a sustainable, aesthetically pleasing, and ecologically responsible alternative to traditional fossil fuels. Its inexhaustible nature, coupled with the continuous desire for innovation, positions wind energy as a linchpin in our pursuit of a sustainable future. As we harness the power of the winds, we not only energize our present but also secure a cleaner, greener planet for generations to come. In the dance of blades and the whisper of the breeze, we find the promise of a transformative and enduring legacy.