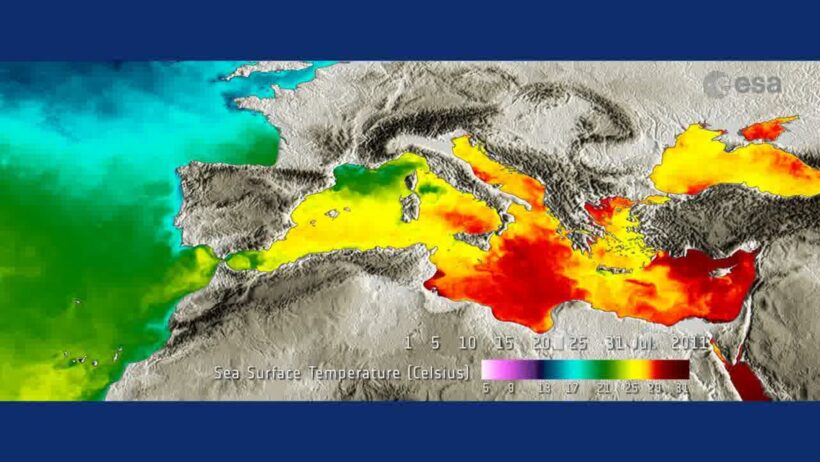
The Mediterranean region is renowned for its picturesque vistas and lush landscapes, yet it is also a stage for complex climatic phenomena that shape its environment. From charming sea breezes that offer a reprieve from intense summer heat to the agonizing droughts that threaten the delicate balance of ecosystem and human life, the Mediterranean climate possesses secrets that merit exploration. This discussion will delve into the intricacies of the Mediterranean climate, examining its distinctive characteristics, the underlying causes of summer droughts, and the potential implications for the future in the face of climate change.
The Mediterranean climate, typified by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, is largely influenced by its geographical setting. Bordered by the Mediterranean Sea, the region encompasses several countries—including Spain, Italy, Greece, and parts of North Africa. The maritime location plays a pivotal role in shaping the local climate, as the sea acts as a thermal reservoir. This phenomenon results in moderated temperatures, creating the perfect backdrop for an array of biodiversity. However, this delicate equilibrium can be easily disrupted, leading to dramatic and adverse climatic events.
One of the secrets of the Mediterranean climate lies in the sea breezes that sweep across the coastal areas during the summer months. These breezes are primarily generated by the differential heating of land and sea. As the sun warms the land, the air above it becomes less dense and rises, creating an area of low pressure. Conversely, the cooler sea air with higher pressure rushes in to fill this void, bringing relief from the oppressive heat. This process not only ameliorates temperatures but also contributes to the dispersal of moisture, which is crucial for sustaining localized ecosystems.
However, the intricate dance of land and sea is not the only player in the Mediterranean’s climatic narrative. The region is also subject to the phenomenon known as the Mediterranean oscillation, which is characterized by fluctuations in sea surface temperatures and atmospheric pressure. Not only does this oscillation influence precipitation patterns, but it also plays a crucial role in determining drought occurrences. The increasing volatility of this oscillation raises crucial questions regarding the sustainability of agriculture and water resources in the region.
The summer droughts that plague the Mediterranean basin have profound implications, leaving an indelible mark on the landscape and its inhabitants. In recent years, these droughts have been exacerbated by a multifaceted array of factors including urbanization, deforestation, and climate change. As land surfaces become increasingly impervious due to development, rainwater cannot infiltrate the soil effectively, leading to heightened runoff and diminished groundwater recharge. This results in a vicious cycle of reduced water availability during critical agricultural periods.
The consequences of summer droughts extend beyond the immediate impacts on irrigation and crop yields; they manifest as broader ecological ramifications. The diminished water supply threatens various flora and fauna, pushing some species toward extinction and altering the fragile balance within ecosystems. Additionally, prolonged drought conditions can lead to an increase in forest fires, with catastrophic consequences for biodiversity, air quality, and human health. With the Mediterranean region being a biodiversity hotspot, the implications of habitat loss and species decline cannot be overstated.
Moreover, these climatic shifts can exacerbate socio-economic disparities within Mediterranean countries. Agriculture, a cornerstone of many local economies, becomes increasingly untenable as farmers struggle to adapt to erratic weather patterns. Smallholder farmers, who lack the resources to implement advanced irrigation technologies or drought-resistant crops, are often the hardest hit. Thus, understanding the underlying climatic secrets is imperative for developing strategies that promote resilience and sustainability in the face of escalating environmental challenges.
Another critical aspect of the Mediterranean climate is the interplay between human activities and natural systems. Urbanization has led to localized heat islands and altered wind patterns, diminishing the restorative effects of sea breezes. This anthropogenic influence underscores the necessity for sustainable urban planning that fosters synergistic relationships between built environments and natural ecosystems. By preserving green corridors and enhancing vegetative cover, cities can mitigate the adverse effects of climate change and promote a more balanced urban climate.
There is also an urgent need for cohesive policies that address water management, conservation, and drought preparedness. As climate models predict an increase in the frequency and severity of droughts, investment in infrastructure for water conservation becomes paramount. Innovative technologies such as rainwater harvesting, advanced irrigation methods, and the reuse of treated wastewater should be prioritized. A concerted effort towards sustainable practices in agriculture, such as organic farming and agroforestry, can also enhance soil health and resilience, ultimately fostering a sustainable balance between human aspirations and ecological integrity.
The Mediterranean climate, with its array of quirks and complexities, requires a multifaceted approach to harness its secrets while safeguarding its inherent richness. The juxtaposition of sea breezes and summer droughts serves as a compelling reminder of the fragility of this extraordinary region. In the pursuit of resilience, collaboration amongst governments, scientists, and local communities is essential. Only through a shared commitment to understanding and adapting to the nuances of the Mediterranean climate can we hope to preserve this invaluable ecosystem for future generations.
As the Mediterranean oscillates between its endearing charm and daunting challenges, it is imperative that we heed the lessons it offers. The narrative of the Mediterranean climate is not simply one of beauty; it is a compelling call to action for sustainable coexistence with nature. In facing the unpredictable realities of climate change, we are compelled to delve deeper into the secrets of the Mediterranean, striving to unlock methods of adaptation that honor both humanity and the environment.