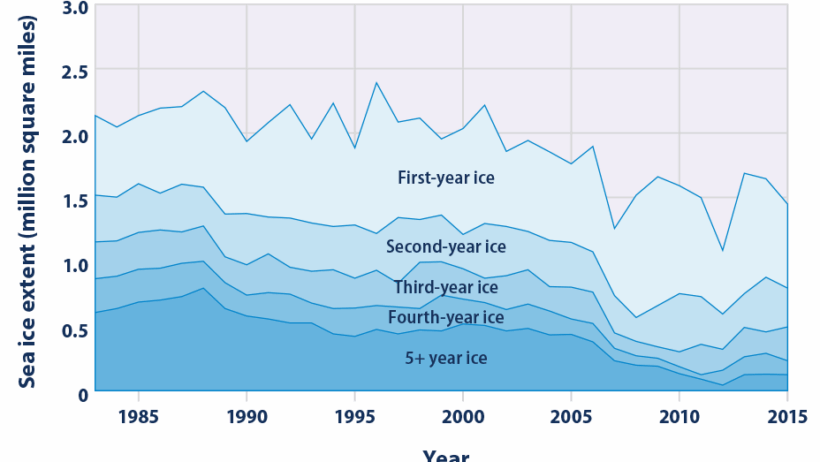
In recent decades, myriad studies have illustrated the profound and alarming effects of global warming, particularly in polar regions. The phenomenon of melting sea ice is one of the most striking indicators of climate change. The Arctic and Antarctic are experiencing unprecedented levels of ice loss, leading to multifaceted environmental consequences. This article endeavors to examine the intricate relationships between global warming and the shrinking sea ice, while also addressing a common observation—our fascination with these delicate ecosystems.
Sea ice serves as a formidable barometer of climate conditions, significantly influencing marine ecosystems, weather patterns, and global sea levels. The Arctic, characterized by its frozen expanse predominantly comprised of multi-year ice, has not only been a symbol of nature’s beauty but also a critical component of the Earth’s climate system. It reflects sunlight, helping to regulate the planet’s temperature. However, as global temperatures rise because of anthropogenic emissions, this icy landscape is undergoing rapid transformation.
One might question why melting sea ice captures the attention of scientists and environmentalists alike. The reason lies beyond its aesthetic allure; it signifies profound changes in the planet’s climatic equilibrium. The polar regions are heating up at a rate significantly faster than the global average—a phenomenon known as Arctic amplification. This means that as the Earth warms, the Arctic experiences even more drastic temperature increases, leading to accelerated ice melt.
The ramifications of diminishing sea ice are manifold. First and foremost, melting ice contributes to rising sea levels, a critical issue facing coastal nations. As glaciers and ice sheets disintegrate, an influx of freshwater enters the ocean, which can lead to catastrophic flooding in vulnerable areas. The World Meteorological Organization has predicted that by the end of the century, global sea levels could rise by over a meter if current trends continue, representing a major threat to millions of people.
Moreover, the loss of sea ice disrupts the delicate balance of marine ecosystems. Sea ice serves as a habitat and hunting ground for various species, including polar bears, seals, and walruses. These creatures depend on the presence of sea ice for breeding and feeding. The decline in ice cover can lead to a cascading effect throughout the food web, threatening biodiversity and revealing the interconnectedness of terrestrial and marine life. As apex predators like polar bears struggle to find food, their populations dwindle, jeopardizing the ecological integrity of their environments.
Another less obvious, yet equally critical impact of melting sea ice involves the feedback loops that exacerbate global warming. As ice retreats, darker ocean waters are exposed. These waters absorb significantly more sunlight than ice, leading to a further increase in surface temperatures. This vicious cycle—where melting leads to warming, which, in turn, leads to further melting—underscores the urgency of addressing climate change as an interrelated global crisis.
The socio-economic implications of sea ice loss are profound as well. Indigenous communities in the Arctic rely on traditional hunting routes that have been in place for generations. The alteration of these patterns due to ice melt not only affects their livelihoods but also erodes their cultural identity. Additionally, the opening of new shipping routes as ice diminishes poses legal and economic considerations, creating potential for geopolitical conflicts. Important maritime passages, such as the Northwest Passage, are becoming increasingly navigable. The rush to exploit these waterways reveals the predatory tendencies of globalization, where natural resources become target commodities.
Yet, amid these alarming changes, there exists a remarkable aspect of human fascination with the Arctic. The imagery of vast, pristine icefields evokes a sense of wonder, kindling a desire to protect these majestic landscapes. Documentaries, art, and literature have drawn attention to the innate beauty and the existential plight of polar regions, fostering a collective environmental consciousness. This fascination can play an essential role in advocacy efforts, inspiring action against climate change and its repercussions.
Furthermore, advancements in technology have enabled scientists to monitor and predict changes in sea ice dynamics more effectively. Satellite imagery and climate models are central to understanding how these shifts impact wider climate patterns. As knowledge expands, so does the potential for informed policy-making and public engagement. The narrative surrounding sea ice thus transforms from one of passive observation to one of proactive intervention.
In conclusion, the phenomenon of melting sea ice serves as a critical touchstone in the discourse on global warming and climate change. While it captivates our attention aesthetically, its implications extend far deeper into ecological, socio-economic, and cultural realms. There is an urgent need to address the threats posed by climate change, not only to preserve the fragile ecosystems of polar regions but also to secure a sustainable future for the planet. The convergence of scientific data, environmental advocacy, and community resilience will determine how effectively we navigate the challenges posed by melting worlds. As stewards of the Earth, it is imperative to take action now, ensuring that the stories of our polar realms do not fade into memory but instead inspire collective efforts towards restoration and sustainability.