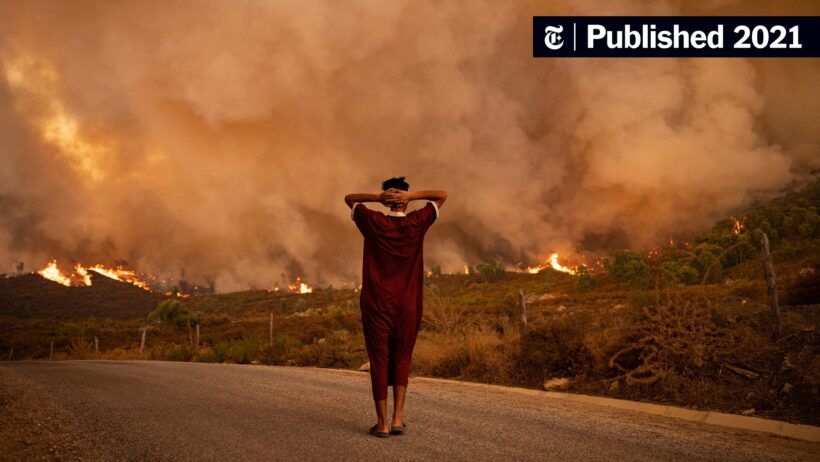
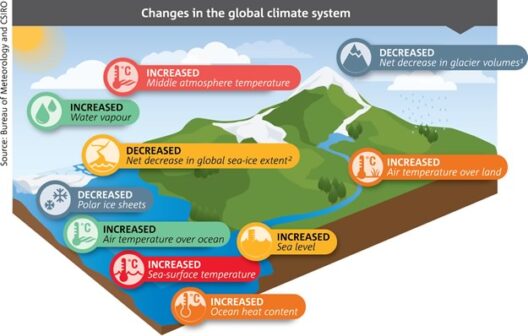
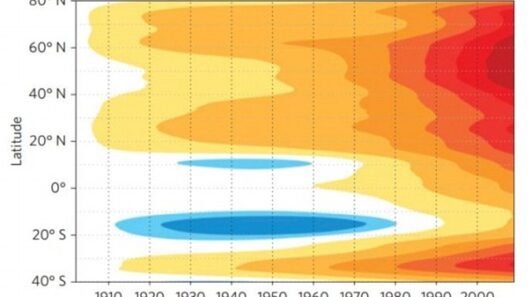
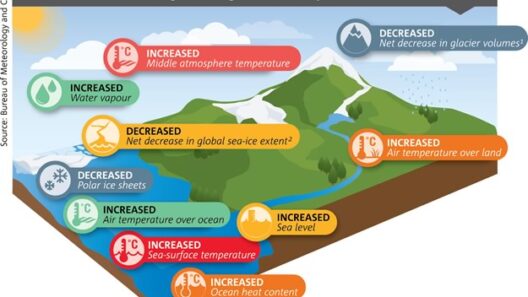
Global warming, a predominant facet of climate change, has insidious ramifications that extend far beyond rising temperatures. It threatens the very fabric of ecosystems, economies, and human health. As the planet warms, we witness a cascade of deleterious effects that span the globe, impacting both the natural world and humanity in profound ways. Herein lies an extensive exploration of these multifaceted adverse consequences, delineating the intersection of environmental degradation and human vulnerability.
Firstly, the escalation of temperatures due to global warming induces severe alterations in weather patterns. As the atmosphere warms, it holds more moisture, resulting in intensified precipitation and extreme weather events—hurricanes, floods, and droughts. These phenomena wreak havoc on infrastructure and agricultural productivity. Agricultural systems, which rely on specific climatic conditions, face profound challenges. Crops that are sensitive to temperature fluctuations may yield less than anticipated, leading to food scarcity and inflated prices. Notably, regions already susceptible to food insecurity experience exacerbated conditions, creating a vicious cycle of hunger and poverty.
Moreover, the phenomenon known as “ocean acidification” arises as oceans absorb excess carbon dioxide. This acidification diminishes the pH level of seawater, adversely affecting marine life. Coral reefs, often dubbed the “rainforests of the sea,” suffer from bleaching—a process that compromises their ability to thrive. As the coral ecosystems decline, the myriad of species dependent on these habitats face extinction. Furthermore, fisheries that support millions of livelihoods across the globe encounter dwindling stocks, threatening economic stability in coastal communities.
Human health also emerges as a critical concern in the context of global warming. The increase in temperature fosters the proliferation of vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever, as mosquitoes expand their habitat into previously inhospitable areas. Heatwaves and extreme weather exacerbate respiratory and cardiovascular ailments, particularly among vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with preexisting health complications. The interplay between heat and air quality can lead to more acute health crises, underscoring the urgent need for comprehensive public health strategies.
Another negative impact manifested through global warming is the phenomenon of sea-level rise. Melting glaciers and ice sheets, coupled with thermal expansion of ocean waters, contribute to increasingly encroaching coastlines. Small island nations and low-lying coastal regions are on the frontlines, facing existential threats as their land diminishes. The prospect of displacement and forced migration looms large, engendering climate refugees as entire communities seek sanctuary from rising tides. This human displacement not only impacts the individuals directly affected but also triggers geopolitical tensions, fostering strife as resources become strained.
Deforestation, often exacerbated by climate change, further compounds the detrimental effects of global warming. The act of burning forests to make way for agriculture releases significant amounts of carbon dioxide, perpetuating the very cycle of global warming. Additionally, forests act as carbon sinks, sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Their removal reduces this capacity, rendering the environment more susceptible to warming. Biodiversity loss ensues, as countless species—the irreplaceable components of Earth’s ecosystems—are thrust into precarious situations, threatening entire ecological balances. The extinction of species irrevocably alters ecosystems, undermining their resilience to change.
Economic repercussions are inextricably linked to the environmental fallout of global warming. Key industries such as agriculture, fishing, and tourism face substantial risks due to climatic unpredictability. The costs associated with disaster response, recovery, and infrastructure rehabilitation soar, diverting funds from critical development initiatives. Additionally, insurance markets grapple with rising claims stemming from climate-related disasters, increasing premiums for consumers and businesses alike. Economic disparities deepen as marginalized communities, often least responsible for carbon emissions, bear the brunt of these changes, amplifying social injustice.
In response to the deleterious impacts of climate change, the global community must engage in concerted action. Prioritizing sustainable practices, transitioning toward renewable energy sources, and fostering resilience in urban infrastructure is paramount. The adoption of circular economy principles can mitigate resource depletion while promoting equitable economic growth. Educational initiatives that raise awareness about climate change can empower individuals to contribute meaningfully to a collective solution.
In summary, the negative ramifications of global warming underscore a pressing need for immediate and multifaceted action. Rising temperatures stir a string of adversities—severe weather events, health crises, and economic instability—that threaten both the environment and humanity. Addressing these challenges requires a unified approach, incorporating scientific innovation, public policy reform, and community engagement. By acknowledging the interconnectedness of our ecosystems and societies, we can forge pathways towards a more sustainable future, ultimately striving to protect the Earth for generations to come.