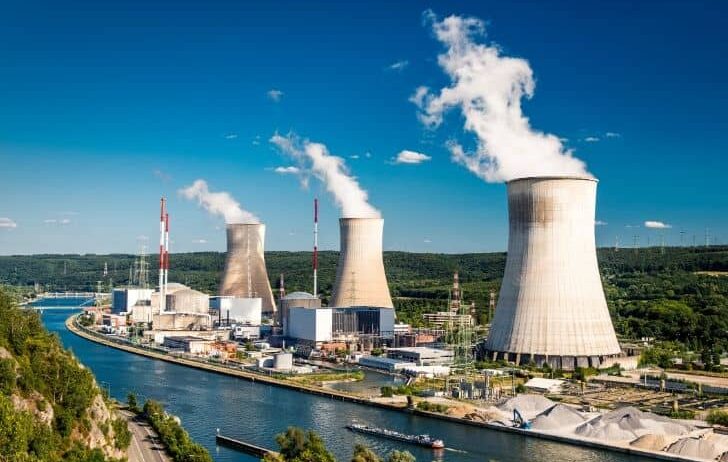
Nuclear energy stands as one of the most compelling components of the contemporary energy landscape. Like a double-edged sword, it offers a plethora of advantages while simultaneously posing significant risks. As the world grapples with climate change and dwindling fossil fuel reserves, understanding how to conserve and use nuclear energy more judiciously has become imperative. Thus, the quest for nuclear know-how emerges as a strategic fulcrum in our ongoing pursuit of sustainability. This exploration will delve into the myriad strategies for conserving nuclear energy, revealing its unique appeal, high efficiency, and the delicate balance of its risks and rewards.
First and foremost, embracing the concept of **energy efficiency** is pivotal. Every watt conserved is a step towards minimizing the reliance on energy sources, including nuclear power. Energy efficiency can be likened to a well-tuned orchestra, where each instrument plays its part to produce harmonious sound without superfluous noise. In the realm of nuclear energy, this means optimizing existing infrastructure to maximize output while minimizing waste. Implementing advanced technologies, such as high-temperature gas-cooled reactors and small modular reactors, can significantly reduce the energy lost during generation, ensuring that the nuanced power of nuclear fission is harnessed to its fullest potential.
In addition to energy efficiency, proactive **maintenance practices** form the backbone of nuclear energy conservation. Just as a seasoned gardener cultivates a lush garden, maintaining the health of nuclear plants is crucial for ensuring operational longevity and performance efficiency. Regular inspections and preemptive maintenance of reactors prevent unplanned outages, thereby avoiding wasted energy. Furthermore, adopting predictive maintenance strategies powered by data analytics allows for the identification of weaknesses in machinery before failure occurs, extending the life of these sophisticated systems.
### Embracing Renewable Energy Integration
Another critical strategy is the **integration of renewable energy sources** with nuclear power. Imagine a vibrant tapestry woven from various threads, where each type of energy contributes to a resilient and sustainable fabric. Wind, solar, hydroelectric, and nuclear energy can synergize to create a balanced energy portfolio. By utilizing nuclear energy as a baseload power source, we can complement intermittent renewable resources, leading to a more harmonious energy ecosystem. This fusion also allows for energy storage solutions, which can capture excess power during peak production times, mitigating the need for fossil fuel backup.
Furthermore, diversifying nuclear energy applications can play a vital role in conservation. Nuclear technology has a reach extending far beyond electricity generation; it can also be employed in **district heating, desalination, and hydrogen production**. By repurposing nuclear energy for these essential processes, we can maximize its utility and solidify its relevance in the global energy mix. For instance, small modular reactors can provide heat to residential areas, thereby reducing reliance on fossil fuels for heating purposes, while simultaneously providing electricity.
### Public Engagement and Education
Additionally, fostering public engagement is indispensable. Education serves as the rudder that steers the societal perception of nuclear energy. As the myths and apprehensions surrounding nuclear power are often fueled by misinformation, providing the public with factual, transparent information can shape a more informed community. Initiatives that promote awareness of nuclear safety measures, waste management policies, and environmental benefits can quell fears, ultimately leading to broader acceptance and support for nuclear initiatives.
Community involvement also plays a transformative role in shaping energy policies. By engaging local stakeholders in discussions about community benefits, job creation, and environmental protection, we can cultivate a strong support network for nuclear energy projects. These partnerships can act as a catalyst for new policies that prioritize energy conservation and advocate for responsible nuclear practices.
Moreover, investing in **research and development (R&D)** is a cornerstone for nuclear energy conservation. Picture an intricate blueprint, where innovation is the lifeblood coursing through its veins. Continuous R&D yields newer, more efficient nuclear technologies, enhancing safety protocols and waste management solutions. Innovations such as thorium reactors and fusion power signal a promising future where nuclear energy can be harnessed with minimal environmental impact, thus appealing to a society increasingly wary of energy-related repercussions.
### Sustainable Waste Management
A crucial aspect that cannot be overlooked is the stewardship of nuclear waste. Proper waste management is akin to the cleaning of a cherished artist’s palette—critical for sustaining the integrity of the medium. Implementing advanced reprocessing techniques can allow us to recycle nuclear fuel, thus reducing the long-term waste burden. The development of deep geological repositories is another avenue for the safe containment of spent nuclear materials. These sites ensure that the remnants of nuclear energy are managed responsibly, reflecting a commitment to environmental conservation.
Lastly, **advocating for a circular nuclear economy** represents a compelling paradigm shift. This model emphasizes minimizing waste and maximizing resource reuse, akin to the natural cycles observed in ecosystems. By adopting a circular approach, the nuclear industry can significantly diminish its environmental footprint and enhance resource utilization. This involves rethinking design processes, transitioning towards recyclable materials, and ensuring that every component of the nuclear energy system contributes to sustainability.
In conclusion, conserving nuclear energy requires a multifaceted strategy encompassing energy efficiency, maintenance, integration of renewables, public engagement, R&D investment, sustainable waste management, and a circular economy approach. Just as a delicate ecosystem relies on interconnected components for stability, the success of nuclear energy conservation hinges on integrating these strategies harmoniously. As society navigates the complexities of our energy future, the nuclear sector must rise to the challenge, illuminating the path towards a sustainable and resilient energy paradigm.