Global warming is no longer a distant threat; it has become an immediate reality that profoundly affects every aspect of our lives, including the animal kingdom. This ecological crisis is not merely an abstract concept; it manifests through tangible changes in habitats, behaviors, and survival rates of various species. The changing climate is intricately reshaping ecosystems, leading us to ponder how our shared future with animals may be irrevocably altered.
The intricate tapestry of life on Earth is interwoven with delicate ecological balances, where every species plays a pivotal role. As global temperatures rise, the subtle shifts in weather patterns result in both direct and indirect consequences for wildlife. The increased frequency of extreme weather events, such as droughts, floods, and hurricanes, disrupts habitats that countless species depend on. These disruptions often lead to habitat loss, fragmenting ecosystems and exacerbating the vulnerability of species that are already endangered.
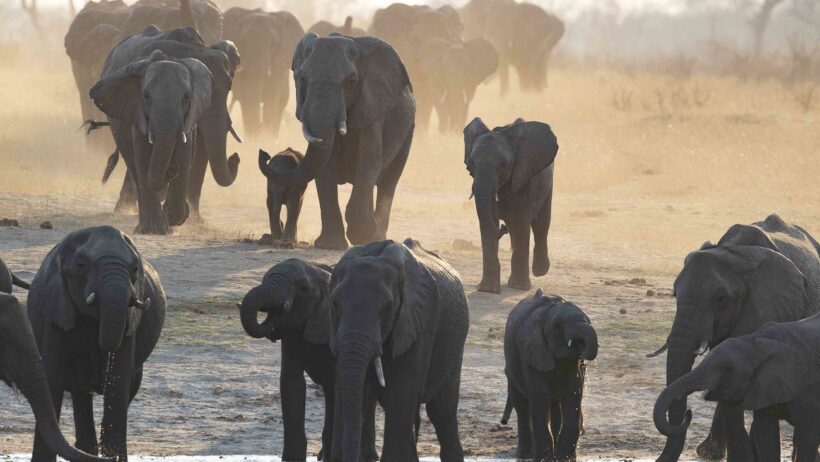
One cannot overlook the camouflage of climate change, where warmer climates will push species into unfamiliar territories in search of suitable habitats. For example, migratory birds are altering their traditional routes, resulting in mismatches between feeding schedules and the seasonal availability of food resources. This disruption, spurred by climate change, can lead to decreased reproductive success and population declines. Such changes underscore an urgent need for conservation efforts that establish adaptable strategies for wildlife protection.
Furthermore, oceanic ecosystems are experiencing parallel transformations. The acidification of oceans, caused by increased carbon dioxide absorption, threatens marine life, with coral reefs—a crucial habitat for numerous species—being particularly susceptible. As sea temperatures escalate, coral bleaching occurs, leading to loss of biodiversity and habitat. The decline of these vibrant ecosystems directly impacts not just fish populations, but also the communities that depend on these marine resources for sustenance and economic stability.
The effects of climate change extend beyond physical transformations; they also induce behavioral changes in animals. Many species exhibit altered mating rituals and reproductive timing, directly influenced by rising temperatures and changing food availability. These adaptive behaviors, while fascinating, often have unforeseen implications. The synchrony between prey and predator is disrupted, leading to potential predation mismatches and threatening the stability of food webs. These behavioral adaptations raise profound questions about the resilience of species in a rapidly altering environment.
Among the most profound impacts of global warming is its role in species extinction. A poignant observation reverberates through the scientific community: as habitats dwindle and competition for resources intensifies, many species teeter on the brink of extinction, struggling to adapt to their changing circumstances. The plight of the polar bear, for instance, highlights the alarming reality that some species may simply be unable to adapt quickly enough to survive. As sea ice diminishes, these majestic creatures face dwindling access to their primary food sources, leading to starvation and a decline in population.
This urgency underlines a broader ethical discussion. Our fascination with the natural world and its myriad wonders compels us to reconsider the consequences of our actions. Each species holds an intrinsic value, contributing to the richness of our planet and providing invaluable ecosystem services. The loss of biodiversity threatens the very foundation of ecological resilience, leading to a cascade of negative consequences for both wildlife and human populations.
The interconnectedness of human activities and their impact on wildlife signifies that our actions greatly matter. Habitat destruction, pollution, and overexploitation further strain the remaining animal populations. This complex interplay underscores the necessity for robust conservation strategies, informed by scientific understanding and community engagement. Implementing measures to mitigate climate change—such as reducing carbon emissions and transitioning to sustainable practices—could significantly alter the course of the future for both animals and humans alike.
As advocates for the urgent protection of our planet and its inhabitants, it is imperative to foster a culture of appreciation and stewardship for wildlife. Education campaigns, conservation initiatives, and public engagement can instill a sense of responsibility that motivates individuals to take action. The plight of endangered species should serve as a clarion call for society to unite in combating climate change and preserving the delicate balance of nature.
Moreover, we should acknowledge the resilience demonstrated by many species. Some animals exhibit remarkable adaptability, finding ways to thrive despite the encroaching changes. For instance, certain species of lizards have been observed to alter their reproductive strategies in response to temperature changes. Such flexibility poses a glimmer of hope for the animal kingdom as it navigates the tempest of changing climates.
Ultimately, the narrative of global warming cannot be told without portraying the animals that inhabit our planet. Each organism is a thread within the intricate weave of life, contributing to a shared legacy that connects us all. The future of these animals is intrinsically linked to the well-being of our environment, urging us to act decisively.
In conclusion, addressing the multifaceted impacts of global warming on the animal kingdom necessitates an acknowledgment of our collective responsibility. It is imperative that we advocate for urgent action to mitigate climate change, protect critical habitats, and promote conservation initiatives. The fate of our animals is inexorably intertwined with our actions; their survival and well-being depend on our commitment to championing the natural world. The time for action is now. Our animals are not just a reflection of the current state of our planet—they are harbingers of its future.