Resource depletion is an increasingly pressing challenge that intertwines with the phenomenon of global warming, prompting urgent dialogues regarding its impact on essential supplies. The perturbations to our environment are not merely theoretical but manifesting in tangible ways, affecting our access to critical resources. This discourse endeavors to scrutinize the myriad facets of resource depletion, examining how global warming accelerates the exhaustion of essential supplies.
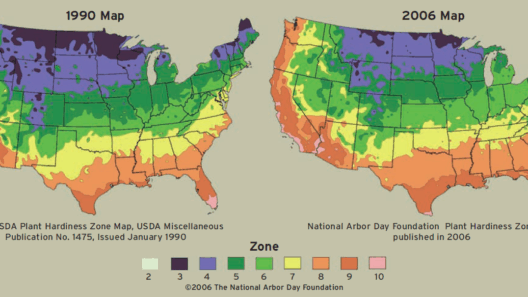
First and foremost, it’s essential to understand what resource depletion entails. This term refers to the consumption of a resource faster than it can be replenished. Renewable resources, such as forests, fisheries, and freshwater, are particularly vulnerable. As the global population burgeons and consumption patterns escalate, the demand for these resources intensifies, straining the balance of nature. Simultaneously, global warming exacerbates weather patterns, leading to droughts, floods, and other climatic extremes that further alter the availability of these vital supplies.
The nexus between global warming and resource depletion can be illustrated through the lens of freshwater scarcity. Approximately 2.2 billion people globally lack reliable access to safe drinking water. Climate change intensifies this issue, as erratic weather patterns impact precipitation levels, thus diminishing water supply. Melting glaciers, which serve as crucial freshwater reservoirs, contribute to short-term abundance but signal a looming crisis as they recede. In times of drought, competition for water escalates, leading to conflicts that may destabilize regions reliant on shared water sources.
Agricultural resources also face the specter of depletion, significantly underlined by climate change. With rising global temperatures, many traditional farming practices are becoming untenable. Crops that once thrived in certain climates are now struggling to survive. This added pressure can lead to food scarcity, elevated prices, and economic instability. The United Nations predicts that by 2050, food production must increase by 70% to feed the growing population. However, climate-induced disruptions such as soil degradation, altered rainfall patterns, and the proliferation of pests compound this already formidable challenge, jeopardizing food security on a global scale.
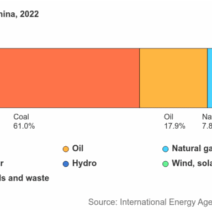
Energy resources are not exempt from these stresses. As fossil fuel reserves dwindle and the implications of burning them become increasingly untenable, the world must transition towards renewable energy sources. However, the extraction of these alternative resources, like lithium for batteries or rare earth elements for clean energy technology, often results in environmental degradation. Mining operations can lead to habitat destruction and water pollution, revealing a complex irony: as we strive for sustainable energy solutions, we inadvertently contribute to another form of resource depletion.
The oceans are another significant area of concern. Overfishing is a direct consequence of the increasing demand for seafood. The depletion of fish stocks poses a severe threat to marine biodiversity and the livelihoods of those who depend on fishing. Climate change exacerbates this situation. Ocean temperatures are rising, which can result in species migration, adjusting ecosystems, and altering food chains. Moreover, ocean acidification, driven by increased carbon dioxide levels, poses an existential threat to coral reefs and other marine life.
Moreover, the phenomenon of deforestation is intricately linked with both resource depletion and climate change. Forests are vital for carbon sequestration, yet they are being felled at an alarming rate to accommodate agriculture, urban development, and other pursuits. The resultant loss of trees means not only the loss of biodiversity but also a decreased ability to mitigate climate change effects. This creates a vicious cycle, where deforestation leads to an increase in carbon emissions, further driving global warming and subsequently harming the ecosystems that once thrived in those forests.
To address these critical issues, awareness, innovative solutions, and robust policy action are paramount. Consider the role of sustainable practices in agriculture and industry. Transitioning to regenerative farming techniques can bolster soil health, enhance biodiversity, and significantly improve water retention. In industries, adopting circular economy principles can mitigate waste and reduce the extraction of virgin resources. Furthermore, governmental policies should incentivize the sustainable management of resources and penalize practices harming the environment.
Technological innovation can also play a critical role in alleviating resource depletion. Advancements in water purification, energy efficiency, and sustainable agriculture can significantly mitigate the impacts of climate change on essential supplies. Furthermore, public awareness campaigns can educate consumers on the importance of sustainable choices, encouraging a shift toward behaviors that prioritize the planet’s health.
In conclusion, resource depletion is not merely an environmental issue; it is a multifaceted challenge that intertwines with social, economic, and political frameworks. The implications of global warming on essential supplies cannot be overstated. As populations surge and consumption rates escalate, immediate and concerted action is warranted. By fostering sustainable practices, championing technological advancements, and reinforcing governance frameworks, society can navigate the complexities of resource depletion in a warming world. The time to act is now, before essential supplies become irreversibly compromised, altering the fabric of life as we know it.