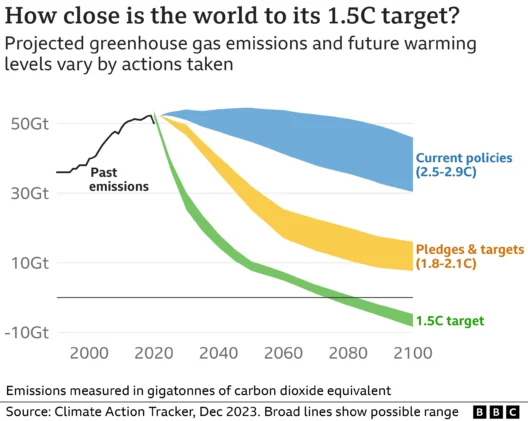
Rural America stands at a critical juncture, a crossroads shaped by the inexorable forces of climate change. This phenomenon, spurred predominantly by anthropogenic activities, is not merely an environmental issue; it proliferates economic ramifications that reverberate through the heart of rural communities. From altered agricultural practices to the precarious state of local economies, the ramifications of global warming are both intricate and far-reaching.
The tapestry of rural economies traditionally weaves through agriculture, forestry, and small-scale manufacturing. However, as the climate continues its drastic transformation, the viability of these sectors is increasingly undermined. Droughts that once punctuated the landscape may become the norm, altering crop yields and threatening the food supply chain. For instance, the Midwest, often heralded as America’s breadbasket, may experience diminished rainfall coupled with erratic weather patterns, resulting in significant agricultural distress.
Moreover, pests and diseases, which were once kept in check by seasonal temperature fluctuations, are now exhibiting resilience and adaptability. Warmer winters and extended growing seasons can trigger surges in insect populations that decimate crops, leading to financial insecurity for farmers who operate on thin margins. The convergence of these variables paints a bleak picture for rural economies, which depend heavily on consistent agricultural output.
In addition to crop failures, the livestock sector is not immune to the impacts of climate change. Higher temperatures can exacerbate heat stress in animals, leading to reduced productivity and increased mortality rates. The economic ripple effect is palpable; diminished livestock yields translate into increased costs for farmers, subsequently leading to higher prices for consumers. The economic landscape is thus reshaped under the mounting pressures of a warming climate.
Compounding the challenges faced by rural America is the phenomenon of water scarcity and quality degradation. As climate change intensifies, water resources become increasingly contested. The competition for water rights among agricultural, industrial, and municipal users is likely to escalate, leaving rural residents grappling with shortages. Moreover, pollution and runoff can severely impact local waterways, compromising both public health and the fishing industries that support rural livelihoods.
The economic vitality of rural America also hinges on its natural resources, particularly forestry. Forest-dependent communities face a dual challenge; while they may initially benefit from longer growing seasons, the increased frequency and severity of wildfires undermine this advantage. Such disasters not only devastate local ecosystems but also wreak havoc on regional economies reliant on timber resources and tourism. The potential destruction of natural habitats also incurs long-term losses that may take generations to recover.
Nevertheless, amid this confluence of adversity lies an opportunity for transformation. Rural America possesses the potential to pivot towards sustainable practices that could mitigate the economic impacts of climate change. Embracing renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, can provide new streams of income for rural communities. The deployment of such technologies can create jobs, decrease reliance on fossil fuels, and ensure more stable energy prices, thereby enhancing economic resilience.
Moreover, diversifying agricultural practices can also bolster economic stability. Agroecological approaches focus on sustainable intensification and organic farming, reducing the climate impact while maintaining productivity. Specialty crops such as berries or organic produce can command higher market prices, positioning farmers to thrive even in the face of adversity. Collaborations between farmers and local governments can foster the development of cooperative structures, enhancing both bargaining power and market access.
The role of innovation in rural economies cannot be overstated. Investing in research and development of climate-resilient crops may offer a pathway to regulatory adaptability that better aligns with shifting environmental conditions. Furthermore, agritech startups are emerging across the country, leveraging technology to optimize agricultural practices and promote resource efficiency. These innovations not only support productivity but also attract investment and talent to rural areas.
Education and awareness also play critical roles in steering rural communities toward sustainable futures. As rural residents become more informed about the impacts of climate change, there is an opportunity for grassroots movements to advocate for policy changes that prioritize economic resilience and sustainability. Collaborating with local universities and organizations can foster a culture of environmental stewardship while equipping future generations with the knowledge necessary to combat climate challenges.
Finally, government interventions are imperative to bolster the transition toward a climate-resilient economy. Policies that incentivize renewable energy developments, sustainable land management, and conservation efforts can create a favorable investment climate for rural enterprises. Supporting access to financial resources, technical assistance, and market opportunities will enable rural communities to navigate the economic complexities of climate change effectively.
In conclusion, rural America stands at a pivotal point where the consequences of global warming intersect with economic realities. The challenges are daunting, yet the potential for innovative solutions and sustainable practices is equally compelling. By harnessing opportunities for diversification, sustainability, and education, rural communities can not only weather the storms of climate change but emerge as leaders in the transition to a resilient and thriving economy. The stories of adaptation and resilience in rural America could serve as a blueprint for other regions grappling with similar climate challenges, underscoring the interconnectedness of our global ecosystem in the face of an uncertain future.