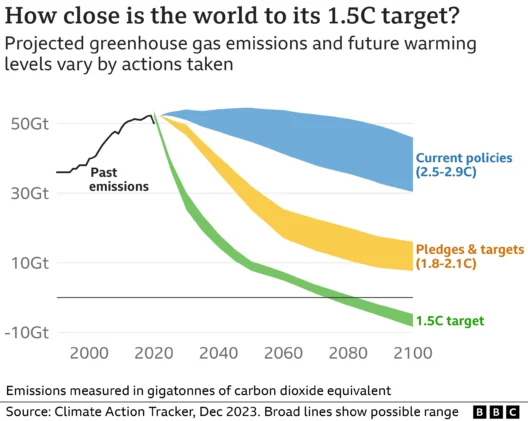
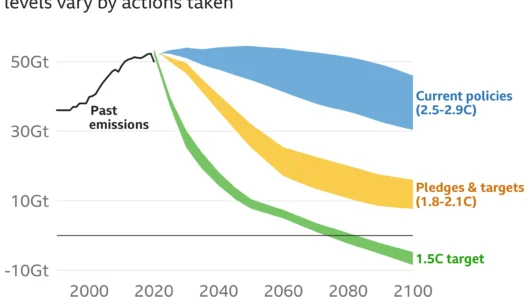
Severe weather patterns are not merely an anomaly, but rather an overt manifestation of the ongoing climate crisis. As global temperatures rise, the intensity and frequency of extreme weather events—such as hurricanes, droughts, heatwaves, and heavy rainfall—are projected to escalate dramatically. This increasing severity is not a distant concern; it is already observable and requires our immediate attention.
One of the most significant factors contributing to the intensification of severe weather is the gradual increase in atmospheric temperature. The Earth’s climate is becoming warmer primarily due to anthropogenic activities, predominantly the combustion of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. This warming leads to a plethora of atmospheric changes. For instance, warmer air can hold more moisture, resulting in heavier rainfall events. This is evidenced by the increasing frequency of flash floods, particularly in regions previously considered to be at minimal risk.
In addition to heavy precipitation, warmer temperatures exacerbate drought conditions. Regions experiencing significant rainfall deficits face prolonged periods of aridity, which can devastate agriculture and lead to food insecurity. The interplay between excessive rainfall, which can lead to flooding, and prolonged drought, creates a precarious balance for ecosystems and human populations alike. It is not merely a question of wet versus dry; these extremes often intersect, leading to a cycle of disaster that is notoriously difficult to predict and manage.
Moreover, the relationship between climate change and tropical storms is particularly alarming. Research indicates that as ocean temperatures rise, so too does the potential energy available to fuel hurricanes and typhoons. These storm systems, now more powerful and destructive, lash coastlines with unprecedented force. The destruction wrought by recent hurricanes is a stark reminder of nature’s fury, and the vulnerability of human infrastructure in the face of such extreme events.
In a world grappling with such transformations, human health also comes to the forefront. Extreme temperatures contribute to heat-related illnesses and exacerbate respiratory conditions due to the proliferation of allergens and pollutants. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with preexisting health conditions, are disproportionately affected. The medical infrastructure in many regions, already strained, faces untenable challenges from increasing weather-related health crises.
The ramifications of severe weather extend beyond immediate impacts. Economic loss is often staggering. Communities are left to reckon with the financial toll of rebuilding after catastrophes. The insurance industry also faces a reckoning as payouts for claims rise. As these events become more frequent, insurers may increase premiums, making it more difficult for individuals and communities to obtain coverage. This cycle further entrenches systemic vulnerabilities.
Climate-related displacement is an ever-growing concern as well. As sea levels rise and certain areas become uninhabitable due to frequent flooding or extreme drought conditions, populations may be forced to migrate. This leads to strain on urban areas that may be ill-equipped to accommodate the influx of displaced individuals. The intersection of climate, migration, and social equity creates a complex tapestry of challenges that demands an equitable and just response.
One might wonder how such intense weather patterns can coexist with regions that seem relatively insulated from climate extremes. The reality is that the ramifications of climate change do not respect geographical boundaries. A drought in one part of the world can influence food prices globally. Just as economic systems are interconnected, so too are ecosystems. The collapse of biodiversity in one region can have cascading effects that reach distant locales. The Lake Victoria Basin, for example, has already seen shifts in weather patterns that affect regional hydrology and biodiversity. Such changes necessitate a nuanced understanding of climate systems and their global implications.
Addressing these profound challenges requires an integrated approach that recognizes the urgency of the climate crisis while fostering resilience and adaptation strategies. Policy intervention is critical, with governments needing to implement rigorous emissions reduction targets. The transition to renewable energy sources can mitigate the reliance on fossil fuels, thereby decreasing the greenhouse gas emissions driving climate change. Innovative technologies, green infrastructure, and sustainable practices in agriculture are pivotal to creating a durable system that is resilient against extreme weather.
Moreover, community engagement cannot be overstated. Grassroots movements play a pivotal role in advocating for systemic change and holding corporations and governments accountable. Public awareness campaigns can foster educational initiatives, empowering individuals to take actions in their own lives that collectively lead to significant change. Increased climate literacy will ensure that future generations are equipped to face the unprecedented challenges posed by severe weather.
Finally, the importance of international cooperation cannot be overlooked. Climate change is a global issue that transcends borders; therefore, the responses need to be equally expansive. Multilateral agreements, like the Paris Agreement, illustrate the necessity for coordinated action against the shared threat of climate change. These frameworks can guide nations in their efforts to reduce emissions while supporting those most affected by climate-related disasters.
The increase in severe weather events intertwined with global warming is undeniably a pressing issue that requires immediate and sustained action. It is our collective responsibility to address the root causes, understand the far-reaching implications, and advocate for transformative strategies that ensure a sustainable and equitable future. The time for dialogue and awareness has passed; we must now mobilize for impactful change to confront the escalating threat of extreme weather in the face of climate change.