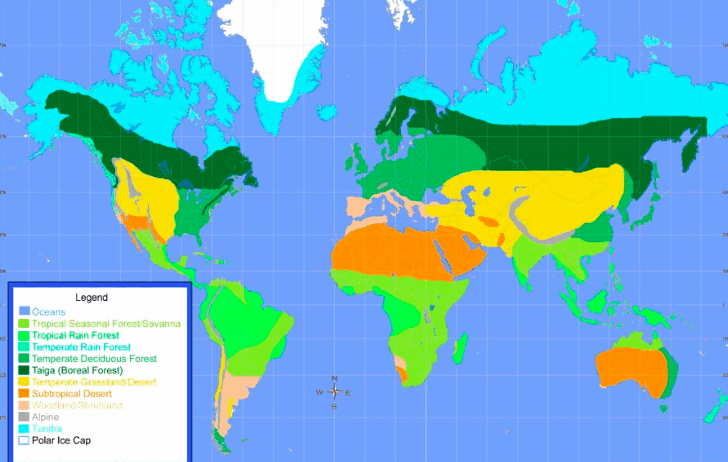
The temperate grasslands, often celebrated for their vast undulating expanses and rich biodiversity, stand at a precipice of transformation driven by climate change. These biomes, characterized by their unique climate and soil profiles, are witnessing a swift and alarming alteration in their ecosystems. This article presents a comprehensive exploration of the current state of temperate grasslands, the tumultuous effects of global warming, and the subsequent ramifications for flora, fauna, and human endeavors.
The Essence of Temperate Grasslands
Temperate grasslands, commonly referred to as prairies or steppes, emerge predominantly in regions with a distinct seasonal climate: warm summers, cold winters, and modest precipitation averaging between 25 to 75 centimeters annually. This biome is defined by expansive grasses interspersed with herbaceous plants and shrubs, shaped significantly by fire and grazing pressure. The soil in these grasslands, rich in organic matter, forms a crucial foundation for agriculture, a fact that underscores their economic importance.
Notably, these ecosystems are home to a plethora of species, including grazing mammals such as bison, pronghorns, and various ground-nesting birds. This ecological richness supports a diverse array of insects and microbial life, all of which contribute to its ecological balance. However, these intricacies are increasingly threatened by shifting climatic patterns.
Global Warming: A Catalyst for Change
Global warming induces a ripple effect on the delicate equilibrium of temperate grasslands. The escalating temperatures not only alter precipitation patterns but also exacerbate the frequency and intensity of droughts and storms. This climatic volatility challenges the resilience of these ecosystems, driving many species towards local extinction.
The increase in temperature catalyzes the migration of species, compelling flora and fauna to adapt to the changing conditions. Certain plant species may flourish under warmer conditions but face intense competition from invasive species, which thrive under similar changes. The resultant biodiversity loss can yield destabilized ecosystems, affecting food chains and the survival of indigenous species.
Soil Degradation and Agricultural Impacts
Soil health acts as the spine supporting the vitality of grasslands. However, intensified periods of drought have led to heightened soil degradation, diminishing the soil’s capacity to retain moisture and nutrients. As organic matter diminishes, marginal lands become increasingly arid, compromising their agricultural viability.
The agricultural sector, heavily reliant on grassland ecosystems for livestock grazing and crop production, faces concurrent challenges. Substantially altered rainfall patterns can result in uneven crop yields. Farmers are compelled to adapt their practices, often resorting to synthetic fertilizers, which may further degrade soil and escalate carbon emissions—a counterproductive cycle.
Fire Regimes and Ecosystem Resilience
Historically, fire has been an instrumental ecological process in temperate grasslands, rejuvenating soil and promoting biodiversity. However, as global temperatures rise, the likelihood of extreme wildfire events increases dramatically. The alteration of fire regimes could not only devastate existing vegetation but also facilitate the encroachment of non-native species, thereby infringing upon the local ecosystem dynamics.
Contrary to popular belief, prescribed burns, when executed judiciously, can mitigate the adverse effects of climate change by maintaining healthy grassland ecosystems. Nevertheless, an understanding of local climates and patterns is paramount when managing such actions to preserve the delicate balance of biodiversity.
Impacts on Wildlife
The wildlife inhabiting temperate grasslands is encountering a cascade of challenges. Species accustomed to specific habitats are being forced to adapt or migrate, often with disastrous results. For instance, ground-nesting birds face increasing threats as rising temperatures disrupt the timing of breeding seasons, leading to mismatches between hatching and peak insect availability.
Mammals such as the prairie dog, a keystone species within these ecosystems, are also under threat. Habitat destruction, alongside increasing predation from new species moving into the area due to climate shifts, destabilizes their populations, with broader implications for the grassland community structure.
Human Interventions: Navigating Consequences
Human activity has invariably influenced the trajectory of temperate grasslands through urbanization, agriculture, and pollution. As the climate crisis escalates, proactive intervention becomes increasingly critical. Restoration efforts, including re-establishing native plant species and implementing sustainable grazing practices, can bolster ecosystem resilience.
Additionally, fostering a deeper appreciation for the intrinsic value of temperate grasslands among local communities is essential. Public awareness campaigns emphasizing the importance of biodiversity and sustainable practices can engage citizens and policymakers alike, galvanizing support for conservation initiatives.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The implications of global warming on temperate grasslands are stark and multifaceted, altering the very fabric of these vibrant ecosystems. The need for immediate action to mitigate climate change and its effects on these vital biomes is undeniable. By prioritizing sustainability, and fostering ecological stewardship, it is possible to advocate for a more resilient future for temperate grasslands, their diverse species, and the communities that depend on them. As stewards of the environment, we must commit to lasting change—our planet’s health and vitality hinge upon it.