The Arctic has long been hailed as the Earth’s barometer, a place where nature’s delicate balance showcases the interplay between climate and ecosystem health. What if we turned the question around: what does the warming Arctic mean for humanity? It’s not just a remote phenomenon; this is a reality that beckons for our attention, for the consequences are consequential and far-reaching.
To start with, let’s consider the changes already observable in this frigid expanse. The Arctic region is warming at approximately twice the rate of the global average. This rapid rate of change is predominantly attributed to the phenomenon known as Arctic amplification, where loss of reflective ice cover leads to increased solar absorption by the ocean and land, generating a feedback loop that escalates warming. Glaciers, once towering ice giants, are now receding at an alarming pace, contributing directly to rising sea levels worldwide.
Imagine coastal cities across the globe, places like Jakarta, New York, and Venice. The less-than-frequent visitor to these iconic locales may ask, “What does melting ice in the Arctic have to do with me?” The answer lies in their vulnerabilities. Rising sea levels, forecasted to inundate low-lying areas, will displace millions and exacerbate existing socio-economic disparities. The imminent challenge of migration and displacement may lead to what is often termed as ‘climate refugees’—individuals who are forced to abandon their homes due to climate-induced transformations.
Another critical dimension of this warming is the release of greenhouse gases trapped in permafrost. Scientists predict that as temperatures rise, the permafrost, which has securely stored vast amounts of methane and carbon dioxide for millennia, will begin to thaw. Methane, a potent greenhouse gas with over 25 times the warming potential of carbon dioxide over a 100-year period, poses a threat of catastrophic proportions. The release of even a fraction of these gases could propel global warming beyond our current trajectories and result in profound climate repercussions that humanity may be ill-equipped to handle.
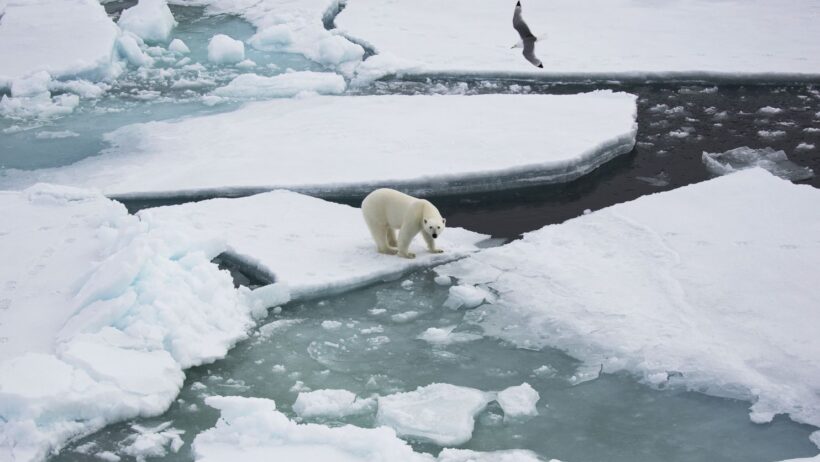
The Arctic ecosystems themselves find themselves in jeopardy. As temperatures rise, species adapted to these cold climates, such as polar bears and walruses, face existential threats. The intricate food web of the Arctic is under siege, with shifts in species distribution and migration patterns. For instance, as sea ice retreats, polar bears are forced to swim longer distances in search of seals, their primary food source. This not only endangers the bears but also disrupts the harmony of their ecosystem, prompting a ripple effect through the entire food chain.
Now, let’s pivot to a lesser-discussed issue: how does the Arctic’s transformation affect global weather patterns? Changes in the Arctic can lead to a phenomenon known as the “wavy jet stream,” which influences weather across the Northern Hemisphere. The Arctic’s warming is causing alterations in the jet stream’s path, resulting in extreme weather events such as prolonged heatwaves, devastating storms, and erratic precipitation. The encroachment of climate instability brings an array of challenges for agriculture, water supply, and overall food security worldwide.
Faced with these overwhelming challenges, we must consider our collective agency. How can we address the escalating crisis sparked by a warming Arctic? Mitigating climate change requires a multifaceted approach. First, transitioning to renewable energy sources must be prioritized. Fossil fuel dependence not only fuels greenhouse gas emissions, but it also exacerbates environmental degradation. Emphasizing the use of solar, wind, and hydroelectric power can drastically reduce our carbon footprint.
In tandem, reforestation and afforestation initiatives can help sequester carbon from the atmosphere, off-setting emissions in a quantifiable manner. Moreover, embracing sustainable agricultural practices mitigates land degradation, preserves biodiversity, and enhances soil health, ultimately leading to a more resilient food system. Simultaneously, developing better policies to curtail pollution and investing in technological innovations for carbon capture can also pave the way for a more sustainable future.
While these actions may appear monumental, they pale in comparison to the larger potential for societal change. Global collaboration is essential. Nations must work together transparently, sharing knowledge and resources to tackle such a pervasive issue. Public awareness campaigns can mobilize communities to advocate for climate policies, emphasizing the significance of personal action. Each individual’s efforts—whether adopting a plant-based diet, reducing waste, or advocating for policy change—can contribute to this global endeavor.
As we examine the consequences of an ever-warming Arctic, the stakes become increasingly clear. The repercussions affect us all, weaving themselves into the fabric of our everyday lives. Climate change is not a distant threat; it’s an immediate challenge demanding innovative solutions, critical thinking, and collective action. What if the key to our survival lies in confronting the realities of the Arctic, advocating for systemic change, and fostering a deeper connection with our planet? The urgency to respond is here, the challenge is ahead, and the solution rests in our hands.