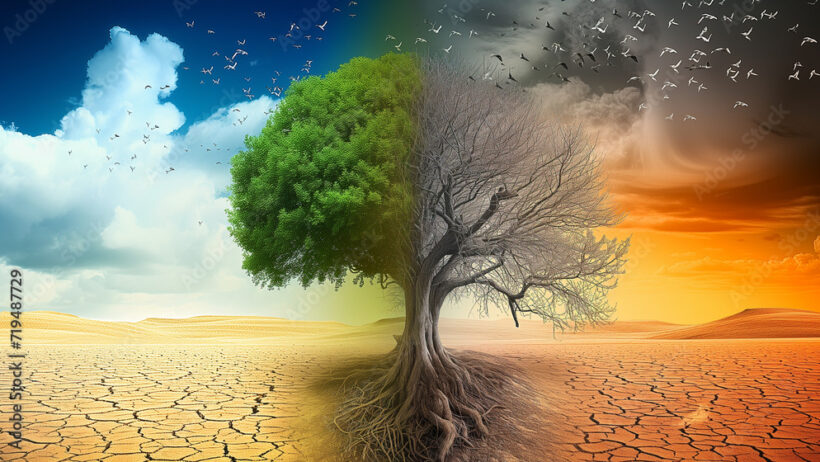
The phenomenon of desertification represents a significant and alarming side effect of global warming. A stark representation of the worsening climate crisis, desertification refers to the process through which fertile land becomes increasingly arid and unproductive, often transitioning into desert-like conditions. This degradation of land has severe ramifications for ecosystems, human livelihoods, and global biodiversity, making it a pressing issue of our time.
Desertification is not merely a local issue; it is an expansive challenge that transcends geographical boundaries. It is primarily driven by a confluence of factors, among which climate change emerges as one of the most influential. As global temperatures rise, altered precipitation patterns emerge, affecting the hydrological cycles essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems. Consequently, regions that traditionally relied on predictable rainfall can experience extended droughts, leading to diminished soil moisture levels and increased evaporation rates.
To understand the sheer magnitude of the desertification dilemma, one must consider its causes, effects, and potential solutions.
Causes of Desertification
Several anthropogenic and natural factors contribute to the devastation of fertile land. Deforestation, agricultural practices, and urbanization rank among the primary drivers. Forests play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance; they stabilize the soil and help regulate the water cycle. When forests are destroyed, the resultant loss of vegetation does not only expose the soil to erosion but undermines its ability to retain moisture.
Agricultural practices can exacerbate desertification, especially when unsustainable methods such as monocropping and excessive irrigation are employed. These practices deplete essential nutrients from the soil, leading to nutrient-poor ground that can no longer support robust plant life. Urbanization further intensifies the problem, as expanding infrastructure consumes arable land, displacing natural habitats and exacerbating the heat island effect.
Effects of Desertification
The adverse repercussions of desertification are manifold. First, the decline of land productivity directly threatens food security, particularly in developing countries where smallholder farmers rely heavily on consistent agricultural output. As soils become less fertile, crop yields diminish, prompting higher food prices and increased hunger and malnutrition.
The environmental impacts are equally dire. As productive areas succumb to desertification, the loss of biodiversity accelerates. Many species of flora and fauna that rely on these ecosystems face extinction, resulting in a decline in biological diversity. The intricate relationships that sustain entire ecosystems begin to unravel, which can lead to a cascading effect harmful not only to the environment but also to human populations dependent on these ecosystems for resources.
Moreover, desertification can trigger socio-political tensions. As viable land grows scarcer, competition for remaining resources escalates. This competition can foster conflict, as communities clash over limited water supplies and arable land. Displacement becomes a stark reality for many, leading to increased migration pressures that can strain urban areas and exacerbate social instability.
Solutions to Combat Desertification
Addressing the desertification dilemma requires a multifaceted approach. First and foremost, sustainable land management practices must be implemented. Smallholder farmers can benefit from agroecological techniques that enhance biodiversity and soil fertility. Practices such as crop rotation, intercropping, and organic fertilization contribute to restoring the health of degraded lands.
Reforestation and afforestation are also vital strategies. Planting trees not only aids in restoring soil health but also contributes to carbon sequestration, thus mitigating some effects of global warming. Governments and organizations worldwide are realizing the need for policies that encourage sustainable land use and promote afforestation initiatives, creating a substantial shift toward environmental stewardship.
Education plays a pivotal role in combating desertification as well. By raising awareness about the causes and effects of desertification, communities can be mobilized to engage in proactive measures. Policy frameworks must support local initiatives aimed at improving land management, encouraging sustainable agriculture, and promoting the restoration of degraded areas.
International cooperation is essential to address desertification effectively. Global partnerships can provide the necessary resources, knowledge, and funding required to combat land degradation on a larger scale. Initiatives such as the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) exemplify collective efforts aimed at tackling this issue.
Conclusion
The desertification dilemma encompasses intricate interrelationships among global warming, land degradation, and human survival. As we face mounting environmental challenges, the significance of combating desertification cannot be understated. By adopting sustainable practices, promoting education, and fostering international cooperation, we can pave the way towards a resilient future. It is imperative that stakeholders across all sectors recognize the urgency of addressing desertification, not only for the sake of our planet but also for the well-being of future generations. In the face of climate change, concerted efforts can make a difference, returning vitality to our once-fertile landscapes.