Global warming stands at the forefront of contemporary environmental discourse, igniting fervent debates and catalyzing urgent actions across the globe. As scientists scrutinize the sprawling effects of climate change, an alarming question emerges: Is global warming accelerating? To grasp the gravity of this inquiry, it is essential to delve into the intricacies of climate dynamics, examine recent trends, and consider the social and economic implications of a warming world.
Understanding Global Warming: A Brief Overview
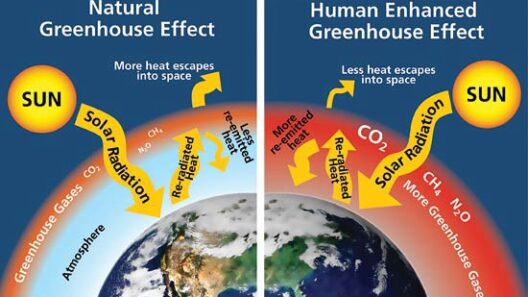
Global warming refers to the long-term increase in Earth’s average surface temperature, primarily driven by human-induced emissions of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4). These emissions result from an array of activities, including the combustion of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. The resultant heat-trapping effect not only elevates temperatures but also disrupts weather patterns, leading to extreme climatic events.
To comprehend whether global warming is indeed accelerating, it is imperative to analyze empirical data and current research findings. Observational records reveal a consistent upward trend in global temperatures over the past century, with the last few decades exhibiting unprecedented warmth. According to climate models, both historical and projection-based data indicate that global temperatures are rising at an increasingly rapid pace.
The Acceleration Phenomenon: Indicators and Evidence
In pursuit of understanding the acceleration of global warming, scientists have identified several key indicators. These markers provide insight into how quickly the climate crisis is evolving.
Rising Ocean Temperatures
One of the most pronounced signs of accelerating global warming is the increase in ocean temperatures. Oceans absorb over 90% of the excess heat generated by greenhouse gas emissions, leading to warmer water temperatures. This phenomenon not only threatens marine ecosystems, result in coral bleaching but also contributes to the melting of polar ice caps. The alarming rate at which ice is disappearing from Greenland and Antarctica serves as a stark reminder: the oceans are sending us clear signals about our rapidly changing climate.
Increased Frequency of Extreme Weather Events
Another compelling indication of an accelerating climate crisis lies in the surge of extreme weather occurrences. Recent years have witnessed a disturbing uptick in the frequency and severity of hurricanes, droughts, floods, and heatwaves. These events are not isolated; they often culminate in cascading impacts on infrastructure, agriculture, and human health. As atmospheric conditions continue to change, the potential for unprecedented weather patterns increases, underscoring the threats posed by a warming planet.
Melting Glaciers and Rising Sea Levels
Glaciers serve as vital indicators of climate stability. Observations show that many glaciers around the world are retreating at an alarmingly fast rate. This melt contributes directly to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities with flooding and erosion. Projections suggest that if global warming continues unabated, entire cities may eventually find themselves beneath the waves. The moral imperative to establish robust climate policies becomes ever clearer as these realities unfold.
The Societal and Economic Fallout of Accelerated Global Warming
As global temperatures continue to rise, the ramifications extend beyond environmental degradation. The societal and economic impacts of accelerated global warming demand urgent attention and action.
Effects on Public Health
In the realm of public health, accelerated global warming poses significant threats. Increased heat exposure can exacerbate cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. Furthermore, the spread of vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever, gains momentum as changing temperatures allow these diseases to flourish in previously inhospitable areas. Addressing these health challenges requires comprehensive strategies to bolster public health infrastructure and enhance community resilience.
Food Security in Jeopardy
The connection between climate change and food security cannot be overlooked. Rising temperatures disrupt agricultural productivity, threatening crops and livestock. Droughts and floods can lead to monumental yield losses, exacerbating hunger and malnutrition in vulnerable populations. Investing in sustainable agricultural practices, including climate-resilient crops and efficient farming techniques, emerges as critical in combating the dual challenges of climate change and food insecurity.
Economic Implications: Cost of Inaction
When weighing the economic implications of accelerating global warming, the cost of inaction becomes glaringly evident. Natural disasters catalyzed by climate change result in substantial financial losses, impacting everything from infrastructure repair to disaster response. Additionally, the potential for mass migrations as people flee uninhabitable regions poses significant challenges for social welfare systems and economies. A transition to a low-carbon economy and green technologies is not merely advantageous—it is imperative for sustainable economic growth.
Strategies for Mitigation: A Call to Action
To address the escalating crisis of global warming, concerted efforts at multiple levels are crucial. Both individuals and societies must engage in proactive approaches to mitigate climate change.
Transitioning to Renewable Energy
A robust shift toward renewable energy sources—solar, wind, and hydroelectric power—can substantively reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Policymakers must incentivize clean energy investments and devise structures that facilitate a transition away from fossil fuels. Therefore, empowering communities to embrace alternative energy solutions is a critical endeavor that requires immediate investment and support.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Implementing energy efficiency measures across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors can yield significant reductions in energy consumption and emissions. From retrofitting buildings to adopting smart technologies, these strategies lay the foundation for a sustainable future. By educating individuals on energy conservation practices, communities can lessen their ecological footprints while simultaneously reaping economic benefits.
Fostering Climate Awareness
Finally, fostering a culture of climate awareness is paramount. Educating citizens on the realities of climate change and its consequences fosters a sense of responsibility. Advocacy for policy reforms and community-level initiatives can mobilize collective action toward more environmentally friendly practices. Climate awareness nurtures an intergenerational dialogue that is essential for meaningful change.
The challenge of global warming is monumental, yet the opportunity for transformation is equally profound. By recognizing the alarming pace at which our planet is warming and diligently pursuing actionable solutions, we can work toward a more sustainable future. The urgency of the situation demands our unwavering commitment to effectuate change—before it is too late.