The Human Contribution to Climate Change and Global Warming
Climate change, a phenomenon that endangers the stability of ecosystems and the very fabric of human society, is primarily driven by human activities. As we delve into the intricate relationship between humanity and the environment, it becomes evident that the fingerprints of industrialization, deforestation, and unsustainable agricultural practices have indelibly marked the planet. Understanding the components of this critical issue is essential for fostering meaningful action and policy reform.
Humanity has become the dominant force influencing the Earth’s climate, with a significant increase in greenhouse gas emissions correlating directly to our reliance on fossil fuels. As we peel back the layers to examine this pressing matter, several areas emerge that warrant attention: the industrial revolution, transportation, agriculture, and deforestation.
As populations burgeon and economies expand, the repercussions of our actions resonate through the atmosphere. The combustion of fossil fuels for energy has dramatically escalated atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, leading to a cascade of climatic anomalies. This discourse will explore these critical aspects in detail.
Revolutionizing Energy: The Industrial Age’s Impact
The industrial revolution, ignited in the late 18th century, catalyzed an era marked by unprecedented technological advancement. However, it also heralded the birth of mass-scale fossil fuel consumption. From coal to oil, the allure of cheap energy transformed economies but unleashed torrents of carbon emissions into the atmosphere. The advent of manufacturing processes and mechanized transportation propelled economic growth but did so at an environmental expense.
As factories sprang up, each belching smoke and soot, the air quality deteriorated, and the climate system became increasingly volatile. Industry accountability is paramount, as the emissions released during production and consumption contribute significantly to global warming. Carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4) are two of the most detrimental greenhouse gases—each possesses a formidable ability to trap heat in the earth’s atmosphere. The pursuit of economic expansion, while essential, has inadvertently expedited climate change.
The modern economy demands a transition towards cleaner energy technologies. Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power present viable alternatives, championing sustainable practices that mitigate emissions and promote environmental stewardship.
The Road We Travel: Transportation’s Role in Emissions
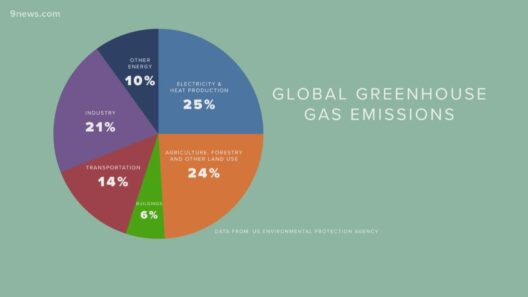
A profound aspect of human contribution to climate change stems from the transportation sector. The ubiquity of vehicles, airplanes, and shipping vessels—each a harbinger of greenhouse gases—continues to surge. On average, the transportation sector accounts for approximately 29% of total greenhouse gas emissions in the United States, presenting a stark reality that cannot be ignored.
The prevalence of fossil-fuel-dependent vehicles and shipping methods exacerbates the climate crisis. Individual automobile use, particularly those powered by gasoline and diesel, emits substantial quantities of CO2, necessitating urgent reforms. Transitioning to electric vehicles (EVs) and investing in public transportation can illuminate a path toward reduced emissions and minimal ecological impact.
Public policies and infrastructure aimed at curtailing vehicular emissions, combined with citizen engagement and awareness, are pivotal. The burgeoning electric vehicle market signifies a decisive shift towards sustainability, yet the transition requires momentum to overhaul existing manufacturing and consumption paradigms.
Feeding Our Future: Agriculture’s Unfolding Consequences
Humanity’s quest for sustenance has engendered grave implications for the climate. Agricultural practices exert tremendous pressure on natural resources, with farming accounting for nearly 24% of greenhouse gas emissions globally. The methods employed in food production, such as cattle ranching and rice cultivation, release substantial methane—an exceedingly potent greenhouse gas—into the atmosphere.
Deforestation to make way for agricultural expansion further exacerbates climate ramifications. Trees, nature’s invaluable carbon sinks, are felled en masse, removing a vital mechanism for cleaning our atmosphere and regulating temperature. The loss of biodiversity associated with such practices impacts ecosystems, impoverishing the intricate balance essential for planetary health.
Sustainable agricultural practices, such as permaculture, regenerative farming, and organic methods provide a counter-narrative. Emphasizing soil health, crop rotation, and agroforestry can bolster food security while promoting planetary wellbeing. A collective shift in dietary preferences and waste reduction strategies are also integral in addressing the agricultural contributions to climate change.
Preserving Our Forests: The Urgency of Deforestation Awareness
Intimately linked to agriculture is the staggering rate of deforestation, which remains an egregious contributor to climate change. Forests act as carbon reservoirs, sequestering CO2 and curbing the greenhouse effect. However, logging, mining, and agricultural practices have decimated millions of acres worldwide.
The repercussions of deforestation extend beyond carbon emissions; critical wildlife habitats are obliterated, leading to species extinction and biodiversity loss. The fragility of ecosystems is laid bare as habitat destruction intensifies. Mounting evidence supports the advocacy for reforestation, afforestation, and the implementation of sustainable forestry practices. The substantial benefits of tree planting strategies extend beyond climate amelioration, enhancing air quality, fostering biodiversity, and promoting community resilience.
Conclusion: A Call to Collective Action
The human contribution to climate change and global warming creates a tapestry of interconnected issues, each strand emphasizing our collective responsibility. As we confront the challenges posed by industrial practices, transportation, agriculture, and deforestation, it is paramount we forge innovative solutions. This includes embracing sustainable practices, investing in renewable energy, and advocating for policy reforms that champion ecological integrity.
Ultimately, fostering awareness and educating individuals on the consequences of their choices can galvanize society towards sustainable action. The climate crisis is an existential threat; thus, it is imperative that humanity heeds the warning signs and commits to preserving the planet for future generations. The time to act is now.