The Earth is often likened to a living organism, pulsating and adapting to the rhythms of nature. Within this intricate tapestry of life, the concept of global warming emerges as a dissonant chord, threatening to disrupt the harmony of our planet’s climate. Understanding the mechanisms behind global warming is akin to deciphering the heart’s intricacies, revealing how human actions are irrevocably altering its pulse.
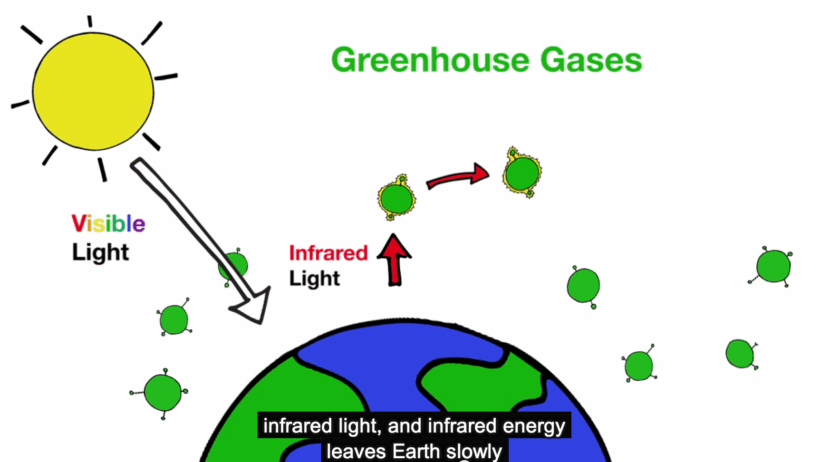
At the core of global warming lies the greenhouse effect, a natural phenomenon critical to maintaining the Earth’s temperature. Imagine the atmosphere as a delicate blanket, woven from gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). These gases trap heat from the sun, preventing it from escaping back into space. This process is essential; without it, our planet would be inhospitably cold, like a desolate winter night.
However, human activity, particularly since the Industrial Revolution, has infused an overwhelming surplus of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The combustion of fossil fuels for energy, deforestation, and industrial processes contribute significantly to this augmentation. Think of it as an ever-increasing number of layers being added to the blanket — each layer amplifying the heat retained, driving temperatures higher and higher.
The ramifications of global warming extend well beyond mere temperature fluctuations. It disrupts weather patterns, intensifying phenomena such as hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves. The frequency and severity of these events are alarming, marking a new era of climate unpredictability. Like a conductor losing control of an orchestra, the atmosphere begins to clash, generating discordant weather systems that pose substantial threats to human societies and ecosystems alike.
Polar regions, often considered the Earth’s refrigerator, are particularly vulnerable to these escalating temperatures. The melting of polar ice caps and glaciers acts as a stark metaphor; it signifies not merely a physical transformation but a profound existential one. As the ice retreats, it reveals darker ocean waters, which absorb more heat, further exacerbating the warming cycle. This prognosis leads not only to rising sea levels — a specter looming over coastal cities worldwide — but also to the loss of habitats utilized by countless species.
The repercussions of global warming extend down to the very foundation of our ecosystems. Oceanic acidification, the result of increased CO2 absorption by seawater, exemplifies this perilous shift. As oceans absorb carbon, they become more acidic, disrupting marine life. Coral reefs, often deemed the “rainforests of the sea,” suffer grievously under these changes, leading to widespread coral bleaching. The demise of these habitats ripples through the marine food web, threatening species population and fishing industries that many communities rely on.
The impact on agriculture is equally daunting. Shifts in climatic conditions call into question the reliability of food production. Many crops are particularly sensitive to temperature and precipitation changes, resulting in diminished yields and increased food insecurity. Farmers, who have relied on predictable seasonal patterns, find themselves grappling with uncertainty, much like navigating through fog without a compass. As droughts become more pronounced and erratic rainfall patterns emerge, the specter of famine grows ever closer.
In addressing global warming, it becomes imperative to acknowledge the power dynamics underpinning climate change. Industrialized nations, historically the largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, hold significant responsibility in addressing the crisis. This dichotomy of accountability raises difficult yet necessary discussions about equity. The most marginalized communities, often bearing the brunt of environmental degradation, contribute least to the problem yet suffer disproportionately from its effects. This inequity demands a concerted global effort, uniting nations towards shared goals for a sustainable future.
Transitioning to renewable energy sources stands as the cornerstone of the fight against global warming. Solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energies promise a way forward, offering cleaner alternatives that mitigate the anthropogenic touch on Earth’s natural systems. Embracing these technologies is akin to nurturing seedlings that will grow into a robust forest; they provide hope for a more sustainable coexistence between humanity and nature.
In conjunction with energy transformation, enhancing energy efficiency serves as an equally significant strategy. By optimizing how we utilize energy in homes, industries, and transportation, we can lessen our carbon footprint effectively. The adoption of energy-efficient technologies acts like tightening a loose belt on the ever-expanding blanket of greenhouse gases, helping to curb the potential excesses.
Another pivotal element in combating global warming is reforestation and afforestation efforts. Trees are natural carbon sinks, playing a quintessential role in sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. By restoring degraded landscapes and promoting forest growth, we can effectively sow the seeds of ecological balance. Each new tree contributes to the collective effort of healing our planet, reminding us that regeneration is possible — even in a world facing such formidable challenges.
The collective consciousness regarding climate change is steadily evolving. Grassroots movements advocating for climate action are gaining momentum, echoing the urgent need for change. From youth activists leading strikes to organizations rallying communities for initiatives, the message is clear — time is of the essence. The transition to a sustainable future requires bold ideas and persistent determination, akin to the unwavering growth of plants stretching toward the sun.
In the end, understanding how global warming works is about grasping the intimate connections between human actions and the Earth’s systems. It is about acknowledging that the planet’s pulse has been altered, and we, as its stewards, have a duty to restore its rhythm. The path forward demands vigilance, unity, and an unwavering commitment to the guardianship of our shared home. It is within our grasp to cultivate a thriving world, where every organism — including humanity — can flourish within the delicate balance of nature.