The climate crisis manifests in multifarious and often paradoxical ways. One phenomenon that has garnered increasing attention in recent years is the polar vortex, a recurring atmospheric pattern that can lead to extreme cold weather, particularly in the Northern Hemisphere. While one might expect a warming planet to banish harsh winter conditions, the polar vortex paradoxically reveals how interconnected and complex our climate system is.
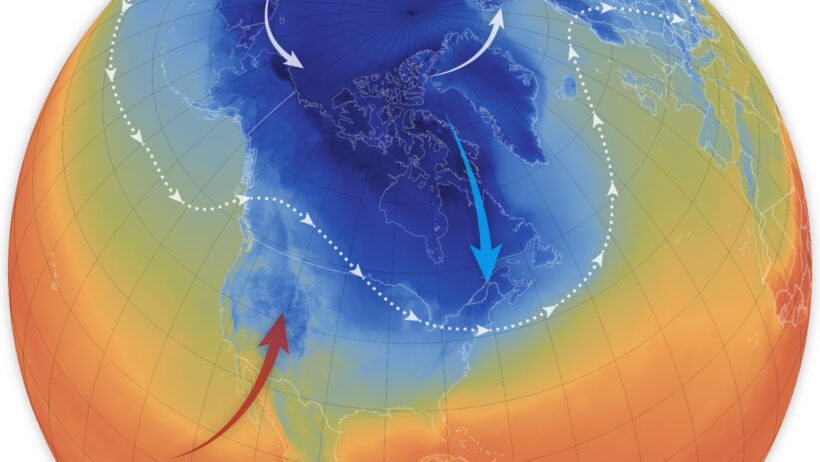
The polar vortex consists of a large area of low pressure and cold air surrounding the Earth’s poles. It is typically stable and contained within the polar regions. However, disruptions to this system can cause it to weaken or split, sending frigid air spiraling southward into mid-latitude regions, including parts of the United States and Europe. This unexpected cold snap may, at first glance, seem contradictory to the overarching narrative of global warming, which suggests rising global temperatures and increasing weather extremes. Yet, this phenomenon is a clear illustration of how climate change is altering traditional weather patterns.
Understanding the mechanics behind the polar vortex is essential. The stability of the vortex is influenced by the temperature difference between the polar regions and the mid-latitudes. As global temperatures rise due to greenhouse gas emissions, it can lead to a reduction in this temperature gradient. A weaker polar vortex is the result, which then becomes more susceptible to disruptions. Such disruptions may allow for the polar air to escape, leading to unusually severe winter weather across the U.S. and Europe.
Moreover, there is ongoing research into the role of Arctic amplification, a phenomenon wherein the Arctic warms at a significantly faster rate than the rest of the planet. This warming exacerbates the polar vortex’s instability, contributing to its erratic behavior. The connections between Arctic temperatures and mid-latitude weather patterns reinforce the intricate tapestry of our climate system, reminding us that changes in one region can have far-reaching impacts elsewhere.
The implications of these cold snaps are significant. When the polar vortex breaks down, regions that experience these extreme cold events face numerous challenges. Firstly, there are the immediate effects on human health and safety. Severe cold can lead to increased cases of hypothermia, frostbite, and other cold-related ailments. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly and the homeless, are particularly at risk during such extreme weather events.
Furthermore, the economic ramifications of a disrupted polar vortex can be profound. Cold snaps often result in increased energy demand for heating, placing an additional burden on already stressed energy systems. Businesses and industries that rely on outdoor operations may also face substantial losses due to harsh weather conditions. Agriculture, too, can suffer, as crops may be damaged by unseasonably low temperatures.
Apart from human impacts, the environment faces significant repercussions as well. The sudden influx of cold air can exacerbate conditions for some species while threatening others. Ecosystems are finely tuned to seasonal changes, and abrupt weather shifts can disrupt the delicate balance of local flora and fauna. Species that are unable to adapt quickly to fluctuating conditions may face population declines or even extinction.
While the polar vortex and its associated cold snaps may seem isolated phenomena, they are symptomatic of larger climate trends. As global temperatures rise, one might expect fewer such events. However, the reality is more nuanced. The increase in extreme weather variability — including extreme heat and extreme cold — underscores the unpredictability of climate change and the importance of ongoing research into these patterns.
To address the challenges posed by the polar vortex and its associated cold snaps, robust adaptive strategies are needed. Communities must invest in infrastructure capable of withstanding extreme weather conditions, bridging the gap between emergency preparedness and long-term resilience. This includes enhancing public health responses, ensuring adequate shelter for vulnerable populations, and improving energy efficiency to mitigate surges in demand during cold weather.
Furthermore, there is an urgent need for policymakers to seriously consider climate mitigation strategies. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is paramount not only to curtail global warming, but also to stabilize atmospheric patterns that influence phenomena like the polar vortex. Comprehensive climate action must prioritize renewable energy, sustainable land use practices, and emissions reductions to foster a more resilient future.
In conclusion, the polar vortex paradox exemplifies the complex nature of climate change. Far from presenting a simple narrative of warming, it elucidates the intricate and often contradictory relationships within our planet’s climate system. As we navigate an uncertain future, it is imperative to understand that every weather event is interwoven with broader climatic shifts. This realization should galvanize collective action to combat climate change — for our communities, our economy, and the ecosystems that sustain us. In confronting the challenges posed by unpredictable weather patterns, we must also cultivate a deeper appreciation for the nuanced interplay between global warming and the ephemeral nature of cold snaps like those brought on by the polar vortex.