The Role of Greenhouse Gases in Earth’s Temperature Regulation
Our planet’s climate system is a complex interplay of natural forces and human activities, but one of the foundational elements that governs Earth’s temperature is found in the elusive realm of greenhouse gases. Understanding their role is essential for grasping the nuances of global warming and climate change. Enveloped in a cloak of gaseous compounds, our atmosphere plays a pivotal role in maintaining the delicate balance that allows life to flourish. However, too much of a good thing can lead to troubling consequences.
As we delve deeper into the atmospheric layers, we uncover the mechanisms by which greenhouse gases function. It is here that the tale begins—a story of evolution, survival, and the new horizons we are encouraged to explore.
Recognizing the Players: A Cast of Greenhouse Gases
When discussing greenhouse gases, one must first identify the key players. Carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor are among the prime contributors to the greenhouse effect. Carbon dioxide, often spotlighted for its anthropogenic emissions from fossil fuel combustion, acts as a long-lived atmospheric presence, slowly saturating the air. Methane, a gas with a far greater heat-trapping potential than CO2 over a short time frame, emerges from agricultural practices, landfills, and fossil fuel extraction. Nitrous oxide, too, is an ardent participant, released primarily through agricultural fertilizers, impacting not only temperature but ozone layer degradation as well. Water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas, plays a unique role: rather than being emitted directly by human activity, its quantity is influenced by temperature itself, creating a feedback loop that enhances warming.
Each of these gases holds its own unique characteristics and resonance within the atmospheric symphony. Without them, Earth would not be the vibrant biosphere we envision today, but a frozen, inhospitable wasteland. Their natural abundance creates a blanket, allowing sunlight to penetrate yet trapping the heat that radiates back into space, thereby maintaining a cozy temperature where life can thrive.
The Greenhouse Effect: Nature’s Ingenious Mechanism
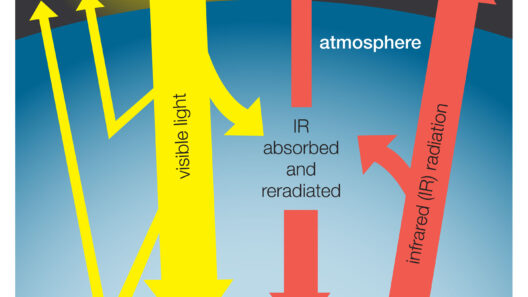
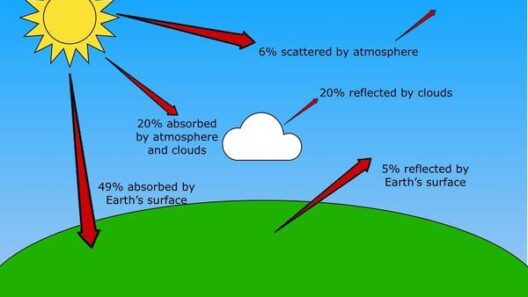
The greenhouse effect is a phenomenon as old as the Earth itself. Imagine the Earth as a verdant garden: when the sun shines down on this garden, radiant energy warms the plants and soil. As night falls, the surface cools, releasing energy back into the atmosphere. This is where greenhouse gases showcase their remarkable utility, absorbing and re-emitting some of this outgoing energy, thus preventing it from escaping into the void of space. This natural mechanism is vital for temperature regulation, offering a stable environment where life has flourished for millennia.
Indeed, the Earth’s average temperature would plummet to about -18 degrees Celsius (0 degrees Fahrenheit) without this pivotal process. Instead, thanks to greenhouse gases, we experience a more hospitable average temperature of approximately 15 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit). The importance of this effect cannot be overstated; it sustains ecosystems, dictates weather patterns, and ultimately shapes our day-to-day experiences.
However, the ever-expanding influences of human activity have evolved this harmony into discord. The Industrial Revolution heralded an era of profound alteration to our climate system as carbon emissions surged, pushing concentrations of greenhouse gases beyond their natural limits. Each increment echoes through the environment, altering precipitation patterns, melting polar ice, and ushering in unprecedented temperature elevations.
The Paradox of Excess: Catastrophic Consequences
While greenhouse gases serve as essential allies in maintaining a stable climate, their overabundance has transformed them into detrimental foes. The post-industrial spike in greenhouse gas concentrations is driving significant shifts in Earth’s climate system. Climate scientists project that continued emissions will culminate in an escalation of global temperatures, likely exceeding 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels within the next century. Such scenarios portend ominous consequences — increased frequency of droughts, heightened storm intensity, and rising sea levels threaten ecosystems, economies, and human livelihoods alike.
This precarious situation incites a demand for a paradigm shift. Instead of seeing greenhouse gases solely through the lens of danger, they can also be understood as indicators of human activity. Acknowledging their presence forces us to confront the realities of our carbon footprint while simultaneously inspiring innovative solutions. The quest for sustainable practices and renewable energy sources becomes not just a necessity but an opportunity to reshape our relationship with the atmosphere.
A New Perspective: Transforming Challenges into Opportunities
In this milieu of adaptation and resilience, the community is presented with an opportunity to champion impactful environmental stewardship. Renewable energy technologies, carbon capture, and sustainable agricultural practices emerge as viable solutions that can mitigate the exuberance of greenhouse gases. The integration of science, technology, and community engagement fosters a renaissance where promoting ecological well-being becomes a shared responsibility.
Furthermore, education acts as an empowering tool, revealing the interconnectedness of our actions with the broader ecological networks. Increased awareness leads to advocacy for policies focused on carbon reduction and sustainable development. Consuming knowledge can ignite a passion for change, inciting curiosity and inspiring grassroots movements that are potent enough to influence the very future of our climate.
In conclusion, while greenhouse gases are integral to life on Earth, understanding their duality as both necessary and perilous reshapes our perspective. We stand at a crossroads, where the choices we make will define our legacy. By embracing sustainable practices and championing innovative solutions, we possess the power to reclaim ecological balance. Through collective action and informed understanding, we can rechart our journey towards a more resilient and harmonious coexistence with the planet we call home.