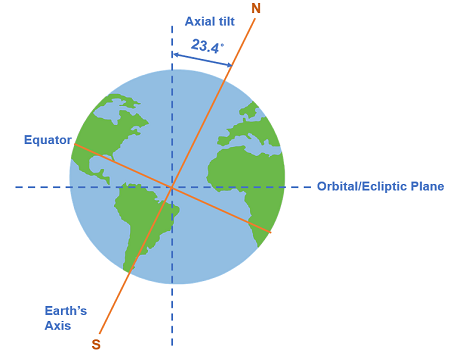
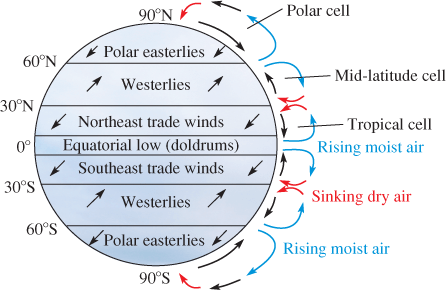
The Earth spins on its axis—an established fact, yet one that underscores a marvel of cosmic engineering. This axial tilt, or obliquity, is not merely a trivial detail; it profoundly influences our planet’s climatic patterns and the rhythms of life that flourish upon its surface. Understanding the intricacies of this inclination reveals a captivating interplay between celestial mechanics and terrestrial phenomena, significantly shaping weather patterns, seasonal cycles, and ultimately, the biosphere itself.
The Obliquity of Earth: An Overview
Earth’s axial tilt measures approximately 23.5 degrees. This non-perpendicular alignment relative to its orbital plane is a defining characteristic that dictates our seasonal changes. As the Earth orbits the Sun, different portions receive varying levels of solar insolation, which drives temperature variations across latitudes. When the Northern Hemisphere tilts toward the Sun, it basks in the warm embrace of summer, while the Southern Hemisphere simultaneously swathes in the cooler shadows of winter.
This eternal dance is the essence of seasons. However, the tilt’s influence extends far beyond mere temperature variations. It orchestrates a symphony of ecological and meteorological transformations that ensure life’s continuity and diversity.
The Climate Constellation
The axial tilt is a principal architect of regional climates. Zones near the equator, where the sun’s rays strike most directly, remain warm year-round. Conversely, higher latitudes oscillate between extremes. Their climatic identity is intricately shaped by the axial tilt, which engenders not only temperate seasons but also allows the formation of diverse ecosystems.
In addition to influencing temperature, axial tilt affects atmospheric circulation. This phenomenon triggers the migration of wind belts and ocean currents, which transport heat across the globe. The result is a complex and interdependent climate system where changes in one locale can reverberate worldwide, affecting monsoons in India or droughts in the American Southwest.
Glacial Epochs and Climatic Shifts
Over geological timescales, variations in Earth’s axial tilt have been pivotal in initiating glacial and interglacial periods. These shifts are part of the Milankovitch cycles, which also encompass eccentricity and precession. The interplay among these cycles engenders significant climate variations that can last thousands of years. During periods of increased obliquity, warmer summers in the higher latitudes may lead to the melting of ice sheets, contributing to rising sea levels—a dynamic that resonates through the ages.
Understanding these long-term changes is paramount, especially in the context of contemporary climate change. The natural cycles of glaciation and warming have been disrupted, leading to unprecedented challenges for ecosystems and human societies. The axial tilt, previously a stable marker of seasonal changes, now operates within a framework altered by anthropogenic influences, raising questions about future climatic stability.
Ecological Implications
The axial tilt’s effect extends into the realm of ecology. Seasonal changes driven by this tilt dictate mating seasons, migration patterns, and food availability across various species. For example, many birds undertake long migrations in response to seasonal shifts, relying on cues from changing day length as the Earth cycles through its yearly journey around the Sun. Similarly, plant life aligns its growth patterns with seasonal variation—flowering earlier in warmer springs and adjusting seed dispersal mechanisms.
Ecosystems are adaptive, yet they are also sensitive. Sudden shifts due to climate change could disrupt ecological relationships. If spring arrives earlier than usual, it may not coincide with the life cycles of species that are reliant on established seasonal timings. This mismatch can precipitate cascading effects throughout entire food webs, emphasizing the delicate balance maintained by Earth’s axial tilt.
Global Climate Debate
The ongoing discussion surrounding climate change magnifies the importance of understanding our planet’s axial mechanisms. Scientists stress that while natural cycles have historically influenced climate, the current rapid changes observed can largely be attributed to human activities—particularly greenhouse gas emissions. The interconnection between anthropogenic factors and Earth’s tilt manifests in heightened weather extremes, loss of polar ice, and significant shifts in biodiversity. Awareness of these influences necessitates a multi-faceted approach to environmental stewardship.
A Shift in Perspective
Embracing an understanding of Earth’s axial tilt cultivates a broader perspective on environmental sustainability. Recognizing our planet as a dynamic entity, shaped by astronomical forces, urges society to approach climate issues with humility and precision. It is not merely the actions of humanity that dictate climate outcomes; instead, it is the interplay between our actions and the intricate mechanisms of our planet that must be understood to forge effective climate policies.
Conclusion
The tilted truth of Earth’s axis serves as a pivotal reminder of the complexities within our climate system. The axial tilt is far from a simple number; it is a gateway into understanding the delicate and intricate balance that supports life. As we confront climate challenges in this era of unprecedented change, a deep appreciation for these celestial mechanics could foster a renewed commitment to preserving the fragile systems that sustain us. Our planet’s future hinges on our ability to adapt and respond, informed by an awareness of the natural rhythms established by the Earth itself.