The phenomenon of global warming has transcended mere speculation and doubts, cementing itself as one of the most pressing challenges humanity faces today. The Earth’s average temperature has risen significantly over the last century, a consequence that many attribute to anthropogenic activities. As we delve into this multifaceted issue, it’s imperative to examine its diverse environmental impacts, ranging from rising sea levels to altered ecosystems.
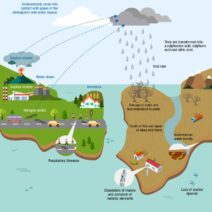
One of the most observable manifestations of climate change is the increase in sea levels. The polar ice caps and glaciers, long revered for their grandeur, are slowly succumbing to the relentless march of warmth. As these frozen reservoirs melt, the oceans swell. According to research, sea levels have risen by about eight inches since 1880, a seemingly innocuous figure that bears immense implications for coastal ecosystems and human settlements. Coastal cities around the globe are now grappling with the specter of chronic flooding. Miami, New York City, and Venice, once bastions of cultural heritage, face an uncertain future, where the line between land and sea blurs alarmingly.
In tandem with rising sea levels, ocean acidification emerges as a critical consequence of climate change. The oceans absorb approximately one-third of the carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere, leading to a decrease in seawater pH levels. Marine ecosystems, particularly coral reefs, are bearing the brunt of this transformation. Coral bleaching, driven by rising sea temperatures and acidification, threatens the rich biodiversity these underwater paradises harbor. Coral reefs, which sustain vast marine species and provide livelihoods for millions, are transforming into ghostly remnants of their former selves. The loss of these vibrant ecosystems could trigger a cascade of extinctions, disrupting the delicate balance of marine life.
Shifts in weather patterns provide another somber reflection of our warming planet. The increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events—hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires—underscore the fragility of our current climate systems. In recent years, incidents of catastrophic wildfires in places like Australia and California have devastated natural habitats and inflicted human suffering. These conflagrations are not merely appetites for destruction; they signal profound changes in vegetation, soil health, and air quality. The ecological repercussions extend beyond the immediate destruction, influencing local weather patterns and further entrenching the climate crisis.
Moreover, altered precipitation patterns have engendered significant shifts in freshwater availability. Regions that once experienced predictable rainfall are now confronting erratic weather systems. The Mediterranean basin, for instance, faces intensified droughts, putting pressure on agriculture and water supplies. Conversely, other areas witness unprecedented flooding, wreaking havoc on infrastructure and ecosystems alike. These disruptions exacerbate resource scarcity and contribute to social unrest, laying the groundwork for conflicts over dwindling freshwater supplies.
In analyzing the impacts of climate change, it is essential to recognize its insidious implications on terrestrial biodiversity. Many species find themselves caught in the throes of habitat loss and shifting climatic zones. The red wolf, once widespread across the southeastern United States, faces an uphill battle against dwindling habitats and encroaching urbanization. As their natural environments transform, species like the red wolf may find themselves unable to adapt, leading to population declines and potential extinction. The interconnectedness of all life on Earth cannot be overstated; the loss of one species can initiate a domino effect, disrupting entire ecosystems.
This precarious situation is further exacerbated by human-induced activities such as deforestation. Forests, often lauded as the lungs of our planet, are dwindling at an alarming rate. The Amazon rainforest, a treasure trove of biodiversity, is experiencing rampant deforestation primarily for agriculture and logging. The consequences are dire—not only do these actions emit vast amounts of carbon dioxide, but they also diminish the forest’s capacity to absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, creating a vicious cycle that further accelerates climate change. Protecting these vital ecosystems is not merely an environmental imperative; it is integral to maintaining the Earth’s overall health.
The ramifications of climate change extend beyond ecological consequences; they touch upon social justice issues that require urgent attention. Vulnerable populations, particularly in developing nations, bear the brunt of its impacts. Rising sea levels, extreme weather conditions, and dwindling resources disproportionately affect communities that lack the infrastructure and means to adapt. Climate refugees—individuals forced to leave their homes due to climatic upheaval—are becoming an increasingly pressing concern. Addressing climate change thus necessitates a commitment to equity and justice, ensuring that those who contribute the least to the crisis are not the ones who suffer the most.
However, amidst the overwhelming challenges posed by climate change, there remains a glimmer of hope. Innovations in renewable energy, sustainable agricultural practices, and reforestation initiatives are burgeoning across the globe. These advances offer viable solutions that not only mitigate the impacts of climate change but also promote resilience. Transitioning towards a low-carbon economy, fostering circular economies, and embracing sustainable practices can catalyze a substantial shift in how societies operate.
In conclusion, the warming Earth presents distinct yet interconnected environmental impacts that challenge the fabric of natural and human systems alike. As we grapple with rising sea levels, weather extremes, and ecosystem disruptions, it becomes evident that our actions today shape the future of our planet. By fostering awareness, advocating for sustainable practices, and promoting equitable solutions, we can aspire to be stewards of the Earth. The time for action is now; the fate of future generations hangs precariously in the balance.