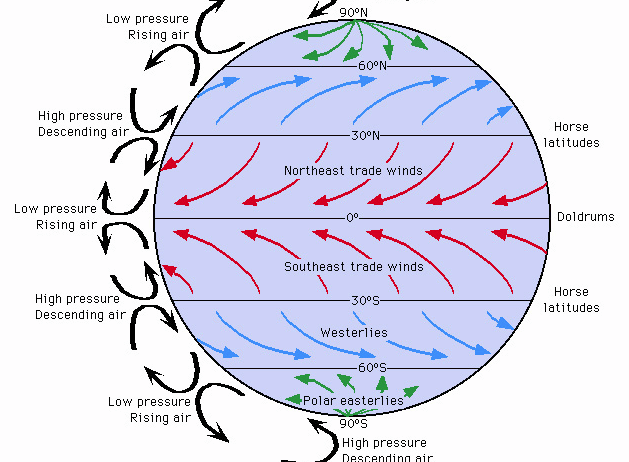
As we traverse the globe, a seemingly innocuous phenomena unfolds: winds sweep across continents, altering landscapes, and influencing weather patterns in profound ways. Atmospheric circulation, characterized by predominant wind patterns, dictates not only climatic conditions but also the broader ecological tapestry of Earth. The urgent specter of global warming, however, has introduced nuanced complexities into this intricate system. This discussion delves into the subtle yet significant influence of anthropogenic climate change on atmospheric circulation, unraveling the interconnections between altered wind patterns and the impending environmental challenges we face.
At its core, atmospheric circulation serves as a dynamic conveyor belt that redistributes heat and moisture across the globe. The interactions between the equator and the poles drive this circulation, creating wind belts that include the trade winds, westerlies, and polar easterlies. These winds are not mere whims of nature; they are the earth’s respiratory pathways, constantly moving air masses that influence temperature and precipitation patterns. Understanding their intricacies is crucial, especially considering the impending shifts wrought by climate change.
One begins to notice that alterations in temperature gradients between the equator and polar regions can lead to profound changes in wind patterns. As the planet warms—a consequence of greenhouse gas emissions—the polar regions experience accelerated warming compared to their tropical counterparts. This differential heating modifies the traditional jet streams, altering their behavior and trajectory. The result? Unpredictable weather patterns, including prolonged droughts in some regions and increased precipitation in others. The ramifications of these shifts are multifaceted and often catastrophic, impacting agriculture, water resources, and biodiversity.
The polar vortex, a significant player in our weather narrative, exemplifies the impact of global warming on atmospheric circulation. This phenomenon represents a large area of low pressure and cold air surrounding the Earth’s poles. As the Arctic warms, the polar vortex can weaken and become distorted. This distortion allows frigid Arctic air to plunge southward into temperate regions, leading to severe winter storms and colder-than-normal temperatures. Conversely, a strengthened polar vortex can contain the cold air, resulting in milder winters and heat surges in the mid-latitudes. Such oscillations reflect the chaotic ballet performed by atmospheric currents exacerbated by climate change.
Furthermore, it is essential to consider how shifts in atmospheric circulation impact ocean currents. The interplay between wind patterns and sea surface temperatures creates thermohaline circulation, often referred to as the “global conveyor belt.” Changes in wind direction can impact the uptake of heat and nutrients by oceans, ultimately affecting marine ecosystems and fisheries. The consequences for food security are immense, as countless communities rely on stable fish populations for their livelihoods and nutrition—highlighting yet another dimension of the climate crisis.
Moreover, the influence of global warming on atmospheric circulation extends beyond mere temperature and precipitation changes. Changes in wind patterns have cascading effects on air quality and the distribution of pollutants. Regions that previously had consistent wind patterns may experience stagnation, trapping heat and pollutants. Such conditions exacerbate health risks, particularly in urban areas where air quality is already a major concern. The rise of respiratory ailments, allergies, and other health issues directly correlates with the prevalence of poor air quality, ushering in a public health dilemma that requires urgent attention.
As the winds change, so too does the distribution of flora and fauna. Ecosystems are intricately connected to prevailing weather patterns, which dictate growing seasons, migration routes, and species interactions. A shift in atmospheric circulation could lead to habitat loss for many species, as their ecological niches are rendered inhospitable by novel climatic conditions. The delicate balance of ecosystems hangs precariously in the balance, with the potential for widespread biodiversity loss as species fail to adapt to rapidly shifting environments.
Moreover, the socioeconomic implications of these atmospheric changes cannot be understated. Vulnerable communities, lacking the resources to adapt, face disproportionate risks. Farmers may struggle to cultivate crops in the face of erratic weather, while coastal regions grapple with rising sea levels and intensified storms. As resources become scarcer and environmental conditions deteriorate, conflicts over water and land may emerge, compounding existing inequalities and undermining social cohesion.
Addressing the intricate relationship between atmospheric circulation and global warming necessitates a multifaceted approach. First, enhanced monitoring and predictive modeling of atmospheric changes will be vital. Understanding how these patterns evolve will equip policymakers and communities with the knowledge needed to respond proactively. Moreover, investing in renewable energy sources and energy-efficient technologies will mitigate greenhouse gas emissions, slowing the pace of climate change and aiding in the maintenance of stable atmospheric conditions.
In addition, public awareness and education are paramount. Understanding the interconnectedness of atmospheric circulation and the issues of climate change empowers individuals to advocate for sustainable practices and policy changes. Cultivating a sense of stewardship for the planet will drive collective action toward mitigating climate impacts.
The winds may change, but our understanding and responses need not falter. By recognizing the subtle influences of global warming on atmospheric circulation, we can appreciate the complexities of our environment and strive towards a sustainable future. The intricate dance of winds is not merely a matter of meteorological curiosity; it is a pressing reminder of our responsibility to act. The future of our climate, ecosystems, and societies rests upon our ability to navigate these changes with urgency and intentionality.