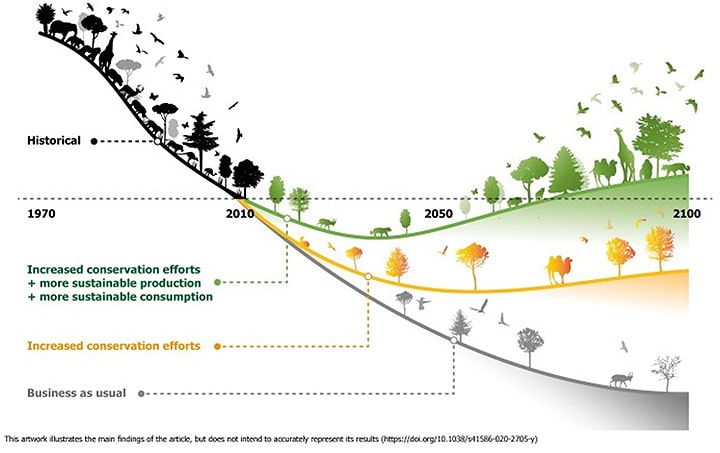
As we traverse the intricate tapestry of the natural world, it becomes increasingly evident that climate change is not a distant threat but an immediate and pressing concern that jeopardizes the existence of various species. Among the most emblematic creatures teetering on the precipice of extinction are tigers, whales, and wolves. Each of these magnificent animals plays a crucial role in their respective ecosystems, and their decline heralds significant repercussions for biodiversity and ecological balance.
Tigers, the apex predators of the lush forests and expansive grasslands, are unfortunately emblematic of wildlife under siege. The loss of their habitat, exacerbated by climate change, is pushing these formidable felids towards the brink of extinction. Due to rising temperatures and shifting weather patterns, tiger habitats, particularly in Southeast Asia, are being radically altered. The wetlands they rely upon are drying up, and dense forests are becoming fragmented, making it increasingly challenging for them to hunt and roam. This not only threatens their survival but disrupts the complex ecosystem dynamics they help sustain. As top predators, their decline can lead to overpopulation of prey species, resulting in further degradation of habitats and reduced biodiversity.
Whales, the behemoths of the ocean, also face myriad challenges posed by a changing climate. As the world warms, polar ice caps are melting, and sea levels are rising, leading to significant alterations in whale migration patterns and breeding grounds. For example, the iconic beluga whale and the narwhal, both dependent on ice-covered regions for their survival, are increasingly threatened as their habitats evaporate. Additionally, warmer waters can shift the distribution of krill and other critical food sources, leaving whales struggling to find sustenance. The ocean is also becoming more acidic, a direct consequence of increased carbon dioxide levels, which can have catastrophic effects on marine life and ecosystems.
Meanwhile, wolves serve as a vital ecological keystone species. Their role in maintaining the health of the ecosystems they inhabit cannot be overstated. As hunters at the top of the food chain, wolves regulate ungulate populations. This balance is necessary to ensure that vegetation does not become overgrazed, which can lead to soil erosion and the decline of other species. However, climate change threatens the delicate ecosystems wolves inhabit. Changing weather patterns disrupt prey availability and alter habitat structure. For example, increased temperatures can lead to more frequent habitat destruction and fragmentation, making it increasingly difficult for wolves to thrive. Climate-related stressors like disease, competition, and access to food sources compound the threats they face.
Understanding the plight of tigers, whales, and wolves provides a glimpse into the larger narrative of climate change and its impact on biodiversity. These animals are not isolated in their struggles; their fates are intricately linked to our shared habitat. A movement towards conservation and reversing the tides of climate change is not merely necessary; it is imperative for the survival of countless species. The systemic collapse of ecosystems can lead to unprecedented consequences, including food shortages for humans who depend on these ecosystems for sustenance.
Conservation efforts must be multifaceted. Firstly, creating protected areas that allow wildlife to thrive is crucial. These safe havens can serve as critical refuges for tigers, wolves, and whales, ensuring that they have the space to hunt, breed, and flourish. Furthermore, habitat restoration projects are essential to combat fragmentation and to recover degraded ecosystems. It is vital to reconnect landscapes to promote genetic diversity and resilience among wildlife populations.
Moreover, addressing the root causes of climate change is paramount. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, reducing carbon emissions, and implementing sustainable agricultural practices are all vital steps. A collective global effort, encompassing local communities, governments, and corporations, can drive this transition and cultivate a culture of conservation. Education and awareness are powerful tools; by fostering a sense of responsibility and connection to the natural world, we can inspire individuals to take action.
The narrative is not solely one of despair but also of hope and resilience. While tigers, whales, and wolves face dire circumstances, numerous organizations, initiatives, and individuals are working tirelessly to mitigate these threats. By engaging with indigenous knowledge and local communities, innovative conservation strategies that honor traditional ecological practices can be developed. Collaborative efforts that include scientific research, policy advocacy, and community engagement can usher in transformative changes and lead to a renewed understanding of our relationship with nature.
In closing, as we navigate this critical juncture, it is essential to recognize the interconnectedness of all life forms. The fate of tigers, whales, and wolves serves as a poignant reminder of the broader environmental crisis looming over us. To safeguard the future of these majestic creatures and, by extension, our own, we must embrace sustainable practices and advocate for policies conducive to environmental restoration and conservation. The time for action is now; the urgency of the moment calls for a collective awakening to the challenges facing our planet.
Let us not wait until these magnificent species are mere specters of what once was. Instead, let us foster a legacy of stewardship, commitment, and passion for the preservation of biodiversity. Together, we can cultivate a harmonious existence with nature, ensuring that tigers, whales, and wolves, alongside countless other species, continue to thrive for generations to come.