The terms “global warming” and “climate change” are often used interchangeably, but they signify distinct phenomena that merit careful exploration. Understanding the nuanced differences is essential for grasping the broader implications of our environmental crisis and encouraging more informed discourse on sustainability. This article aims to dissect the distinctions between global warming and climate change, emphasizing their interrelatedness while illuminating the urgency of addressing both issues.
In the quest to decode these concepts, we embark on a journey that promises a shift in perspective, urging the inquisitive to ponder their roles in the unfolding narrative of our planet’s future.
Global Warming: An Overview of Rising Temperatures
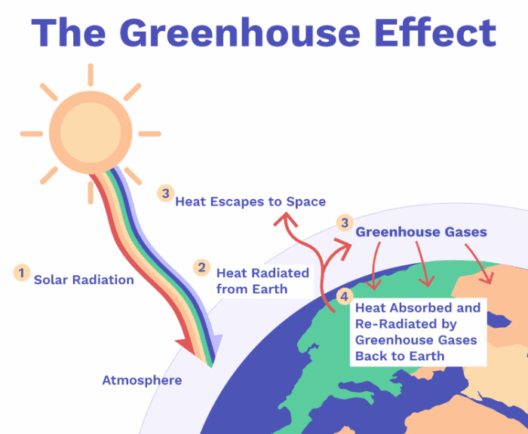
When we refer to global warming, we are specifically discussing the increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to rising levels of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4). This phenomenon is primarily attributed to human activities, such as the combustion of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. The resulting accumulation of these gases in the atmosphere creates a “greenhouse effect,” trapping heat and leading to an overall warming trend.
The repercussions of global warming are multifaceted. Not only does it lead to rising temperatures across continents, but it also causes significant disruptions in weather patterns. Heatwaves become more frequent and severe, leading to detrimental effects on agriculture, water supplies, and public health. For instance, the tumultuous shifts in temperature can undermine crops, leading to food insecurity and economic disparities between nations.
A critical aspect of global warming is its quantifiable nature. Scientists utilize an array of methodologies to track temperature changes, relying on satellite data, oceanic measurements, and surface records to establish a clear upward trend. The last century alone has witnessed an increase in global temperatures by approximately 1.2 degrees Celsius since the late 19th century. This stark statistic underscores the immediacy of global warming’s ramifications.
Climate Change: A Broader Perspective
Climate change, on the other hand, encompasses a more extensive array of transformations within Earth’s climate system. While global warming is a crucial component of climate change, the latter also includes alterations in precipitation patterns, extreme weather events, and shifts in seasonal cues. Thus, climate change represents the aggregate impacts of both natural phenomena and anthropogenic influences acting upon the environment.
One notable aspect of climate change is its non-linear progression. While temperature increases might be relatively straightforward to measure, the multitude of effects stemming from climate change can be divergent and unpredictable. For instance, as glaciers and polar ice caps melt, sea levels rise, posing significant threats to coastal ecosystems and human settlements. Similarly, altered precipitation patterns can lead to increased flooding in some areas while simultaneously causing drought in others.
This variability complicates efforts to formulate effective responses. Policymakers must consider localized impacts when designing strategies to combat climate change, recognizing that communities will experience its effects differently based on geographical, socio-economic, and cultural factors. Such tailored approaches are vital for addressing the unique challenges posed by changing climates, emphasizing adaptation and resilience.
Interconnectedness: How Global Warming Fuels Climate Change
A pivotal aspect of understanding the interplay between global warming and climate change lies in recognizing their interconnectedness. The warming of the planet exacerbates climate change effects, leading to a feedback loop that intensifies environmental challenges. For example, as temperatures rise, ice sheets in the Arctic regions melt, diminishing their ability to reflect sunlight and thereby further warming the Earth—a phenomenon known as the albedo effect.
This interplay has significant implications for the global ecosystem. Changes in species distributions, habitat loss, and increased extinction rates are direct consequences of the interrelationship between global warming and climate change. Marine ecosystems, in particular, face unprecedented challenges as warmer temperatures lead to ocean acidification and coral bleaching, threatening biodiversity and fishing livelihoods worldwide.
Another critical aspect to consider is the socio-economic implications of this interconnectedness. Vulnerable populations, particularly in developing countries, often lack the resources to adapt to climate change impacts, which can exacerbate poverty and inequality. Hence, addressing global warming is not only an environmental imperative but also a matter of social justice, as those least responsible for greenhouse gas emissions are often the most greatly affected.
Taking Action: The Path Forward
Understanding the distinctions and connections between global warming and climate change is vital for fostering informed conversations about climate action. This entails supporting policies that mitigate emissions, promoting renewable energy sources, and advocating for sustainable practices across all sectors of society. Communities and individuals alike must recognize their capacity to make a difference, engaging in local initiatives that contribute to a global response.
Furthermore, education plays a crucial role in broadening public awareness about these complex issues. By equipping individuals with knowledge about sustainable practices and climate science, we can inspire change at grassroots levels, cultivating a culture of environmental stewardship that transcends political or ideological divides.
Ultimately, global warming and climate change are not merely scientific terms; they represent the lived experiences of millions and shape the future of our planet. By decoding their differences and understanding their interconnectedness, we pave the way for strategic and meaningful action aimed at preserving Earth’s delicate balance. Acting with urgency is paramount; the time to address these pressing issues is now.
In closing, the journey to combat global warming and climate change is fraught with challenges but also brimming with opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and a profound reconciliation with the natural world. As we delve deeper into these concepts, let us remain curious and determined to usher in a new era of environmental consciousness and responsibility.