Wind energy has emerged as a significant force in the global pursuit of renewable energy sources. Harnessing the wind to generate electricity is lauded for its potential environmental benefits and cost-effectiveness. However, it is imperative to scrutinize both the advantages and disadvantages of wind power to form a balanced perspective on its viability as a sustainable energy solution. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of wind energy, weighing its virtues against its drawbacks.
Understanding the Mechanisms of Wind Energy
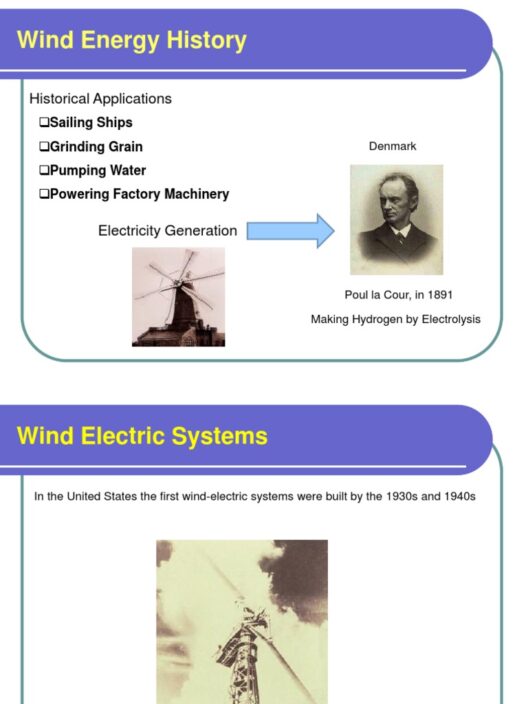
Wind energy is produced through the conversion of kinetic energy from wind into mechanical power, which is then transformed into electricity by turbines. This process is straightforward and has gained traction as technology has improved. Wind farms, which consist of numerous turbines, are often located in areas with optimal wind conditions. Thus, the geographical selection significantly impacts the effectiveness of wind energy generation.
Environmental Impact: A Breath of Fresh Air
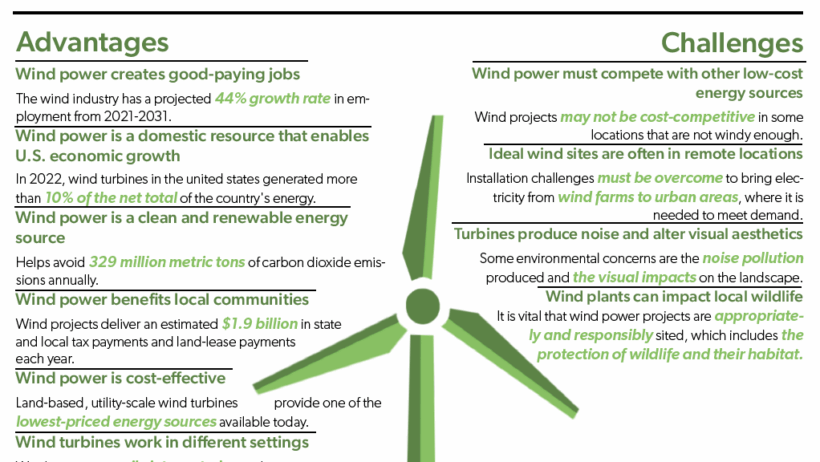
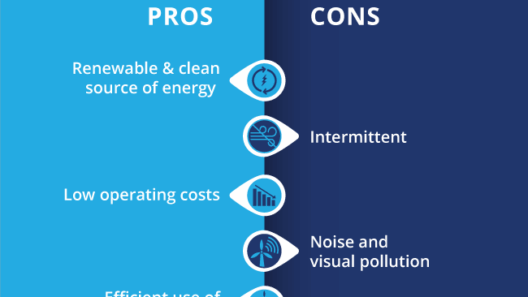
One of the most compelling advantages of wind energy is its minimal environmental footprint. Unlike fossil fuels, wind power generation does not emit greenhouse gases during operation, which significantly contributes to the reduction of air pollution. This aspect is crucial in mitigating climate change and fostering a more sustainable world for future generations.
Moreover, wind energy has a lower water usage compared to conventional energy sources. Water-intensive processes such as cooling in fossil fuel and nuclear power plants are largely eliminated in wind energy production. This not only preserves vital freshwater resources but also protects aquatic ecosystems from thermal pollution.
Job Creation and Economic Growth: Harnessing Opportunities
The wind sector is a burgeoning industry that fuels job creation. From manufacturing turbines to installation and maintenance, the sector requires a diverse workforce. As of recent statistics, thousands of jobs in the United States alone are attributed to wind energy production, with numbers steadily increasing. This growth not only revitalizes rural economies but also contributes to technological advancement and innovation.
Cost-Effectiveness Over Time: The Financial Equation
Furthermore, as technology advances and experience in the field accumulates, the cost of wind energy is plummeting. The initial investment for wind farms is considerable, but the levelized cost of electricity has become competitive with traditional energy sources. Due to low operational and maintenance costs, wind energy can offer long-term savings for consumers and businesses alike.
Challenges of Wind Energy: The Wind’s Whims
Despite its advantages, wind energy is not without its challenges. One of the most significant disadvantages is the intermittent nature of wind. Unlike fossil fuels or nuclear energy, which provide a constant energy supply, wind power generation fluctuates based on wind availability. This intermittency necessitates the development of robust energy storage solutions and backup systems, which can complicate grid management and increase operational costs.
Noise Pollution: The Industrial Serenade
Another concern that oftentimes emerges in discussions about wind farms relates to noise pollution. Wind turbines generate sound during operation, which some individuals living in proximity find disruptive. Although technological advancements have reduced noise levels, the presence of turbines may still pose a nuisance for nearby residents. This concern is both valid and warrants consideration during the planning and placement of wind energy projects.
Impact on Wildlife: Balancing Conservation and Generation
The impact of wind farms on wildlife, particularly avian and bat populations, raises ecological concerns. Birds and bats can be susceptible to collisions with turbine blades, leading to fatalities. Although studies and mitigation strategies are evolving to minimize these risks, they remain a contentious issue in the expansion of wind energy infrastructure. Proponents of wind energy must balance the commitment to renewable energy with the ecological responsibility of protecting biodiversity.
Socioeconomic Implications: Community Perspectives
The establishment of wind farms can ignite local controversy. While some communities applaud the economic benefits and environmental contributions of wind energy, others may express apprehension regarding visual impacts on landscapes or perceived threats to property values. Engaging local stakeholders throughout the planning phase is essential to ensure their concerns are addressed and to foster acceptance of wind energy projects.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Wind Power
In summary, wind energy presents a mosaic of advantages and disadvantages that must be carefully evaluated. The ecological benefits, potential for job creation, and declining costs are compelling arguments for its adoption. However, challenges such as intermittency, noise pollution, and wildlife impacts cannot be overlooked. As society endeavors to transition to cleaner energy sources, the role of wind power will undoubtedly remain pivotal.
Assessing the future of wind energy demands a nuanced approach, where ongoing innovation and community engagement play vital roles. By weighing the pros and cons judiciously, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of wind power while working towards a sustainable energy landscape. The wind may indeed be a powerful ally in the global pursuit of a cleaner and greener planet.