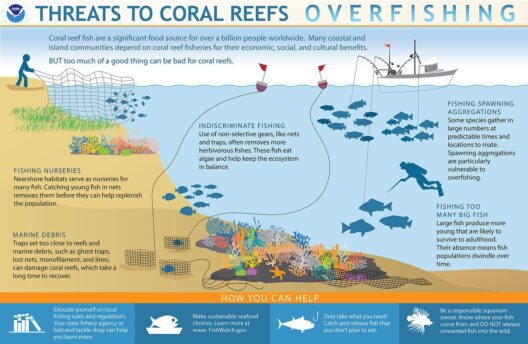
Wind energy has emerged as a leading contender in the quest for sustainable and renewable power sources. As nations pivot towards environmentally friendly energy solutions, the advantages and disadvantages of wind energy necessitate thorough examination. Understanding both the promising potential and the inherent challenges is essential for informed decision-making in urban planning, policy development, and individual energy choices.
The Promising Advantages of Wind Energy
Wind energy presents a plethora of benefits that align with global efforts to reduce dependency on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change. The following key advantages demonstrate why wind power stands as a pivotal component of our energy future.
Renewable and Abundant Resource
Wind energy is a renewable resource, continually replenished by nature. Unlike fossil fuels, which can be depleted, wind is inexhaustible over human timescales. In most regions, especially those with favorable geographic and climatic conditions, wind can provide a consistent and robust source of energy. With the appropriate technology, the harvesting of wind becomes a self-sustaining cycle, providing a steady flow of energy without depleting Earth’s resources.
Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
One of the most significant advantages of wind power is its potential to drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Traditional energy sources, such as coal and natural gas, release substantial amounts of carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the atmosphere. Wind energy, on the other hand, produces electricity without emitting harmful gases during operation. This transition is crucial in the battle against climate change and in enhancing air quality, subsequently leading to improved public health outcomes.
Economic Benefits and Job Creation
The wind energy sector not only fosters a cleaner environment but also stimulates economic growth. The construction, operation, and maintenance of wind farms create numerous jobs—ranging from engineering and manufacturing to logistics and installation. As governments and private companies invest in wind energy, they cultivate a burgeoning industry that can buoy local economies and provide stable employment opportunities. Additionally, wind power projects often lead to increased local tax revenues, which can be invested back into the community.
Challenges and Disadvantages of Wind Energy
While the benefits of wind energy are compelling, it is imperative to address the drawbacks that accompany this form of energy generation. Understanding these challenges enables stakeholders to mitigate risks and develop more resilient energy infrastructures.
Intermittent Energy Supply
Wind energy is inherently intermittent; it relies on natural wind patterns that can be unpredictable. This variability poses challenges for energy grid management. In times of low wind speeds, energy output can dwindle significantly, leading to potential energy shortages if alternative sources are not adequately integrated into the grid. Consequently, maintaining a balanced energy supply necessitates the exploration of complementary energy systems, such as solar, hydro, or energy storage solutions, to ensure stability.
Impact on Wildlife and Ecosystems
The deployment of wind turbines can have adverse effects on local wildlife, particularly bird and bat populations. Collisions with turbine blades pose a significant threat to these creatures, potentially disrupting local ecosystems. Moreover, the construction and maintenance of wind farms can alter habitats, impacting flora and fauna. Therefore, it becomes essential for developers to conduct thorough environmental assessments before establishing wind projects to minimize biodiversity loss.
Aesthetic and Noise Considerations
Wind farms often face opposition from local communities, primarily due to concerns over aesthetics and noise. The visual impact of large turbines on landscapes can be considered detrimental by residents who value the natural scenery. Additionally, the sound generated by wind turbines can be disruptive, particularly in quiet, rural areas. Addressing these concerns through thoughtful design, location selection, and community engagement is vital for achieving public acceptance and integration of wind energy projects.
Balancing the Scales: Wind Energy’s Future
As we contemplate the trajectory of wind energy, it is evident that its integration into our energy systems will require a balanced approach. The advantages—renewability, reduced emissions, and economic stimulation—must be weighed against the challenges of intermittency, environmental impact, and social acceptance. Innovations in technology, such as advanced predictive analytics and quiet turbine designs, are already addressing many of these issues. Moreover, on a policy level, governments can establish frameworks that support sustainable development while encouraging community engagement and stakeholder cooperation.
Ultimately, wind energy embodies a significant step towards a sustainable future. Striking the right balance between its advantages and disadvantages presents an opportunity to develop a reliable, clean, and economically viable energy landscape. Through informed decision-making and collaborative effort, we can harness the potential of wind power, paving the way for a greener, more sustainable world.