Wind power, a renewable energy source harnessing the kinetic energy of the wind, has gained momentum in recent years due to its myriad advantages. This article delves into the benefits of wind energy, a crucial player in the transition toward a sustainable future. Understanding these advantages unveils the essential role that wind power plays in shaping a cleaner environment and a more resilient economy.
The allure of wind energy lies not only in its apparent ecological benefits but also in the social, economic, and technical implications that emerge from its widespread adoption. The advantages of wind power extend beyond mere energy production, embracing a comprehensive framework that supports sustainable development, community engagement, and global cooperation.
As the world grapples with climate change and the quest for energy independence, wind power emerges as an attractive solution. Below, we explore the multifaceted benefits of wind energy, revealing why it captivates the imagination and serves as a cornerstone in the fight for a sustainable planet.
Environmental Advantages: A Breath of Fresh Air
One of the most compelling reasons to embrace wind energy is its minimal environmental impact. Unlike fossil fuels, wind energy generation produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, significantly reducing the carbon footprint. This crucial advantage addresses climate change, as traditional energy sources contribute to harmful emissions that exacerbate global warming.
Moreover, wind energy is remarkably efficient in resource utilization. A single wind turbine can generate enough electricity to power hundreds of homes, maximizing energy output without depleting natural resources. The use of wind also conserves water, an increasingly precious resource. Conventional energy generation methods, such as coal and natural gas, require substantial water for cooling processes, while wind power operates without such demands, thus preserving vital water supplies.
Furthermore, wind installations can be strategically located in areas that do not interfere with agricultural activities. With land that is often compatible with farming or grazing, wind farms can coalesce with existing land uses, promoting biodiversity and securing additional income streams for farmers. Not only does this coexistence protect ecosystems, but it also enhances the sustainability of local economies.
Economic Impacts: Wind Power as a Job Creator
The economic benefits of wind power are profound. As the industry continues to grow, it has become a significant source of employment, especially in regions where traditional energy jobs are diminishing. Wind energy jobs are diverse, ranging from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and research and development. This diversity fosters an inclusive job market, catering to varying skill sets and educational backgrounds.
Investing in wind energy also bolsters local economies. Federal and state incentives encourage the development of wind farms, leading to substantial capital expenditures in local communities. These investments often stimulate related sectors, including construction, transportation, and electrical engineering, contributing to a vibrant economic ecosystem.
Moreover, wind power reduces dependency on imported fuels. By harnessing indigenous wind resources, countries can fortify their energy security, insulate themselves from volatile fossil fuel markets, and promote energy independence. This shift cultivates not only self-sufficiency but also stimulates local economic growth by retaining energy dollars within communities.
Technological Advancements: Innovations in Wind Energy
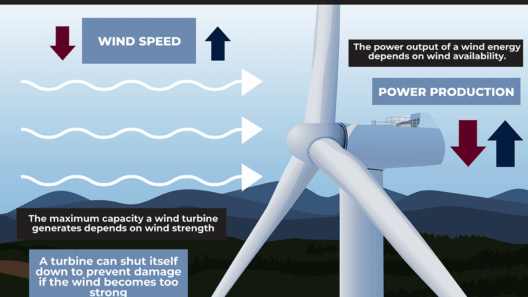
Technological innovation in the wind energy sector is remarkable and serves as a catalyst for enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. Advances in turbine design have led to the development of larger, more powerful turbines capable of generating increased energy output. The integration of digital technologies, such as predictive maintenance and data analytics, optimizes performance and extends the lifespan of wind assets, further solidifying wind energy’s viability.
Furthermore, the wind energy sector is at the forefront of research and development, driving innovation that extends beyond the industry itself. Wind technologies are being adapted for offshore installations, expanding the potential for energy generation while minimizing land use impacts. This expansion into offshore wind has the potential to harness stronger and more consistent winds, unlocking a treasure trove of untapped energy resources.
The interplay between policy and technology also deserves attention. Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing the importance of supportive frameworks for wind energy. Policies such as renewable portfolio standards and tax incentives are helping to catalyze investment and drive technological advancements, promoting a cycle of innovation that enhances the overall effectiveness of wind energy.
Community Engagement: Empowering Local Voices
Wind energy projects often involve substantial community participation and engagement. Communities can benefit from shared ownership models, where local residents have a stake in the wind farm’s success, reaping both financial and social rewards. This inclusiveness fosters a sense of collective ownership, creating a conducive environment for collaboration and dialogue.
Moreover, wind energy development often leads to investments in local infrastructure, including roads and utilities, which serve a dual purpose. These enhancements benefit both the wind farm and the broader community, resulting in improved local amenities. Education initiatives, often funded by wind energy projects, can help demystify renewable energy, empowering communities to embrace sustainable practices and become advocates for clean energy.
The future of wind energy is bright, filled with opportunities that extend well beyond the realm of electricity generation. By understanding the key advantages of wind power—environmental resilience, economic growth, technological advancement, and community involvement—we can appreciate the multifaceted nature of this renewable resource as a beacon of hope in the ongoing transition to a sustainable future.
Ultimately, the appeal of wind energy lies in its ability to address pressing global challenges while fostering prosperity and sustainability. As we stand on the precipice of an energy revolution, wind power stands out as a vital ally, enabling humanity to harness the invisible currents of nature while nurturing the planet for future generations.