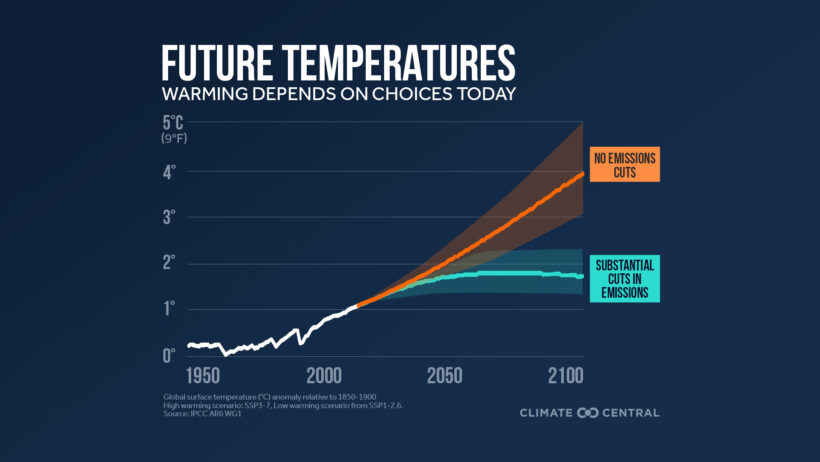
Climate change, an intricate web of phenomena triggered by anthropogenic activities, embodies far more than the singular narrative of escalating global temperatures. As the spectral fog of climate perturbation envelops our ecosystems and societies, diverse impacts unfurl in alarming tandem. Herein, we shall delve into the multifaceted repercussions of climate change, traversing its influence beyond mere thermometric records.
The most conspicuous manifestation often invoked is the rise in average global temperatures; however, this disquisition shall illuminate other formidable consequences that proliferate as a result. Perhaps the most immediate implication is the progressive alteration of weather patterns, which has engendered an increase in the frequency and severity of extreme weather events. Hurricanes, floods, and droughts have become far more commonplace, wreaking havoc on infrastructure and displacing communities. For instance, regions that once experienced moderate precipitation may confront unrelenting floods, while others grapple with severe droughts, rendering agricultural practices perilous.
Inextricably linked to these climatic shifts are the ecological ramifications witnessed across diverse biomes. Marine ecosystems, the vast blue expanses that cover over 70% of Earth’s surface, stand on the precipice of imbalance. Ocean acidification, resulting from elevated atmospheric CO2 levels, jeopardizes coral reef health, home to innumerable species, and disrupts entire marine food webs. Acidification decreases the availability of calcium carbonate, essential for species such as mollusks, which rely on it to form their shells. Consequently, as these organisms decline, the ramifications propagate through the marine environment, with ripple effects impacting fishing industries and food security for millions who depend on these resources.
Moreover, terrestrial ecosystems illustrate a similarly alarming narrative. Shifts in temperature and precipitation have precipitated alterations in species distribution and phenology—the timing of biological events. Certain flora and fauna are unable to adapt fast enough to the changing conditions, inevitably leading to declining populations and, in extreme cases, extinction. The iconic polar bears are emblematic of this crisis; as sea ice diminishes, their hunting grounds evaporate, forcing these apex predators into dwindling habitats and drastically affecting their survival chances.
The human dimensions of climate change are equally salient, encompassing public health ramifications that are often underappreciated. Higher temperatures exacerbate air quality issues, leading to increased respiratory ailments and heat-related illnesses. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions, bear the brunt of these adverse health outcomes. Additionally, shifting climate regimes can alter the ranges of disease vectors, such as mosquitos. Malaria and dengue fever, historically confined to specific locales, may find new breeding grounds in previously temperate regions, introducing public health challenges that demand immediate attention.
Another critical dimension of climate change is its socioeconomic impact. As agricultural yields fluctuate due to erratic weather, food security becomes a pressing concern. According to forecasts, staple crops such as wheat and rice are poised to decline in productivity, compelling nations to grapple with food shortages and rising prices. This destabilization in food supply chains may incite unrest and exacerbate global inequality, as those in lower-income regions often lack the resources to mitigate against food scarcity.
Climate migration represents a poignant consequence of these socioeconomic strains. Individuals and communities grappling with deteriorating living conditions may find themselves compelled to abandon their homes. This phenomenon, often termed as “climate refugees,” poses significant challenges for governments and international organizations as they must reconcile the displacement of populations with existing infrastructure and social services. This interplay sparks tensions, often resulting in xenophobic sentiments and conflict over dwindling resources.
Furthermore, climate change is intricately woven into the fabric of global geopolitical dynamics. Nations blessed with abundant natural resources may find themselves embroiled in conflicts as competition for these dwindling assets intensifies. Equitable resource management becomes increasingly paramount, leading to the emergence of new alliances and confrontations on the world stage. This landscape fosters uncertainty and can have far-reaching implications for international relations.
The economics of climate change warrant significant consideration as well. Mitigation strategies and adaptation measures demand vast investments, igniting dialogues on fiscal policy and economic restructuring. Renewable energy endeavors, carbon credits, and green technologies symbolize the pivot toward sustainability, yet the transition can also engender economic displacement in traditional energy sectors. As workforces adapt to new paradigms, easing this transition for impacted laborers is essential to fostering equitable economic practices.
In addition to these dimensions, the psychological impacts of climate change can be insidious, manifesting as eco-anxiety. The recognition of an uncertain future and the tangible risks associated with environmental degradation can foster feelings of helplessness and despair. Addressing these mental health implications is paramount, as individuals and communities navigate the complexities arising from their changing environments.
In conclusion, the effects of climate change extend far beyond the simplistic narrative of rising temperatures. They permeate every corner of our biosphere and human societies, spawning a myriad of challenges that mirror the complexity of climate systems themselves. From ecological imbalances and socioeconomic turmoil to geopolitical tensions and public health crises, the repercussions underscore a clarion call for sustained and unified action. Only through a comprehensive understanding of these multifaceted effects can we truly grasp the urgency surrounding this planetary crisis and the collaborative efforts needed to combat its detrimental impacts on our world.