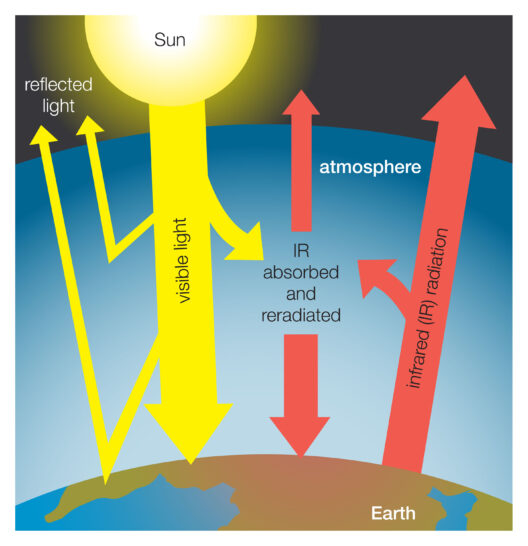
Global warming is an urgent concern that looms over us, manifesting its repercussions in myriad ways. As the planet’s temperature continues to rise due to human activities, primarily from the burning of fossil fuels, understanding the effects of global warming is vital to fostering awareness and inciting action. The following sections will explore the various impacts of climate change on our environment, human health, economy, and biodiversity.
Climate variability, natural disasters, and systemic shifts in ecosystems are becoming more pronounced. It’s essential to dissect these effects to grasp the enormity of the crisis we face.
Environmental Consequences of Rising Temperatures
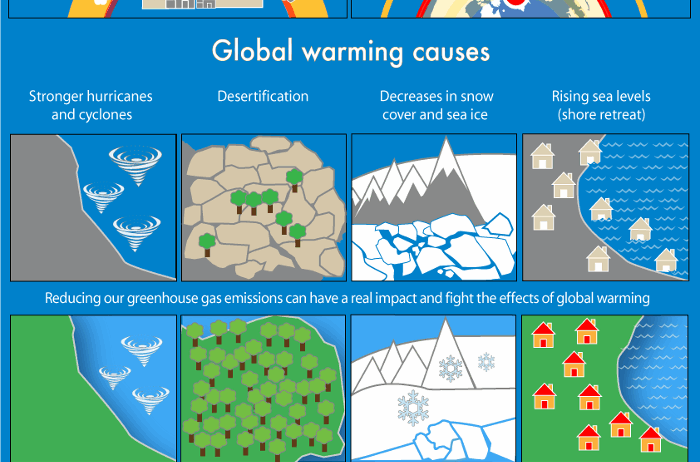
The most apparent effects of global warming are found within our environment. As temperatures inch higher, we observe a series of alarming environmental shifts. One of the crucial phenomena is the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers. The Arctic and Antarctic regions have borne the brunt of this changing climate, where ice shelves are disintegrating at unprecedented rates. Increased melting contributes not only to rising sea levels but also disrupts marine ecosystems that depend on stable ice formations.
Furthermore, elevated temperatures are causing ocean waters to warm, leading to thermal expansion — a major contributor to sea-level rise. The ramifications are dire. Coastal cities face the imminent threat of flooding, displacing countless communities and challenging infrastructure integrity. As shorelines recede, land becomes scarce, and natural habitats for numerous species are encroached upon.
In addition to rising sea levels, we are witnessing the phenomenon of ocean acidification, resulting from increased carbon dioxide emissions that dissolve in seawater. This change in ocean chemistry adversely affects marine life, particularly organisms like corals and shells, which struggle to maintain their calcium carbonate structures. The degradation of coral reefs, often referred to as the “rainforests of the sea,” threatens the biodiversity of marine ecosystems and compromises the livelihoods of those who depend on fishing and tourism.
Temperature Extremes and Ecosystem Disruption
Global warming is not only about an overall increase in temperature; it also brings with it great variability in weather phenomena. Heatwaves are becoming more frequent and severe, spiking the likelihood of droughts and wildfires. Regions previously defined by temperate climates now grapple with extreme conditions, leading to devastating consequences for agriculture. Crops that once thrived may fail, and food security is jeopardized. These agricultural disruptions push farmers into precarious positions, often forcing them to adapt to new realities or abandon their lands altogether.
On the other hand, heavier rainfall patterns lead to flooding and myriad challenges for cultivated land and natural habitats. Soil erosion becomes an issue, stripping the land of nutrients vital for crop growth. Wetlands, crucial for biodiversity and flood control, face inundation, further destabilizing ecosystems. The delicate balance within habitats is disrupted, with species migrating to find climates more hospitable or facing extinction if they cannot adapt swiftly enough.
Human Health Risks: The Silent Crisis
As we delve deeper into the implications of climate change, one troubling aspect emerges: the health risks posed to human populations. Increased temperatures are linked to heightened incidence of heat-related illnesses, such as heat exhaustion and heat stroke. Vulnerable populations — the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing health conditions — are particularly at risk.
Additionally, climate change has far-reaching implications for the spread of infectious diseases. Mosquitoes and ticks thrive in warmer conditions, expanding their range and increasing the prevalence of vector-borne diseases like malaria and Lyme disease. As seasons change, patterns of disease transmission may also shift, compounding challenges for public health systems that must adapt to evolving threats.
Air quality is another area of concern; rising temperatures intensify the formation of ground-level ozone, a key component of smog. Poor air quality exacerbates respiratory conditions, such as asthma, and leads to rising healthcare costs. The interplay between environmental factors and human health underscores the urgency of addressing climate change and implementing effective public health strategies.
Economic Implications: A Rising Toll
The financial repercussions of global warming are as daunting as the environmental and health-related issues. Governments and businesses are already witnessing the financial strain on infrastructure from extreme weather events. Consider the cost of repairs and recovery following hurricanes, floods, and wildfires — expenses that can run into the billions. Investment in resilient infrastructure becomes imperative, yet the funds allocated often draw from already limited budgets, affecting public services.
Furthermore, industries dependent on natural resources, such as agriculture, forestry, and fisheries, face increasing uncertainty. Economic stability relies heavily on predictable weather patterns and stable ecosystems, both of which are being eroded by climate change. As crop yields fluctuate and resources dwindle, prices will likely climb, hitting consumers hard and exacerbating socioeconomic disparities.
Conservation and Sustainability: A Path Forward
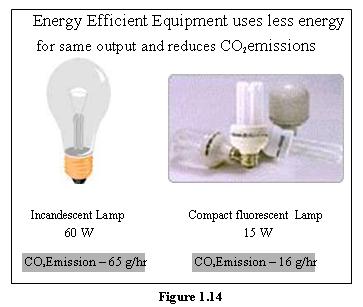
In the face of these challenges, there is hope — hope rooted in awareness, education, and activism. Conservation efforts and sustainable practices can mitigate the impacts of global warming. Individuals are empowered to contribute through lifestyle changes that reduce carbon footprints, such as embracing renewable energy sources, increasing energy efficiency, and supporting sustainable agriculture.
Moreover, robust policy measures can drive large-scale change. Governments must adopt and enforce stringent environmental regulations, incentivize green technology development, and invest in renewable energy projects. Collaborative efforts at local, national, and international levels stand as our strongest weapon against the effects of global warming.
In conclusion, the effects of global warming are far-reaching and interwoven with various facets of life on this planet. The urgency to act cannot be overstated, as these repercussions threaten not only our environmental stability but also public health and economic viability. Through awareness, innovation, and collective action, there remains a path toward a sustainable future — one where we can coexist harmoniously with our planet. It is our responsibility to embrace this challenge and work together toward solutions that preserve the Earth for generations to come.