Understanding the greenhouse effect is crucial in unraveling the complexities of climate change and its implications on Earth’s ecosystems and humankind. While the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that warms the planet, human activities have intensified this process, leading to alarming consequences. This article meticulously explores the various repercussions of the greenhouse effect and the resultant increase in global temperatures.
As humanity grapples with escalating environmental issues, it is vital to shift our perspective on the interrelated nature of these phenomena, examining how they affect not only the planet but also our societies and economies.
Defining the Greenhouse Effect and Its Roots
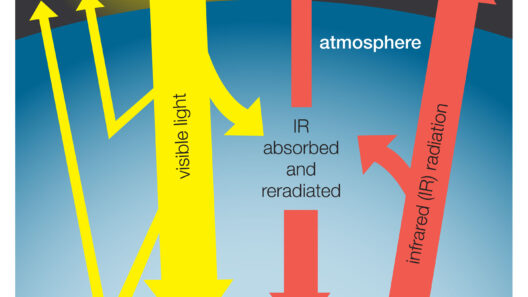
To appreciate the profound effects of the greenhouse effect, one must comprehend its basic mechanics. Solar radiation traverses the atmosphere, warms the Earth’s surface, and is then radiated back into space as infrared energy. However, greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide absorb and re-emit some of this energy, creating a “blanket” around the planet that retains heat.
This natural process is indispensable for maintaining temperatures conducive to life. However, anthropogenic activities, including the combustion of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial practices, have remarkably increased the concentration of these gases in the atmosphere. This alteration exacerbates the natural greenhouse effect, leading to an unprecedented rise in global temperatures.
Climate Change: The Evolution of Extremes
As average global temperatures rise, the probability and severity of extreme weather events proliferate. Heatwaves are becoming increasingly frequent, with unprecedented high temperatures reported across continents. Such drastic shifts compromise human health, as heat-related illnesses, including heat stroke and dehydration, surge during periods of extreme heat.
Moreover, shifting weather patterns give rise to crippling storms, floods, and droughts. The frequency of hurricanes and cyclones has escalated, leaving economic devastation in their wake. For instance, storm surges and heavy rainfall engender coastal erosion and flooding, inundating communities and decimating infrastructure.
Conversely, droughts exacerbate water scarcity in regions already grappling with limited resources. Agriculture, which relies heavily on predictable weather patterns, suffers significantly, leading to crop failures and reduced yields. The ripple effects extend beyond the agricultural sector, inducing food shortages and escalating food prices worldwide.
Melting Ice Caps: The Tipping Point
One of the most demonstrable impacts of rising global temperatures is the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers. As temperatures rise, vast swathes of ice in the Arctic and Antarctic regions are vanishing at an alarming rate. This phenomenon threatens not only the habitats of iconic species like polar bears and seals but also contributes to rising sea levels.
Rising sea levels pose an existential threat to low-lying coastal regions and island nations. Cities such as Miami, New Orleans, and parts of Bangladesh face increasingly dire prospects as flooding becomes more prevalent. The potential displacement of millions of people creates climate refugees, underscoring the urgency of addressing climate change as a global priority.
Ocean Acidification: The Hidden Peril
Rising temperatures do not merely affect the atmosphere; they impose drastic changes on aquatic ecosystems. The oceans absorb a substantial portion of excess carbon dioxide. This absorption leads to ocean acidification, diminishing the water’s pH and adversely impacting marine life, particularly coral reefs and shellfish.
Coral reefs, often referred to as the “rainforests of the sea,” are particularly susceptible to changes in temperature and acidity. Warming waters result in coral bleaching, where symbiotic algae are expelled, leaving the corals vulnerable to disease and death. The loss of these biodiverse ecosystems would have cascading effects on fisheries, tourism, and coastal protection.
Economic Ramifications: A Global Dilemma
The ramifications of the greenhouse effect extend into economic realms. As environmental catastrophes escalate, the financial burden on governments and communities intensifies. Infrastructure repair and disaster response costs strain budgets, diverting resources from other pressing societal needs such as education and healthcare.
Farming, already a precarious endeavor for many, has become increasingly unpredictable due to climatic changes. Farmers face an uphill battle against changing rainfall patterns, insect infestations, and soil degradation. Consequently, agricultural economies are under siege, driving up food prices and threatening food security across the globe.
Social Justice Issues: A Matter of Equity
The impact of climate change disproportionately affects marginalized communities, amplifying existing social inequalities. Vulnerable populations lacking resources and political clout are least able to adapt or recover from environmental shocks. For them, rising temperatures and extreme weather events can signify loss of livelihood, home, and health.
Thus, addressing the greenhouse effect transcends environmental stewardship; it intersects with social justice movements. Climate action must acknowledge and prioritize the voices of those disproportionately affected, ensuring equity is at the forefront of sustainability efforts.
Hope Amidst the Crisis: A Call to Action
While the effects of the greenhouse effect and rising temperatures present formidable challenges, they also underline the imperative for transformative action. Sustainable practices, such as renewable energy adoption, reforestation efforts, and community resilience programs, showcase humanity’s capacity for innovation and resilience.
When societies confront these challenges, a renewed focus on sustainability can yield benefits across environmental, economic, and social dimensions. Educational initiatives can empower individuals to make informed choices that contribute to a healthier planet.
In conclusion, understanding the effects of the greenhouse effect is vital in navigating the intricacies of climate change. The urgency to address this global crisis cannot be overstated; our actions today will determine the livability of our planet for generations to come. The intersection of environmental, social, and economic issues demands a holistic approach, urging all of humanity to collaborate in creating a sustainable future.