Wind energy is heralded as one of the leading renewable energy sources, capable of transforming the world’s energy landscape. However, like any energy source, it has its advantages and disadvantages. This article provides a balanced exploration of the promises and pitfalls associated with wind energy, helping readers understand both sides of the equation.
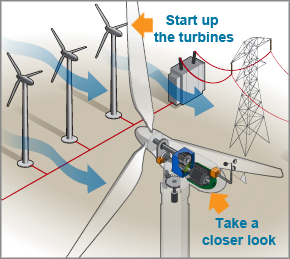
In recent years, the global push towards sustainable energy has intensified, with wind power emerging as a frontrunner. Harnessing the kinetic energy of the wind, wind turbines convert it into electricity with remarkable efficiency. But before the wind energy boom becomes a universal standard, it is critical to sift through its benefits and drawbacks.
Let’s delve into the various pros and cons of using wind energy, examining its potential to revolutionize energy consumption while also acknowledging the challenges it presents.
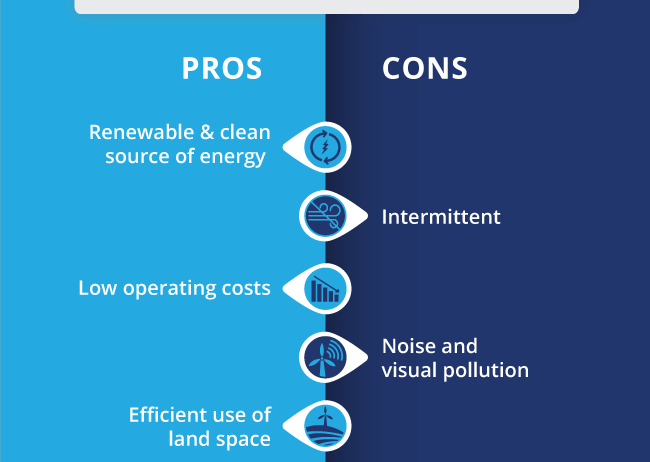
Benefits of Wind Energy: Harnessing Nature’s Bounty
Wind energy is abundant, renewable, and has a minimal carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels. Its potential to contribute meaningfully to combating climate change is considerable.
Clean and Renewable
Wind energy is inherently clean. Unlike fossil fuels, wind power generation produces no harmful emissions. As a renewable resource, wind is inexhaustible on a human timescale, making it a sustainable energy choice. By using wind energy, societies can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, thereby contributing to environmental preservation and public health.
Economic Job Creation
The wind energy sector has rapidly proliferated, creating numerous jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and management. The growing demand for wind turbines and infrastructure has led to significant employment opportunities across various skill levels. Additionally, many of these jobs cannot be outsourced, providing local communities with sustainable economic growth. This aspect of wind energy helps foster regional development and self-sufficiency.
Energy Independence
Utilizing wind energy can help nations reduce their dependence on imported fossil fuels. By investing in domestic wind resources, countries can bolster their energy security, stabilize energy costs, and shield themselves from geopolitical tensions linked to traditional energy sources. Furthermore, localizing energy production diminishes market volatility often influenced by global events.
Grid Stability and Technological Innovations
The integration of wind energy can bolster the resilience of electricity grids by diversifying the energy mix. As technology advances, developments in energy storage and turbine efficiency continue to emerge. Innovations such as floating wind farms and vertical-axis turbines are enhancing the feasibility of wind energy in various geographical contexts, amplifying its viability as a primary energy source.
Drawbacks of Wind Energy: Facing the Headwinds
While wind energy exudes potential, it is not without its challenges. From aesthetic concerns to ecological impacts, it is vital to evaluate the cons associated with wind power.
Intermittency and Reliability Concerns
Wind energy generation is contingent on weather conditions. Wind availability can fluctuate, leading to variable electricity outputs. This intermittency poses challenges for grid operators trying to maintain a steady supply of power. Although advancements in energy storage technologies are facilitating solutions, the reliance on wind alone may not be sufficient to meet baseload energy demands.
Environmental and Wildlife Impact
Wind farms can have unintended consequences for local wildlife and ecosystems. Birds and bats can be adversely affected by turbine blades, leading to fatal collisions. The construction and operation of wind farms may also disrupt natural habitats. Consequently, careful site assessments are essential to minimize the ecological footprint of wind energy development.
Aesthetic and Societal Considerations
Wind turbines, while often viewed as symbols of progress, can also evoke opposition from communities due to concerns about their visual impact on landscapes. Additionally, concerns about noise pollution and reduced property values may arise among residents living near wind farms. Understanding and addressing these societal apprehensions through community engagement is crucial for successful wind energy projects.
High Initial Costs and Infrastructure Investment
Despite declining costs in recent years, the initial investment required to develop wind energy infrastructure can be substantial. The construction of wind farms requires considerable financial backing, and the associated costs of connecting to the grid must also be accounted for. Although operation and maintenance costs are generally low, financing the upfront capital remains a barrier for many stakeholders.
Concluding Thoughts: The Way Forward
Wind energy stands at a compelling crossroads of opportunity and challenge. Its potential to contribute to a cleaner future is matched by the realities of its implementation. As with any energy source, a comprehensive approach that considers both the advantages and disadvantages of wind energy is imperative.
While the transition to renewable energy sources is critical for addressing climate change and fostering sustainability, it must be pursued thoughtfully and with respect to local communities and ecosystems. By addressing the headwinds while leveraging the strengths of wind energy, we can indeed harness this natural resource to build a more sustainable future. Each stakeholder has a role in this transition, and through collaboration and innovative solutions, the promises of wind energy can be fully realized.