Wind energy has emerged as one of the most promising renewable energy sources, offering a clean alternative to fossil fuels. As the world grapples with the ever-growing concerns of climate change and energy sustainability, understanding the multifaceted nature of wind energy, including its advantages and disadvantages, becomes imperative. This exploration reveals both its potent strengths and potential weaknesses, thereby providing a well-rounded perspective for individuals and institutions contemplating its adoption.
In recent years, there has been a significant escalation in interest surrounding wind energy, spurred by technological advancement, economic feasibility, and a global push towards decarbonization. However, the journey towards a greener future is often fraught with challenges. Let’s delve deeper into the strengths and weaknesses of wind energy to better equip proponents and skeptics alike with informed insights.
Advantages of Wind Energy
Renewable and Sustainable Energy Source
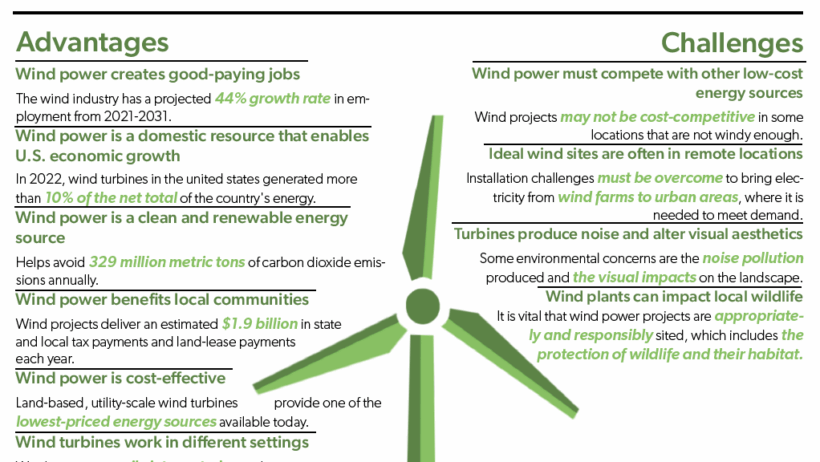
One of the most compelling advantages of wind energy is its inexhaustible nature. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and will deplete over time, wind is a continuously replenishing resource. Wind farms harness the kinetic energy produced by air movement, converting it into electricity without depleting any natural resources. This intrinsic sustainability positions wind energy as a cornerstone in the transition away from traditional energy sources, helping mitigate the impending energy crisis.
Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Wind energy plays a pivotal role in decreasing greenhouse gas emissions. The combustion of fossil fuels for energy is a primary contributor to carbon dioxide emissions, a significant driver of climate change. In contrast, wind power generation emits little to no greenhouse gases during operation. By facilitating a decline in reliance on fossil fuels, transitioning to wind energy contributes to the global effort to curtail climate change, fostering a healthier planet for future generations.
Economic Benefits and Job Creation
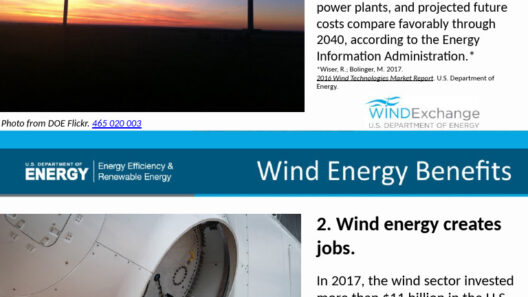
Investing in wind energy catalyzes economic growth through the creation of jobs. The wind energy sector has witnessed substantial job growth, spanning from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and operation. Moreover, wind farms can provide additional revenue streams for local communities through land leases and tax revenues. This economic stimulation is particularly vital for rural areas where many wind farms are located, providing an alternative source of income for farmers and landowners.
Energy Independence
Transitioning to wind energy fortifies national energy security. By harnessing indigenous wind resources, countries can reduce dependence on imported fuels, insulating themselves from market volatility and geopolitical tensions associated with energy supply chains. This energy independence ultimately bolsters national resilience and fosters a more stable economic climate.
Disadvantages of Wind Energy
Intermittent Energy Source
One of the chief criticisms of wind energy lies in its intermittency. The availability of wind is not constant; it fluctuates based on weather conditions and geographic location. This variability can pose challenges for energy production, potentially leading to supply gaps. Consequently, sectors relying heavily on wind energy must complement it with energy storage systems or backup generation methods to ensure a stable energy supply.
Impact on Wildlife and Ecosystems
Wind farms, while environmentally friendly, can have adverse effects on local wildlife and ecosystems. Birds and bats, in particular, face threats from turbine blades, resulting in fatalities from collision. Furthermore, the siting of wind farms can disrupt habitats and migratory patterns. It is crucial for developers to conduct thorough environmental assessments to mitigate these impacts, ensuring that wind energy development is done responsibly and sustainably.
Noisy and Aesthetic Concerns
The installation of wind turbines often raises concerns regarding noise pollution and visual impact. The mechanical sounds produced by turbines can be disruptive, particularly for nearby residents. Additionally, the physical presence of wind farms can alter landscapes, leading to opposition from local communities who value natural scenery. These objections underline the importance of community engagement and transparency in the planning and development of wind energy projects.
High Initial Costs
While the operational costs of wind energy are relatively low, the initial capital required for infrastructure development can be considerable. The expense associated with purchasing and installing turbines, as well as constructing the necessary electricity transmission systems, presents a significant hurdle. However, as technology advances and economies of scale are realized, costs are expected to decrease, making wind energy more competitive compared to traditional sources.
Conclusion
In summary, wind energy is a formidable contender in the arena of renewable energy sources. Its advantages—ranging from sustainability and emission reductions to economic benefits—are compelling. Nevertheless, potential drawbacks must not be overlooked. The intermittency, ecological impacts, noise concerns, and high initial investments all merit careful consideration.
As energy policies evolve and public awareness grows, understanding the nuanced dialogue surrounding wind energy is essential. Stakeholders from all walks of life must weigh the pros and cons before embarking on a journey towards integrating wind energy into the larger energy landscape. Through informed decision-making and collaborative efforts, society can harness the potential of wind energy while addressing its inherent challenges.