Energy conservation is an essential aspect of sustainable living and climate action. As our global energy demands surge, it becomes increasingly vital to implement strategies that facilitate the efficient use of resources. A multitude of tools and technologies are at our disposal to accomplish energy conservation across various sectors, including residential, commercial, and industrial domains. This discourse delves into diverse methodologies, elucidating their transformative potential.
At the forefront of energy conservation technologies are smart meters and energy management systems. Smart meters provide real-time data on energy consumption, enabling users to monitor and adjust their usage accordingly. The granularity of data gathered can reveal patterns, uncover inefficiencies, and ultimately foster informed decision-making. Energy management systems extend this functionality by integrating multiple sources of data, such as weather forecasts and operational schedules, guiding users toward optimized consumption.
Next, consider the advancements in lighting technologies. Traditional incandescent bulbs have largely been supplanted by light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs). These options consume significantly less electricity, providing the same level of illumination. Moreover, LED technology has progressed to include smart lighting solutions that can be programmed or remotely controlled. Such innovations contribute to substantial reductions in energy use, especially in commercial and municipal applications where lighting constitutes a major portion of overall energy expenditure.
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems serve as another critical focal point for energy conservation. Modern HVAC technologies employ a variety of methods to enhance efficiency. Variable refrigerant flow (VRF) systems, for example, adjust the amount of energy used based on real-time occupancy and weather conditions. Additionally, technologies such as programmable thermostats and zoning systems allow for precise control over heating and cooling, ensuring energy is not wasted in unoccupied spaces.
Insulation materials represent an often-overlooked but indispensable component in the energy conservation toolkit. High-performance insulation can significantly reduce the energy required for heating and cooling, thus decreasing overall consumption. Advanced materials, such as spray foam and reflective barriers, offer superior thermal resistance, minimizing energy loss through conduction. Furthermore, the implementation of energy-efficient windows equipped with double-glazing or Low-E coatings serves to further enhance thermal performance, reducing the need for extensive HVAC operation.
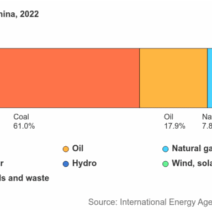
Another remarkable innovation lies in the field of renewable energy technologies. Solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal systems are rapidly revolutionizing how we harness and utilize energy. Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems convert sunlight directly into electricity, while solar thermal systems can provide hot water for residential and commercial use. Wind energy, with its increasing efficiency and decreasing cost, plays a pivotal role in diversifying energy portfolios. Geothermal systems tap into the Earth’s natural heat to provide a sustainable climate control solution, illustrating the myriad possibilities for reducing dependency on conventional fossil fuels.
In industrial applications, energy-intensive processes can be optimized through the use of energy-efficient machinery and advanced manufacturing techniques. The adoption of robotics and automation can lead to significant reductions in energy consumption, while practices such as waste heat recovery systems minimize losses from thermal processes. Combined heat and power (CHP) systems exemplify how industries can maximize efficiency by simultaneously producing electricity and useful heat from the same energy source, thus enhancing overall productivity.
The concept of demand response offers a novel approach to managing energy consumption during peak periods. This system involves adjusting demand in response to supply conditions, typically incentivized through time-based pricing structures. By shifting energy usage to off-peak hours, consumers can benefit from lower rates, resulting in conservation of energy and mitigation of grid strain. Such programs empower consumers and businesses to take an active role in energy management while contributing to the stability of the broader energy system.
In transportation, energy conservation technologies are equally paramount. The advent of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid technologies marks a significant shift away from fossil fuels. Charging infrastructure, coupled with advancements in battery technology, is facilitating the transition to greener transport solutions. Moreover, the incorporation of intelligent transportation systems (ITS) enhances the efficiency of urban mobility, optimizing traffic flow and reducing congestion, which in turn decreases overall energy consumption.
Furthermore, behavioral interventions are essential in the realm of energy conservation. Education and awareness campaigns can profoundly influence public attitudes towards energy use. Community programs aimed at fostering energy-saving habits, like turning off lights when leaving a room or unplugging devices not in use, serve to instill a culture of conservation. These social change initiatives can lead to collective shifts in consumption patterns that reinforce the benefits of energy-efficient practices.
Lastly, robust government policies and incentives catalyze the widespread adoption of energy conservation technologies. Through tax credits, grants, or rebates, governments can encourage individuals and businesses to invest in energy-efficient systems and renewable technologies. Energy efficiency standards and regulations ensure that new products adhere to performance guidelines, fostering an environment of sustainability.
In conclusion, the pursuit of energy conservation is multifaceted encompassing a plethora of tools and technologies that cater to diverse contexts. From smart meters and advanced HVAC systems to renewable energy technologies and behavioral interventions, each component plays a crucial role in mitigating energy consumption. As global energy demands continue to rise, the integration of these innovations is imperative. A commitment to harnessing the power of technology, supported by informed behavior and effective policies, can lead us toward a more sustainable and efficient energy future.