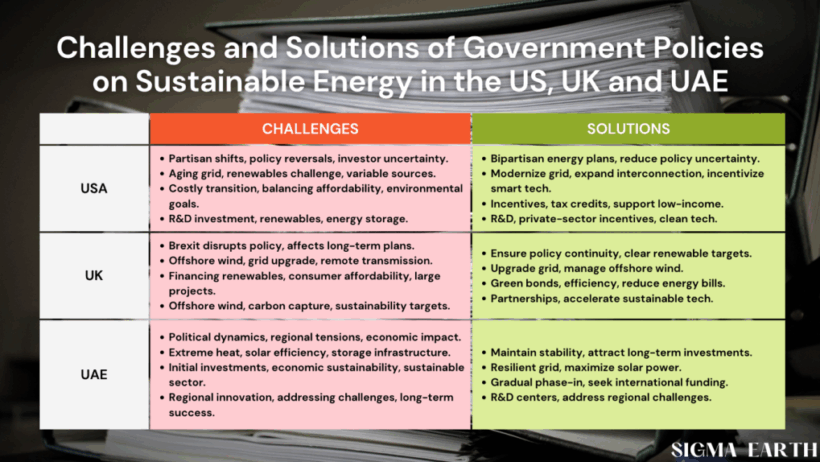
In the contemporary landscape, the imperative for energy conservation has never been more pronounced. Governments across the globe are cognizant of the challenges posed by energy consumption, climate change, and geopolitical tensions affecting energy supplies. The ramifications of excessive energy use extend beyond mere economic implications; they infiltrate environmental, social, and health domains as well. Thus, the pertinence of government policies in mitigating energy wastage cannot be overstated. This discourse delves into the multifaceted strategies that governments can employ to conserve energy and highlights policies that have made a palpable difference in various jurisdictions.
1. Regulatory Frameworks
At the forefront of energy conservation initiatives lie regulatory frameworks. Governments have the capacity to establish stringent energy efficiency standards for appliances, buildings, and vehicles. These regulations ensure that products entering the market adhere to specific efficiency criteria, thereby curbing energy waste at the consumer level. For instance, implementing mandatory energy labeling allows consumers to make informed decisions regarding energy usage.
Additionally, governments can enact laws that mandate the retrofitting of existing buildings to meet modern energy efficiency standards. This often requires financial incentives to encourage property owners to invest in sustainability measures. Some municipalities have pioneered measures such as energy audits, providing detailed assessments of energy consumption and recommending actionable improvements. These proactive approaches not only reduce energy consumption but also foster a culture of conservation.
2. Financial Incentives and Subsidies
Financial incentives serve as a powerful catalyst for encouraging both businesses and individuals to prioritize energy conservation. Tax rebates, subsidies, and low-interest loans for energy-efficient home improvements or renewable energy installations can significantly alleviate upfront costs. Such policies are designed to spur investment in technologies that otherwise might be financially prohibitive.
Furthermore, governments may implement systems of rewards for companies that demonstrate tangible reductions in energy consumption. This could manifest in the form of grants for research and development of innovative energy-saving technologies. By fostering a supportive fiscal environment, governments catalyze the private sector’s engagement in energy conservation efforts.
3. Public Awareness Campaigns
Education and public awareness have profound effects on energy conservation. Governments can initiate comprehensive public campaigns that illuminate the importance of energy efficiency and the myriad ways individuals can contribute. These campaigns can take various forms: workshops, informational websites, and social media initiatives are just a few methods to disseminate vital messages regarding energy-saving practices.
Moreover, integrating energy conservation into school curricula can cultivate a generation that prioritizes sustainability. When communities understand the impact of their choices on energy resources, the collective behavior shifts towards more sustainable practices, reinforcing the need for conservation.
4. Promoting Renewable Energy Sources
Shifting away from fossil fuels is essential for advancing energy conservation goals. Governments can accelerate the transition to renewable energy sources by establishing supportive policies. These might include feed-in tariffs, which guarantee a fixed price for renewable energy production, making it economically viable for producers and thereby increasing supply.
Furthermore, governments can promote research and development in renewable technologies, enhancing the efficiency and affordability of solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy systems. Banning or phasing out subsidies for fossil fuels will redirect investments towards renewables, catalyzing the shift to cleaner energy sources. As renewables become more accessible, societies can significantly reduce their carbon footprint while maintaining energy reliability.
5. Incentivizing Smart Grid Technologies
The emergence of smart grid technologies represents a pivotal advancement in energy conservation strategies. Governments can facilitate the development and deployment of smart grids, which utilize digital communication to detect and react to local changes in usage. These technologies enable consumers to monitor their energy consumption in real time, facilitating more disciplined energy use.
In addition, smart grids empower utility companies to optimize energy distribution, reducing waste and ensuring that supply meets demand efficiently. Investment in smart infrastructure is not just a technical upgrade; it is an essential element in the overarching strategy for energy conservation. Government policies should focus on integrating these technologies into existing grids and providing supportive financial frameworks for their implementation.
6. Building Resiliency in Energy Systems
Finally, building resiliency within energy systems is critical for long-term sustainability. Governments must consider the potential risks posed by climate change, natural disasters, and systemic failures. By investing in diversified energy supplies, including local renewable sources, governments can mitigate dependency on any single energy source.
Additionally, policies encouraging decentralized energy production, such as community solar projects, allow localities to benefit from increased energy independence, ultimately leading to lower overall consumption rates. These initiatives not only bolster local economies but also create communities that are better prepared to address energy shortages.
In conclusion, the role of government in energy conservation is both impactful and essential. Through a rigorous mix of regulatory frameworks, financial incentives, public awareness initiatives, promotion of renewable resources, and investment in innovative technologies, governments can significantly reduce energy consumption. Addressing energy conservation not only entails immediate economic benefits but also contributes to the overarching goal of a sustainable, responsible energy future. Ultimately, a collaborative effort involving governments, businesses, and individuals can yield a more energy-efficient society, securing ecological stability for generations to come.