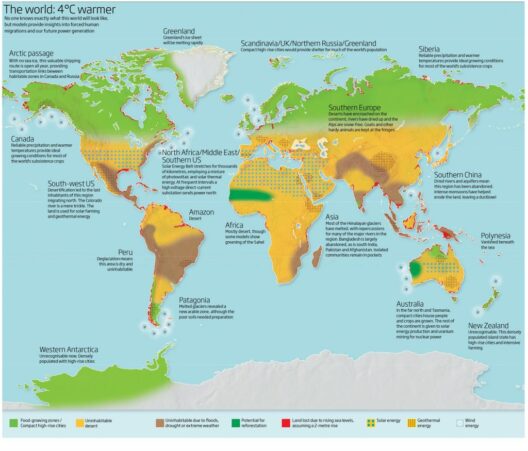
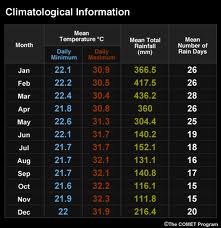
The imperative to mitigate climate change has never been more pressing. As the scientific consensus reveals increasingly alarming predictions about future climate scenarios, governments around the globe possess both the responsibility and the capacity to enact transformative policies that can curtail environmental degradation. Their role is crucial, not merely as arbiters of regulation but as visionary architects of a sustainable future.
Firstly, governments must prioritize the transition to renewable energy resources. The reliance on fossil fuels remains a primary contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. By investing in solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal technologies, nations can drastically reduce their carbon footprints. Moreover, substantial monetary incentives for research and development can spur innovation in energy storage and efficiency, ensuring these resources are available and viable long-term.
Additionally, governments should implement stringent regulations on emissions. This involves establishing ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gases across various sectors, such as transportation, manufacturing, and agriculture. By instituting cap-and-trade systems or carbon taxation, nations can create economic incentives for companies to adopt greener practices. These mechanisms not only encourage industries to innovate towards cleaner processes but also generate revenue that can be reinvested into further environmental initiatives.
Furthermore, fostering public transportation systems is an often-overlooked strategy that governments can employ. Expanding and modernizing public transit, such as buses, trains, and subways, can reduce reliance on individual automobiles, thus decreasing emissions significantly. Cities that promote bicycle usage and pedestrian-friendly infrastructure enhance mobility while simultaneously improving air quality and public health.
In the realm of agriculture, governments have a pivotal role in promoting sustainable practices. Initiatives that support organic farming, regenerative agriculture, and agroforestry not only sequester carbon but also enhance biodiversity and food security. Implementing subsidies for farmers who engage in these practices encourages a systemic shift towards environmentally friendly agriculture. Educational programs that inform farmers about sustainable practices are equally vital; knowledge is a catalyst for change.
Additionally, urban planning must become an essential facet of governmental strategy. As urban areas expand, governments should prioritize green spaces and sustainable building practices. Urban heat islands exacerbate climate issues, and integrating green roofs, parks, and community gardens can mitigate these effects while providing residents with recreational and ecological benefits. Moreover, enforcing building standards that mandate energy efficiency in new constructions will propel cities towards carbon neutrality.
Moreover, international cooperation is indispensable in the fight against climate change. One nation’s efforts can be rendered moot if neighboring countries neglect their environmental responsibilities. Therefore, governments need to foster global partnerships to share technologies, strategies, and resources. Initiatives like the Paris Agreement serve as foundational frameworks: they establish targets and encourage nations to hold each other accountable. Collaboration, particularly with developing nations that may lack the resources to combat climate change independently, enables a holistic approach that benefits the entire planet.
Education plays a critical role as well. Governments should initiate campaigns to raise public awareness about climate change, emphasizing the urgency of collective action. When citizens understand the implications of their lifestyle choices on the environment, they are more likely to support, advocate for, and participate in sustainable practices. Schools should incorporate environmental education into their curricula, fostering a culture of sustainability amongst youth that will last into adulthood.
The circular economy represents another innovative approach for governments to consider. Moving away from the traditional linear model of “take, make, dispose,” this framework encourages systems where waste is minimized, and materials are reused. Legislation that mandates recycling, encourages upcycling, and incentivizes companies to adopt sustainable practices can contribute to a significant reduction in waste and environmental impact.
Governments must also promote innovation in electric vehicle (EV) technology. With transportation accounting for a significant portion of global emissions, incentives for the adoption of EVs, coupled with investments in charging infrastructure, can accelerate the shift towards sustainable transportation. Additionally, policies that encourage research into alternative fuels can diversify transportation methods and reduce dependence on oil.
Importantly, legislative frameworks should include a focus on climate justice. Often, marginalized communities are disproportionately affected by climate change and environmental degradation. Ensuring that policies consider equitable treatment and inclusion of these communities is not only a moral imperative but will also enhance the effectiveness of initiatives by ensuring all voices and needs are represented in climate action plans.
In conclusion, the role of governments in addressing climate change is multi-faceted and requires an interdisciplinary approach. By embracing renewable energy sources, imposing regulatory frameworks, investing in public transportation, supporting sustainable agriculture, fostering international collaboration, enhancing educational initiatives, promoting the circular economy, advancing electric vehicle infrastructure, and committing to climate justice, governments can catalyze a substantial shift toward sustainability. This comprehensive strategy demands both ambition and perseverance; yet, it also heralds the promise of a resilient and thriving planet for future generations. As we stand at this juncture, the question remains: How will governments rise to this momentous challenge?