Wind energy stands as one of the most promising renewable energy sources of our time. Embracing technology that captures the kinetic energy of moving air, it plays a pivotal role in reducing dependence on fossil fuels and curbing nature’s detrimental impacts. Its versatility is boundless, with applications spanning various sectors. This article delves into the multifaceted uses of wind energy, illustrating its potential beyond merely generating electricity.
Harnessing a natural element with grounded potential, wind energy is evolving into more than just a clean power solution. By tapping into its innovative applications, we can explore a sustainable future that enhances economic viability, fosters energy independence, and minimizes environmental degradation.
Understanding the broad spectrum of wind power applications is essential for realizing its immense capabilities. From generating electricity to driving industrial processes, wind energy has significant implications across various domains.
Generating Electricity: The Cornerstone of Wind Power
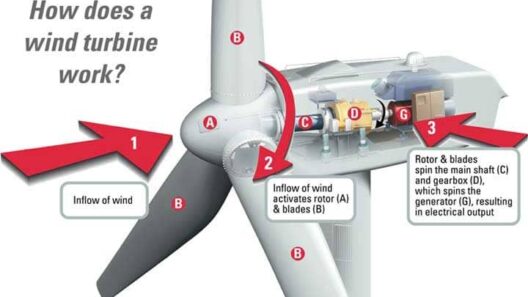
At the heart of wind energy is its primary application—electricity generation. Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy contained in wind into electrical energy. These turbines, strategically positioned in wind farms, capture wind from various directions, ensuring consistent energy production. As technology advances, the efficiency of these turbines continues to soar, enabling higher energy yields.
The impact of wind-generated electricity is profound. It contributes to grid stability, diversifies the energy mix, and supports efforts to combat climate change. Regions that harness wind power substantially reduce carbon emissions, while households and businesses benefit from lower energy costs. Furthermore, the integration of wind energy into the grid promotes energy independence, minimizing reliance on imported fuels.
Wind energy’s ubiquity ensures it is not confined to one geographic area or climate. Coastal areas, plains, and even offshore locations serve as ideal environments for wind turbine installations. This adaptability allows countries and communities across the globe to capitalize on local wind resources.
Manufacturing and Industrial Processes: Beyond Electricity
Wind energy’s capacity extends beyond the realm of electricity generation. It can bolster industrial operations, offering opportunities to replace fossil fuel consumption with renewable alternatives in various manufacturing processes. For instance, direct mechanical drive from wind turbines can power machinery in industries such as agriculture, textiles, and cement production.
In agricultural contexts, wind energy can automate processes that traditionally consume vast amounts of energy. Farmers can deploy wind-driven systems for irrigation, crop drying, and even livestock feeding. By harnessing wind energy, agricultural operations can lower costs and enhance sustainability.
Innovative companies are also utilizing wind power in the production of hydrogen—a fuel that promises a carbon-free future. Wind turbines can generate excess electricity that, when used to electrolyze water, produces hydrogen. This hydrogen can then be employed in various sectors, from manufacturing to transportation, rendering it a versatile and eco-friendly energy source.
Heating Applications: Harnessing Wind for Warmth
In addition to generating electricity and powering industrial operations, wind energy can be utilized for heating applications, promoting energy efficiency in residential and commercial contexts. Wind-driven systems can facilitate the production of hot water through direct mechanical energy conversions or by powering heat pumps.
Communities can deploy wind energy heating solutions, especially in regions with considerable seasonal temperature fluctuations. A combined approach of wind-generated electricity and heating technologies can reduce reliance on conventional heating methods, thereby decreasing greenhouse gas emissions and supporting sustainability objectives.
Additionally, wind energy systems can be integrated with district heating networks. By connecting multiple households or municipal buildings to wind-driven heating solutions, communities can leverage economies of scale and minimize reliance on fossil fuels, which have significant environmental impacts.
Transportation: Redefining Mobility with Wind
The transportation sector, notorious for its greenhouse gas emissions, can greatly benefit from wind energy applications. Electric vehicles (EVs) emerging in popularity can be charged through wind-generated electricity, promoting the transition towards a cleaner transportation infrastructure.
Wind farms can create charging stations specially equipped with wind turbines. These stations can provide real-time energy boosts for EVs, enhancing energy accessibility. Additionally, shipping vessels are beginning to integrate wind technology into their operations. Innovative designs incorporate wind-assisted propulsion, such as rotating sails, to harness natural wind currents and bolster fuel efficiency.
Moreover, wind energy serves as a catalyst for the production of biofuels from organic waste. As wind-powered equipment processes waste materials, it can simultaneously produce biofuels, offering a renewable and sustainable alternative to traditional transportation fuels.
Community Empowerment: Economic Growth through Wind Initiatives
Wind energy holds enormous potential for community empowerment and economic development. Investments in local wind projects generate jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, fostering a workforce skilled in renewable technologies. As communities cultivate their wind resources, they can enjoy economic revitalization, stimulating local spending and enhancing long-term prosperity.
Furthermore, energy ownership initiatives empower communities to take charge of their energy resources. By investing in local wind farms, residents can secure affordable and reliable energy while reaping financial benefits from surplus electricity sold back to the grid. Such initiatives instill a sense of ownership and responsibility regarding sustainable development.
Conclusion: Charting a Sustainable Path with Wind Energy
Wind energy powers an array of applications—spanning electricity generation, industrial processes, heating, and transportation—each contributing uniquely to a sustainable future. As technology continues to evolve, the landscape of wind energy applications will only expand, fostering innovation and resilience in a world increasingly reliant on renewable energy sources.
Harnessing the transformative potential of wind energy is not merely an environmental necessity but an opportunity for communities and industries to thrive sustainably. By investing in and embracing wind power, we pave the way toward a cleaner, greener, and more prosperous tomorrow.