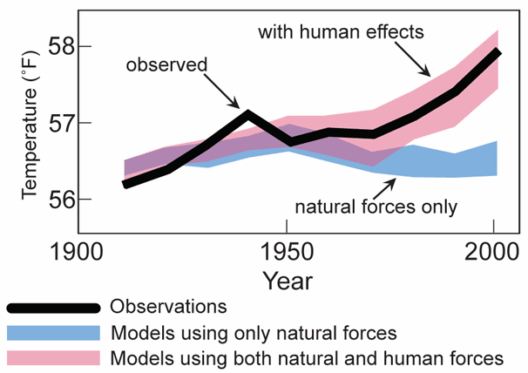
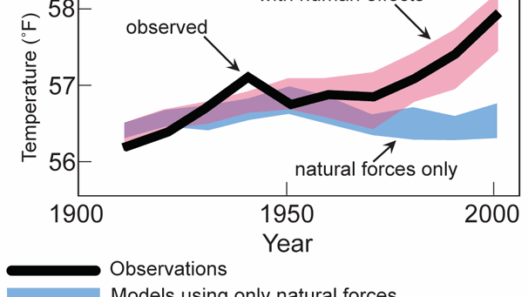
Climate change is undeniably one of the most pressing challenges facing humanity today. The phenomenon is driven by a myriad of factors that stem from both natural processes and human activities. Understanding what causes climate change is essential for developing effective mitigation strategies. This article delves into the main drivers of climate change, offering a comprehensive overview of both anthropogenic and natural influences.
Human Activity: The Major Culprit
At the forefront of climate change is human activity, which has significantly intensified over the last century. Industrialization, urbanization, and population growth have led to increased emissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs), which trap heat in the atmosphere and disrupt natural climatic patterns. The following aspects are pivotal in understanding how human actions contribute to climate change.
Fossil Fuel Combustion
The combustion of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas for energy production is the largest single source of GHG emissions. Power plants, motor vehicles, and industrial machinery are prime culprits, releasing vast amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) into the atmosphere. The urgency of transitioning to renewable energy sources cannot be overstated, as the reliance on fossil fuels is a significant impediment to curbing climate change.
Deforestation and Land Use Changes
Human encroachment on natural landscapes through deforestation, urban sprawl, and agricultural expansion drastically alters carbon storage mechanisms in the biosphere. Forests act as carbon sinks, sequestering CO2. Therefore, when trees are cut down or burned, not only is the carbon stored in the trees released back into the atmosphere, but the capacity to absorb future emissions is also diminished. Additionally, land use changes can release stored carbon in soil and peatlands, further exacerbating climate warming.
Agriculture and Livestock Farming
The agricultural sector is another significant driver of climate change. Livestock farming, in particular, produces large volumes of methane, a potent greenhouse gas that is over 25 times more effective at trapping heat over a 100-year period compared to CO2. The use of synthetic fertilizers also contributes to nitrous oxide emissions, which have a global warming potential almost 300 times greater than CO2. Sustainable farming practices and dietary shifts toward plant-based foods are imperative for lessening agriculture’s climate impact.
The Role of Industrial Processes
Industrial processes contribute significantly to climate change through the release of various pollutants and greenhouse gases. The production of cement, for example, is highly carbon-intensive. In addition, chemical manufacturing and waste management practices can emit powerful GHGs, highlighting the need for stringent environmental regulations and innovative approaches to industrial production.
Natural Drivers of Climate Change
While human activities are the primary contributors to climate change, natural drivers also play an essential role in shaping global temperatures and weather patterns.
Solar Variability
Solar activity can influence the Earth’s climate. Variations in solar radiation, whether from natural cycles or phenomena like sunspots, can impact surface temperatures. While these natural fluctuations are generally minor compared to human-induced changes, they still contribute to the broader context of climate variability and should be accounted for in climate models.
Volcanic Eruptions
Volcanic eruptions release significant amounts of sulfur dioxide and particulate matter into the atmosphere, which can lead to short-term cooling effects as these particles reflect sunlight. However, over long periods, the release of carbon dioxide from volcanic activity can contribute to warming. Understanding these natural events is crucial for deciphering the climate’s complex narrative.
Ocean Currents and Atmospheric Circulation
Oceans act as a major climate regulator, with currents transferring heat around the planet. Phenomena such as El Niño and La Niña can lead to substantial short-term climate variability. These oscillations can influence weather patterns, with repercussions that can be felt across the globe. Understanding these dynamic systems is vital for predicting and adapting to climate change’s impacts.
Impacts of Climate Change: A Call to Action
The ramifications of climate change are profound and far-reaching. Rising global temperatures, more frequent and severe weather events, loss of biodiversity, and altered ecosystems are just a few of the consequences that threaten both human and ecological systems. It is imperative that society acknowledges and addresses these drivers through collective action and policy reform.
Leveraging Innovations for a Sustainable Future
To combat climate change effectively, embracing innovation is crucial. Renewable energy technologies, improvements in energy efficiency, carbon capture and storage, and sustainable agriculture practices can significantly reduce emissions. Furthermore, policy frameworks must encompass ambitious targets aligned with climate science, promoting a transition to a low-carbon economy. Individuals also have a role to play, from reducing energy consumption to advocating for sustainability in their communities.
In conclusion, comprehending the causes of climate change and their implications is vital for fostering an informed and proactive response. Both human activities and natural processes intricately intertwine to shape our planet’s future. As awareness grows, so too does the collective resolve to address this existential threat. Fortifying our response to climate change will not only mitigate its impacts but also enhance the resilience of ecosystems and future generations.