Energy conservation is a fundamental principle in physics that governs the behavior of systems, whether mechanical, thermal, or electrical. This principle asserts that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transformed from one form to another. Understanding the criteria for energy conservation is essential for anyone interested in the mechanics of nature and the intricate balance of ecosystems.
To comprehend energy conservation, one must first recognize the various forms of energy. Kinetic energy, for example, is the energy of motion. An object in motion possesses kinetic energy that depends on its mass and velocity. Potential energy, in contrast, is stored energy based on an object’s position or configuration. Gravitational potential energy, for instance, increases with height, while elastic potential energy accumulates when an elastic object is stretched or compressed.
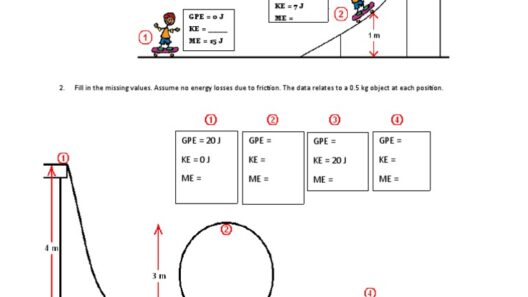
The key to energy conservation lies in the concept of isolation. In an isolated system, the total energy remains constant over time. This principle can initially seem counterintuitive because energy appears to fluctuate in everyday life; however, deeper examination reveals the interplay of various energy transformations. When a ball is thrown in the air, its kinetic energy decreases as it ascends, while its gravitational potential energy correspondingly increases. At the peak of its ascent, kinetic energy is at its minimum, while potential energy reaches its maximum. Upon falling, the reverse occurs, demonstrating how energy is conserved through transformation rather than extinction.
Another critical criterion for energy conservation is the principle of closed systems. In an ideal closed system, no external forces act upon it, meaning all energy interactions are contained within. Earth and its atmosphere serve as a practical example of a closed system, wherein energy from the sun drives weather patterns, ocean currents, and photosynthesis, whilst the resulting energy transformations maintain the equilibrium of life on the planet. This concept not only underscores the interconnectedness of all natural phenomena but also highlights the need for conscious stewardship of energy resources within a closed ecological system.
Moreover, thermodynamics plays a pivotal role in understanding energy conservation. The laws of thermodynamics, particularly the first law, articulate that the total energy of a closed system is constant. This law intricately links mechanical energy and thermal energy, revealing that energy transformations are often accompanied by changes in temperature. For instance, during combustion, chemical potential energy contained in fuel is converted into thermal energy and kinetic energy. However, not all energy conversions are perfectly efficient; some energy dissipates as waste heat due to entropy, a measure of disorder within a system. This raises further questions about how efficiently energy is utilized in various processes.
In the realm of technology, the implications of energy conservation are profound. Engineers and scientists continually seek ways to optimize energy use, minimize waste, and innovate more sustainable practices. Renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, harness solar energy, transforming it into electricity. However, the efficiency of these systems relies heavily on understanding energy conversion processes and the principles governing energy flow. As society grapples with the pressing challenge of climate change, the pursuit of energy efficiency takes on heightened urgency, emphasizing the need for conservation as both a scientific and ethical imperative.
Moreover, sociocultural factors influence energy conservation behavior. Awareness and education about energy efficiency can lead to significant behavioral change in individuals and communities. Engaging people with the concept of the environmental impact of energy consumption fosters deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of energy use and ecological health. This awareness is often catalyzed through grassroots movements, educational programs, and policy advocacy, promoting a shift towards sustainable practices.
In the context of physics, the conservation of energy also implies a profound philosophical perspective. It engenders respect for natural order and the phenomenon of equilibrium. Understanding that energy transformations occur constantly within our surroundings engenders a sense of responsibility for our actions; every choice related to energy consumption reverberates through the ecological fabric of our planet. Therefore, energy conservation transcends mere calculations and formulates the basis for environmental ethics.
The processes of innovation and technology often challenge our traditional understanding of energy conservation. For instance, advancements in nuclear physics have led to energy generation methods that rely on fission – the splitting of an atomic nucleus – which releases tremendous energy. Conversely, the question arises regarding the safety and sustainability of such methods. The residue of unused nuclear fuel presents substantial challenges, necessitating ongoing investigation into long-term consequences on the ecological landscape.
In conclusion, the criteria for energy conservation in physics encompass a multifaceted understanding of various energy forms, systems, and transformations. It reflects the need for isolation in closed systems, adheres to the laws of thermodynamics, and resonates deeply with ethical considerations surrounding our environmental responsibilities. By promoting awareness, fostering technological innovations, and advocating for responsible practices, society can work towards a harmonious equilibrium that not only conserves energy but also sustains the delicate web of life on Earth. Thus, the fascination surrounding energy conservation also serves as a reminder of our role as stewards of this planet, inspiring deeper inquiry and collective action towards a sustainable future.