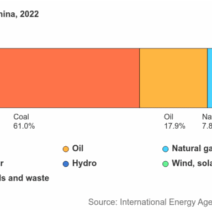
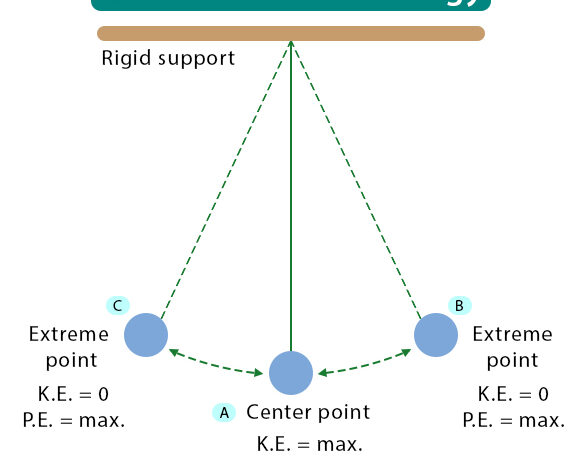
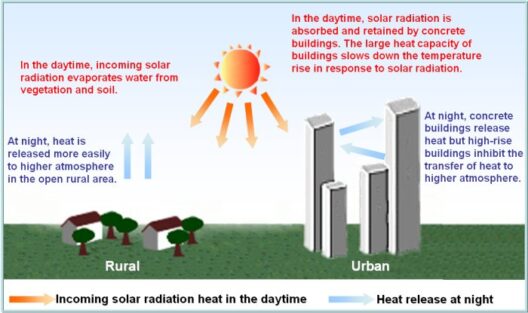
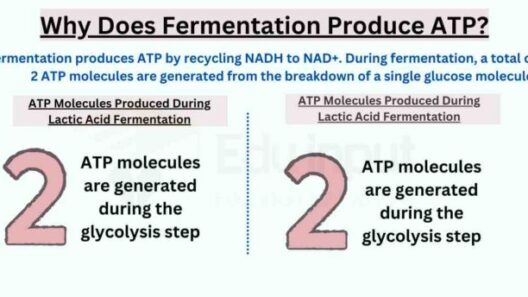
The Law of Conservation of Energy is a fundamental principle in physics that encapsulates the essence of energy’s constancy in our universe. It asserts that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transformed from one form to another. This principle is a cornerstone in understanding various scientific phenomena and underlies numerous processes in both nature and technology. Given the importance of energy conservation in addressing modern environmental challenges, a comprehensive exploration of this law reveals both its elegance and its profound implications.
To fully comprehend the Law of Conservation of Energy, it is essential to first define what energy is. Energy is an abstract quantity that represents the ability to perform work or produce change in a system. It manifests in various forms, including kinetic, potential, thermal, chemical, electrical, and nuclear energy. The dynamic interplay between these forms of energy characterizes much of the natural world, leading to a myriad of observations, from the simple act of a ball rolling down a hill to the intricate processes that power the sun.
A key aspect of the Law of Conservation of Energy is its profound implications in real-world applications. For instance, when a roller coaster ascends, it gains potential energy relative to its height. As it descends, this potential energy converts to kinetic energy, propelling the train forward at high speed. In an ideal scenario, ignoring factors like friction and air resistance, the sum of the potential and kinetic energies remains constant throughout the ride. This conservation principle is not merely anecdotal; it is a pivotal concept that aids engineers in designing safe amusement park rides. Understanding energy transformations allows for the innovation of more efficient systems in various domains, from transportation to renewable energy technologies.
Moreover, investigations into thermodynamics—the branch of physics that deals with heat and temperature—further illustrate the law’s significance. The first law of thermodynamics, often referred to in tandem with the conservation principle, states that the internal energy of a closed system changes due to heat transfer and work done on or by the system. It fortifies the idea that while energy can change states or forms, the total quantity remains constant. This becomes exceptionally relevant in understanding energy transfer processes such as combustion in engines, where chemical energy transforms into thermal energy, subsequently converted into mechanical energy. By applying the law, engineers can develop engines that maximize energy efficiency, reducing waste and promoting environmental sustainability.
The fascination with the Law of Conservation of Energy extends beyond practical applications. It invites contemplation about the universe’s underlying symmetry and balance. Consider the cosmos: stars, planets, and galaxies all engage in colossal exchanges of energy. For example, the nuclear fusion process within stars converts hydrogen into helium, releasing tremendous energy in the form of light and heat. This stellar energy is fundamental for life on Earth. It is curious how such vast celestial mechanisms adhere to the same conservation principles that govern our daily interactions with energy.
A commonly observed phenomenon that showcases this law is the functioning of ecological systems. In a forest, trees convert sunlight (solar energy) into chemical energy through photosynthesis, providing sustenance for myriad organisms. When these organisms consume the trees, energy is transferred along food chains and webs. This ecological dynamic exemplifies the conservation of energy in biological contexts. Energy flow in ecosystems adheres strictly to the conservation principle: while energy loses some potential as it disperses into the environment (often in the form of heat), the total energy in the system remains accounted for, influencing the distribution of life and ecosystems’ sustainability.
Additionally, beyond the confines of physical sciences, the law inspires philosophical discourse. It raises questions about existence, resource management, and the interconnectedness of all things. In a world grappling with energy crises and climate change, recognition of energy’s conservation prompts society to rethink how we utilize resources. The shift towards renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power exemplifies a collective acknowledgment of this law. By harnessing natural energy flows rather than depleting finite resources, humanity can align practices with the principle of conservation, sustaining a balance with the environment.
However, this transition is not devoid of complexity. Society faces challenges in energy storage, transmission, and technological advancement. Understanding the physics behind energy conservation is only the first step. Bridging the gap between scientific intricacies and sociocultural acceptance of sustainable practices presents a formidable task. Technological innovation must be pursued alongside public education to ensure that the importance of energy conservation is understood, appreciated, and implemented in daily lives. This knowledge sparks curiosity about how individuals can contribute to preserving this balance in their communities and globally.
In summary, the Law of Conservation of Energy provides a compelling framework that governs not only physical systems but also ecological and societal structures. It elucidates the interconnectedness of various energy forms and highlights the importance of this principle in facilitating sustainable practices. As modern society continues to unravel the complexities of energy utilization, maintaining an awareness of conservation principles will ensure that future generations inherit a balanced and flourishing planet. Understanding and embracing the Law of Conservation of Energy is essential for addressing current environmental challenges and fostering resilience in the face of change.