Wind energy is a formidable force in the quest for sustainable power sources. It is a product of nature, harnessed through advanced technology, transforming kinetic energy from wind into electricity. As the quest for cleaner energy intensifies in the face of climate change, understanding the mechanisms by which wind energy operates and its consequential impacts is vital. This examination delves deep into how wind power functions and its significance in contemporary society.
Understanding the Mechanics of Wind Power Generation
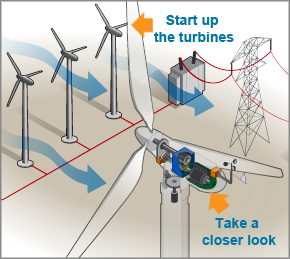
At its essence, wind energy conversion involves a straightforward yet elegant mechanism. Wind turbines—typically towering structures with large blades—capture wind kinetic energy. As air currents flow over the blades, they create lift, causing the blades to rotate. This rotation turns a shaft connected to a generator, producing electricity. But what are the components that facilitate this remarkable transmutation from wind to watt?
Modern wind turbines commonly feature three primary components: the rotor, the nacelle, and the tower. The rotor comprises the blades and hub, where energy first begins its conversion process. The nacelle houses critical elements such as the gearbox and generator, while the tower elevates the rotor to capture the most potent wind currents, often situated at heights exceeding 300 feet. This configuration is crucial, as wind speeds increase with altitude, maximizing energy output.
Moreover, technology in wind energy continues to evolve rapidly, introducing innovations such as variable speed generators and advanced control systems. These advancements enhance the reliability and efficiency of energy production, further solidifying wind power’s role in the energy sector. With the global commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, the need for improved energy conversion technologies has never been more pressing.
The Environmental Impact of Wind Energy
When analyzing the impact of wind energy, one must consider its environmental ramification holistically. Unlike fossil fuel-derived electricity, wind power generation is characterized by its remarkably low emissions. According to numerous studies, wind energy emits virtually no carbon dioxide during operation, positioning it as a clean energy alternative. Consequently, this technology contributes significantly to decarbonizing power grids worldwide.
Furthermore, wind farms can be strategically integrated into agricultural environments, leading to a dual-use system known as “agrivoltaics.” Here, wind turbines coexist alongside crops, offering farmers an opportunity for diversified income while enhancing land productivity without inordinate land-use changes. This integration promotes sustainable land stewardship, aligning energy production with agricultural viability.
However, while the benefits are indisputable, specific environmental concerns warrant attention. The construction and placement of wind farms can disrupt local wildlife habitats, particularly birds and bats. Mitigating these impacts demands careful site selection and innovative strategies like radar systems, which help monitor avian activity, or employing turbine designs that reduce the risk of collisions. Balancing clean energy production with environmental stewardship is paramount.
Socioeconomic Implications of Wind Energy Deployment
The socioeconomic dimensions of wind energy deployment extend beyond mere electricity generation. The proliferation of wind farms translates to significant job creation, from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and operation. In regions transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable sources, retraining programs empower displaced workers, ensuring that economic shifts facilitate a just transition.
Moreover, the surge in wind energy investments propels local economies. Communities often benefit from increased tax revenues, which can enhance public services and infrastructure. Wind projects frequently engage local stakeholders, fostering a sense of community ownership and involvement. This participatory approach aligns with the growing public demand for clean energy, which in turn cultivates broader support for renewable initiatives.
Additionally, as global markets shift towards renewables, countries that invest in wind energy gain a competitive edge in the global economy. By positioning themselves as leaders in clean energy technology, nations can capitalize on the export potential of wind technology, fostering international partnerships and trade relations while reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels.
Challenges Facing the Wind Energy Sector
Despite its many merits, the wind energy sector is not without challenges. The intermittency of wind poses a significant hurdle. Wind energy production is inherently variable, dependent on local wind patterns. This variability necessitates the integration of energy storage systems and complementary energy sources to ensure a reliable power supply. As battery technologies advance, they present promising solutions for balancing supply and demand, yet costs and scalability remain critical considerations.
Moreover, public perception and policy frameworks directly influence wind energy adoption. Misconceptions about noise, visual impact, and environmental hazards can impede project development. Implementing educational initiatives and community engagement strategies is essential for fostering public understanding and acceptance of wind energy projects. Transparent communication regarding potential benefits and mitigations can help assuage concerns and build cooperative relationships between stakeholders.
The dynamic landscape of energy production global necessitates a steadfast commitment to innovation and adaptation. With ongoing technological advancements and increased collaboration among industry stakeholders, the future of wind energy looks promising. By embracing this renewable energy source, society can progress towards achieving energy independence, economic stability, and environmental sustainability.
In summary, wind energy is more than just electricity generation; it is a catalyst for economic transformation and environmental preservation. As the world grapples with the pressing repercussions of climate change, harnessing the wind’s potential is not merely beneficial; it is essential. Wind energy stands as a testament to humanity’s capacity to embrace clean, renewable solutions while pursuing a sustainable and resilient future.