The Law of Conservation of Energy is a fundamental concept in physics that asserts energy cannot be created or destroyed, but only transformed from one form to another. This principle underpins numerous natural phenomena and technological applications, forming the basis for understanding how energy moves through different systems and is utilized or conserved. To appreciate the intricacies of this law, one must explore its various facets, implications, and applications in our daily lives.
This article delves into the core concept of energy conservation, unpacking its nuances and providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance in both a scientific context and practical applications.
Understanding Energy: The Many Forms and Transformations
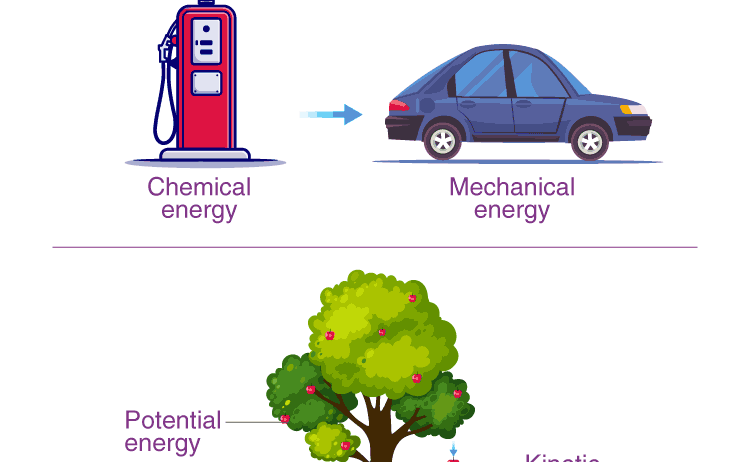
Energy exists in many forms, including kinetic energy, potential energy, thermal energy, chemical energy, and nuclear energy. Each type serves different purposes, yet they are interconnected through various transformations. Kinetic energy, initially harnessed through movement, can be converted into thermal energy, such as when friction generates heat. Similarly, potential energy stored in a compressed spring can be released as kinetic energy once the spring is allowed to expand.
This interplay illustrates the Law of Conservation of Energy. Although energy may change its form, the total energy within a closed system remains constant. For instance, consider a pendulum. At its highest point, the energy is primarily potential, while at its lowest point, it is primarily kinetic. Throughout its swing, energy oscillates between these two forms, illustrating the seamless transitions dictated by the conservation principle.
Everyday Implications: From Appliances to Ecosystems
The ramifications of the Law of Conservation of Energy are palpable in everyday life. This principle governs how we harness energy for use in appliances, vehicles, and even entire facilities. For instance, conventional power plants convert chemical energy from fossil fuels into electrical energy, powering homes and businesses. However, this transformation is not without its inefficiencies, as some energy invariably dissipates as heat—an aspect of energy management that underscores the need for sustainable practices.
Moreover, understanding this law is essential for grasping ecological dynamics. Ecosystems rely on the transfer and conservation of energy through food webs. Energy from the sun is captured by plants during photosynthesis, storing it as chemical energy. Herbivores consume these plants, converting this energy into a different form, and when they are eaten by carnivores, the cycle continues. This chain of energy transfer exemplifies the conservation law and highlights the importance of each species in maintaining ecological balance.
Conservation in Action: Renewable Energy and Sustainable Solutions
In the quest for sustainable solutions, the Law of Conservation of Energy plays a pivotal role. The shift from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources—such as solar, wind, and hydropower—represents an effort to harness and utilize energy more efficiently. Renewable energy captures naturally occurring energy flows and transforms them into usable forms, promoting sustainability and reducing dependence on finite resources.
Solar Power Revolution
Consider solar energy. Solar panels convert sunlight—radiant energy—into electrical energy. This transition underscores energy conservation principles while simultaneously reducing carbon emissions. By investing in solar infrastructure, societies can capture and utilize renewable energy, effectively decreasing reliance on fossil fuels.
Wind Energy Harnessing
Wind energy serves as another exemplary case. Turbines convert kinetic energy from wind into electrical energy. This transformation not only complies with the conservation laws but also exemplifies an innovative approach to minimizing environmental impact. Countries leading the way in wind energy installation not only secure their energy future but also contribute to global efforts in combating climate change.
Innovative Technologies: Smart Grids and Energy Storage
The future of energy conservation lies in advanced technologies that maximize efficiency. Smart grids, equipped with digital technology, optimize electricity distribution, manage supply and demand in real-time, and minimize energy wastage. By integrating renewable sources, smart grids enhance overall energy conservation efforts, exemplifying a modern approach to sustainability.
Energy storage technologies, such as batteries and capacitors, harness energy generated during peak production (e.g., from solar panels during the day) and release it during times of high demand. This capacity to store and regulate energy flow emphasizes the importance of conservation during periods of excess production and high consumption.
Educational Implications: Spreading Awareness and Fostering Responsibility
The Law of Conservation of Energy is a vital educational topic that fosters awareness about energy usage and responsibility. Teaching this principle in schools empowers future generations with the knowledge necessary to approach energy consumption thoughtfully. Understanding the balance of energy transfer in ecosystems, industries, and society at large encourages sustainable practices and innovative solutions.
Moreover, promoting energy literacy cultivates a sense of stewardship among individuals and communities. This awareness can lead to more responsible energy choices, reduced wastage, and a collective push towards a sustainable future.
Conclusion: The Inexorable Truth of Energy Conservation
The Law of Conservation of Energy is not merely an abstract scientific principle; it is a crucial tenet that informs various facets of our lives. From the myriad forms of energy around us to its fundamental role in ecological systems, understanding this law equips individuals and societies to harness energy sustainably. By advocating for renewable solutions and innovative technologies, we can honor the sacred balance of energy flows and promote a more responsible interaction with our planet’s resources. Recognizing that energy conservation plays a central role in both environmental stewardship and technological advancement is essential for creating a sustainable and prosperous future.