The phenomenon known as the runaway greenhouse effect represents one of the most alarming concepts in climate science. It describes an extreme and uncontrollable rise in a planet’s temperature due to the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. While the Earth’s climate has experienced considerable fluctuations throughout its history, the runaway greenhouse effect symbolizes a threshold that, when crossed, could yield catastrophic consequences for life as we know it.
To better comprehend this phenomenon, it’s essential to delve into its underlying mechanisms, historical context, potential implications, and proactive measures that can be taken to avert such a calamitous event.
Understanding Greenhouse Gases and Their Impact
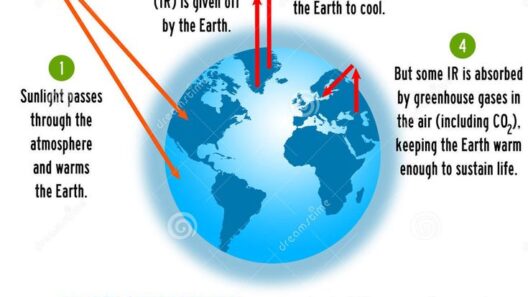
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) allow sunlight to enter the atmosphere but inhibit the escape of heat into space. This process is analogous to how a blanket retains body heat, thereby warming the Earth’s surface. The natural greenhouse effect is critical for maintaining temperatures conducive to life, but an excess of these gases can lead to untenable conditions.
An unchecked release of GHGs primarily results from human activities, such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes. Each of these activities contributes to atmospheric concentrations of gases that trap heat. When the balance tilts too far toward GHG emission, the result can be a runaway situation, where warming accelerates due to feedback loops. For instance, as ice melts, less sunlight is reflected back into space, further exacerbating warming.
The Historical Prelude to Runaway Greenhouse Effects
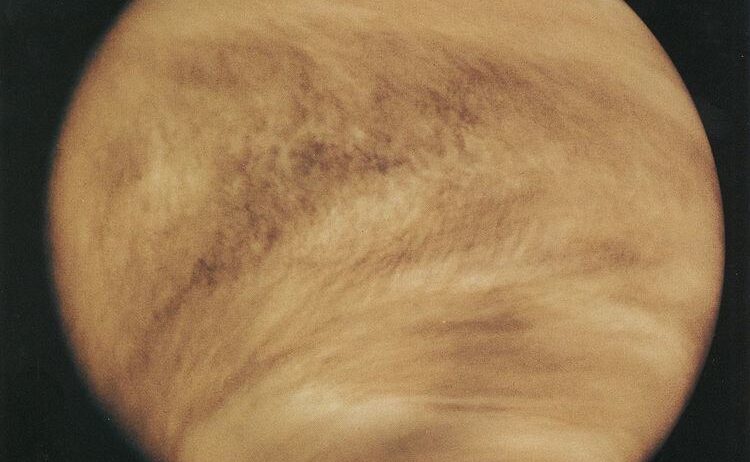
History is littered with examples of planets that have suffered from runaway greenhouse effects, most notably Venus. Venus, with its thick atmosphere composed primarily of carbon dioxide, experiences surface temperatures hot enough to melt lead. What was once a potentially habitable world devolved into an inhospitable environment, demonstrating how extreme warming can render a planet lifeless.
Scientists hypothesize that early in its history, Venus may have had substantial water bodies similar to Earth. However, as the Sun intensified over billions of years, the planet’s water vapor evaporated, leading to a greenhouse effect that spiraled out of control. The story of Venus serves as a chilling reminder of the fine line between habitability and desolation.
The Mechanisms Behind a Runaway Greenhouse Effect
The core mechanism that drives a runaway greenhouse effect involves various positive feedback loops. As temperatures rise, several things can occur:
– **Water Vapor Amplification**: Warmer temperatures increase evaporation rates, leading to more water vapor in the atmosphere. Given that water vapor is a potent greenhouse gas, its rising concentration further enhances warming, creating a vicious cycle.
– **Permafrost Thawing**: The melting of permafrost releases large amounts of methane, a greenhouse gas with a heat-trapping capacity significantly greater than carbon dioxide over a short timescale. This release exacerbates warming, leading to further permafrost degradation.
– **Oceanic Absorption Limits**: The world’s oceans absorb vast quantities of CO2, serving as a buffer against rising atmospheric levels. However, as oceans warm, their ability to absorb CO2 diminishes. When they reach saturation, the atmosphere will inevitably experience elevated greenhouse gas concentrations, intensifying the greenhouse effect.
The Consequences: A World Altered
Should a runaway greenhouse effect occur, the repercussions for life on Earth would be severe. Entire ecosystems would face collapse, agricultural practices would be rendered moot, and the human population could see unprecedented displacement due to rising sea levels and uninhabitable land. Wildlife would struggle to adapt to rapidly shifting conditions, leading to cascading extinctions.
Moreover, the psychological and social ramifications must not go unnoticed. The strain on resources could engender conflict, deepening socio-economic divides and impacting global stability. Human civilization as we know it operates at the interface of delicate climatic conditions. Disruption of this balance renders the future profoundly uncertain.
Mitigating Risks: Combatting Climate Change
The prospect of a runaway greenhouse effect underscores the pressing need for rigorous climate action. Steps must be taken to curtail greenhouse gas emissions significantly and implement sustainable practices. Some proposed measures include:
– **Transitioning to Renewable Energy**: Utilizing solar, wind, and hydroelectric power can drastically reduce reliance on fossil fuels. The sooner societies pivot to sustainable energy sources, the lower the emissions will remain.
– **Reforestation and Afforestation**: Planting trees not only captures carbon dioxide but also restores biodiversity and enhances local climates. Forests are crucial allies in the fight against climate change.
– **Innovative Technologies**: Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies should be further developed and deployed. These technologies can help mitigate emissions from the most challenging sectors, such as heavy industry.
Conclusion: An Urgent Call for Action
The runaway greenhouse effect poses one of the most dire threats faced by our planet. It is a complex interplay of climate systems that could lead to unalterable changes in the conditions that sustain life. The historical lesson from Venus is clear: without vigilant environmental stewardship, humanity risks tumbling down a path toward irreversible damage. Awareness, education, and concerted action are paramount in our efforts to prevent such catastrophic outcomes. It is incumbent upon every individual, community, and nation to unite against this looming crisis and inculcate sustainable practices that can preserve our planet for generations to come.