Climate change is an intricate and pressing issue that has captivated the attention of scientists, policymakers, and the general public alike. It refers to significant alterations in temperature, precipitation, wind patterns, and other elements of the Earth’s climate that persist over an extended period—often years or even decades. But what exactly do we mean by climate change, and why is it so crucial to understand?
At its core, climate change is primarily driven by human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas. These activities release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, trapping heat and leading to a gradual rise in global temperatures. Imagine a greenhouse, where sunlight enters and warms the interior, but the heat cannot escape. This is akin to how greenhouse gases operate in our planet’s atmosphere.
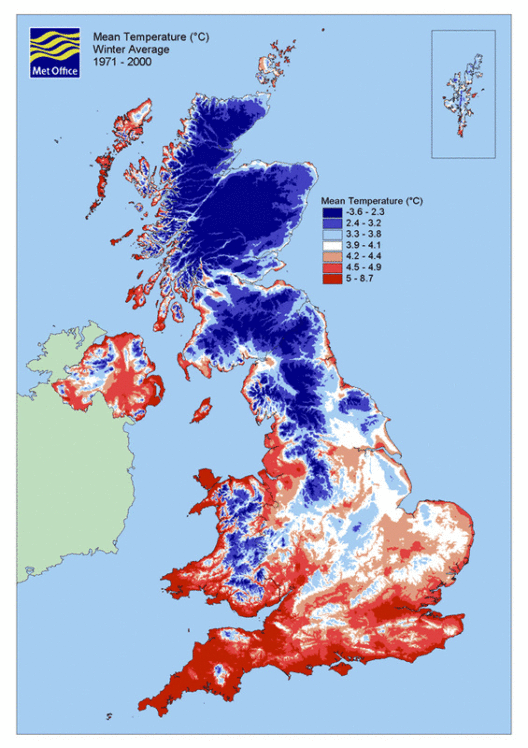
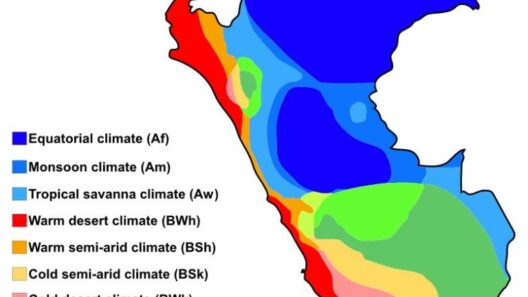
Have you ever stopped to ponder how this warming climate alters the world around us? As the temperature escalates, it unleashes profound consequences on ecosystems, weather patterns, and human societies. For instance, warmer temperatures are intricately linked to more severe and frequent weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and floods. What would happen if your hometown suddenly became prone to such extreme weather? The resilience of communities is constantly challenged in the face of an increasingly unstable climate.
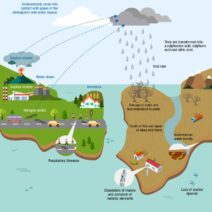
The definition of climate change is not merely an environmental catchphrase; it encompasses a complex interplay of scientific principles. The planet’s climate system comprises various components, including the atmosphere, oceans, land surface, and ice masses. The interconnectivity of these systems means that changes in one area can precipitate shifts in another. For instance, melting glaciers and the polar ice caps contribute to rising sea levels, endangering coastal cities and ecosystems worldwide.
Furthermore, climate change engenders biodiversity loss, threatening species’ survival and disrupting the balance of ecosystems. Coral reefs, often dubbed the “rainforests of the sea,” are particularly vulnerable to rising sea temperatures and acidification. If these vibrant underwater cities diminish, what does that imply for the myriad of species that rely on them for sustenance and habitat? The ramifications extend far beyond the aquatic realm, as the loss of biodiversity can destabilize food webs and diminish natural resources crucial for human survival.
As the climate warms, we also witness rapid shifts in agricultural systems. Crop yields can be adversely affected by changes in temperature and precipitation patterns. Many regions may become less hospitable for traditional farming, compelling communities to adapt to new crops or face food insecurity. If you were a farmer, how would you confront the uncertainties posed by a warming planet? This question highlights the pressing need for adaptation strategies in agricultural practices.
Moreover, climate change elucidates the concept of social justice. Vulnerable communities, often those least responsible for greenhouse gas emissions, bear the brunt of its impacts. This disparity raises ethical considerations about responsibility and equity. As climate change exacerbates poverty, displacement, and health issues, how can we ensure that solutions are inclusive and equitable? This challenge invites us to rethink our priorities and advocate for policies that support the most affected populations while addressing the broader environmental crisis.
To counteract climate change, scientists and researchers emphasize mitigation strategies. These initiatives aim to reduce or eliminate the sources of greenhouse gas emissions, thereby curbing the effects of climate change. Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower is pivotal in this endeavor. But is the technology and infrastructure in place to support such a transition on a global scale? The answer lies in collective action and investment in sustainable solutions.
Furthermore, protecting and enhancing natural carbon sinks—forests, wetlands, and oceans—is equally vital in absorbing CO₂ from the atmosphere. These ecosystems not only help mitigate climate change but also provide invaluable services such as clean water, biodiversity, and recreational spaces. Imagine the transformative potential of restoring degraded landscapes and the myriad benefits that would follow for communities and wildlife alike.
Public awareness and education play critical roles in our quest to conquer climate change. Understanding its multifaceted impacts can inspire individuals to take actionable steps in their own lives. Simple acts of conservation—reducing waste, conserving energy, and choosing sustainable products—can collectively make a significant difference. Have you ever considered how your daily choices can contribute to a more sustainable world? Each decision, no matter how small, carries weight in the larger environmental tapestry.
Moreover, policy changes at local, national, and international levels are paramount in aligning societal goals with sustainable practices. Governments must prioritize climate action, invest in clean energy infrastructure, and enforce regulations that limit carbon emissions. As citizens, advocating for these changes requires engagement and persistence. Are you willing to take up the challenge of holding leaders accountable and demanding action on climate change?
In conclusion, climate change is a complex phenomenon arising from human activity that has far-reaching consequences across the globe. Understanding the intricacies of this issue is paramount for fostering informed conversation and inspiring action. By recognizing our individual and collective responsibilities, we can tackle the challenges posed by climate change head-on. Indeed, it is a formidable task, but together, we possess the ingenuity and resolve to effect meaningful change. The time to act is now; the future of our planet depends on it.