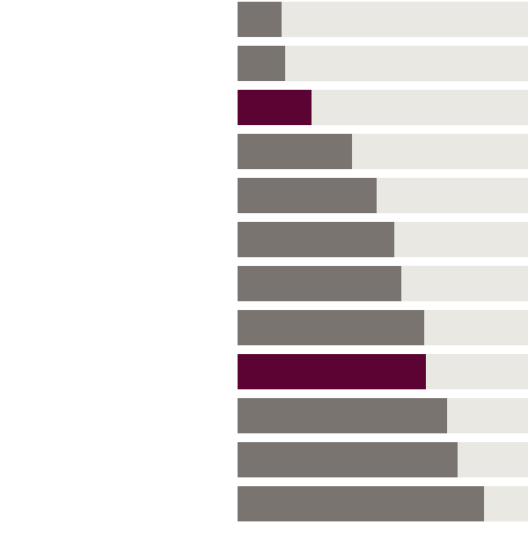Climate protection encompasses a broad range of actions and initiatives aimed at safeguarding the Earth’s atmosphere and ecosystems. This practice is born out of an urgent need to address the increasing threats posed by climate change, driven by human activities such as deforestation, fossil fuel consumption, and industrial pollution. At its most basic level, climate protection is not merely about conservation, but rather a holistic approach that combines environmental stewardship with social and economic elements.
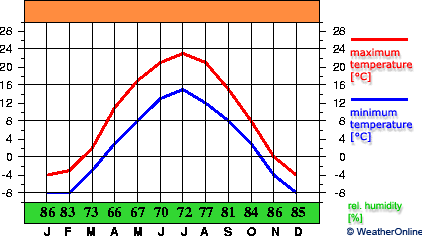
Understanding the scope of climate protection necessitates an exploration of its foundational concepts. The phenomenon of climate change is rather insidious; it reveals itself through rising temperatures, erratic weather patterns, and the proliferation of extreme weather events. These changes have cascading effects on biodiversity, human health, and global food security. Therefore, efforts to protect our climate are critically important.
The significance of climate protection cannot be overstated. It is imperative for enhancing the resilience of ecosystems, securing the health and welfare of current and future generations, and maintaining the Earth’s natural resources. As stewards of the planet, humanity possesses the capacity and responsibility to enact change. This responsibility evokes emotions ranging from dread to hope, as the potential for restoration exists within our collective actions.
Addressing climate change requires multifaceted strategies. One prominent approach is the transition to renewable energy sources. The reliance on fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, has been a prime contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. By shifting towards solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, society can mitigate these emissions significantly. Moreover, advancements in technology are paving the way for more efficient energy solutions, allowing industries and households alike to reduce their carbon footprints.
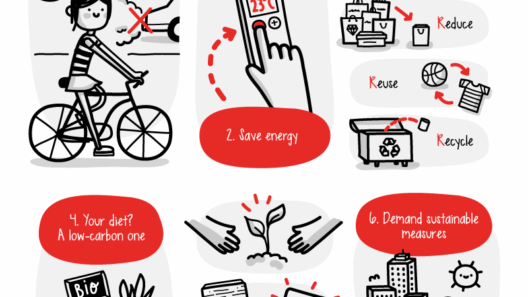
Complementing energy transition is the critical practice of energy conservation. Simple actions such as improving energy efficiency in homes, promoting public transportation, and utilizing energy-efficient appliances can lead to substantial reductions in energy consumption. Building codes and organizational policies that prioritize energy efficiency not only help combat climate change but can also result in significant cost savings for individuals and businesses alike.
Another essential component of climate protection involves reforestation and conservation of natural habitats. Forests act as carbon sinks, capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide. Consequently, preserving existing forests and planting new trees forms a key strategy in addressing climate change. Additionally, conserving biodiversity is paramount. An array of species contributes to ecological balance, which is crucial in adapting to climate challenges. Protecting wildlife habitats and promoting sustainable land use practices play an integral role in this endeavor.
Climate protection also encompasses sustainable agricultural practices. Agriculture is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, yet it is also vulnerable to climate change. Sustainable agriculture emphasizes practices such as crop rotation, reduced pesticide use, and organic farming methods which improve resilience against climate impacts and enhance soil health. By adopting these methods, food security is reinforced while simultaneously reducing environmental repercussions.
Education and awareness campaigns are indispensable tools in the climate protection toolkit. Engaging communities, schools, and organizations in discussions about climate change elevates understanding and fosters a culture of sustainability. Raising awareness about the consequences of climate change and the importance of individual actions propels collective momentum toward systemic change. It empowers individuals to adopt eco-friendly practices, such as recycling, water conservation, and reduced consumption of single-use plastics.
Policy frameworks and governmental advocacy play a crucial role in promoting climate protection at scale. Legislation aimed at regulating emissions, protecting vulnerable ecosystems, and incentivizing green technologies drives larger systemic changes. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, underscore the need for nations to collaborate in mitigating climate change effects. By adopting binding targets and regularly reporting progress, countries can enhance accountability and foster a cooperative approach to this global concern.
Moreover, the intersection of climate justice and protection must not be overlooked. Marginalized communities often endure the brunt of climate impacts despite contributing the least to the problem. Fair and equitable climate policies that incorporate diverse voices into decision-making processes are essential. Addressing the disparities in vulnerability and capacity to respond to climate change ensures that climate action benefits all, rather than exacerbating existing inequalities.
Ultimately, each individual holds power in the quest for climate protection. Simple lifestyle changes can accumulate into significant impact. This includes reducing meat consumption, opting for public transport or cycling, and supporting local, sustainable businesses. By making conscious choices, individuals contribute to a larger movement aimed at collective change. Awareness and education ultimately serve as catalysts for broader societal shifts towards sustainability.
In conclusion, climate protection is an imperative journey that necessitates collaborative action across multiple spheres of society. From transitioning to renewable energy sources to nurturing ecosystems and implementing sustainable practices, the mechanisms for climate protection are both complex and deeply interconnected. The commitment to safeguarding our planet is not only an ethical obligation but a practical necessity for the survival of future generations. Encouraging collective efforts towards sustainability enhances resilience, promotes equity, and underpins the foundation of a thriving Earth. It is our collective responsibility to advocate for and build a sustainable future, for the longevity of our planet depends on it.