Cogeneration, often referred to as combined heat and power (CHP), is an innovative energy conservation strategy that significantly enhances the overall efficiency of energy use. This dual-purpose technology simultaneously generates electricity and captures usable heat that would otherwise be wasted during traditional energy generation processes. With cogeneration, industries and buildings can take a substantial step towards reducing their energy expenditures and environmental impacts while maximizing the utilization of their fuel resources.
As the demand for energy continues to rise, cogeneration stands out as a practical solution. It addresses key buyer concerns regarding energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and operational costs. By harnessing the power of cogeneration, businesses and facilities can adopt a more responsible and economically viable path towards energy management.
Understanding the principles and advantages of cogeneration is essential for anyone interested in energy conservation and sustainability. This article will explore the intricacies of cogeneration, how it operates, its myriad benefits, and its impact on energy conservation.
The Fundamentals of Cogeneration: An Overview
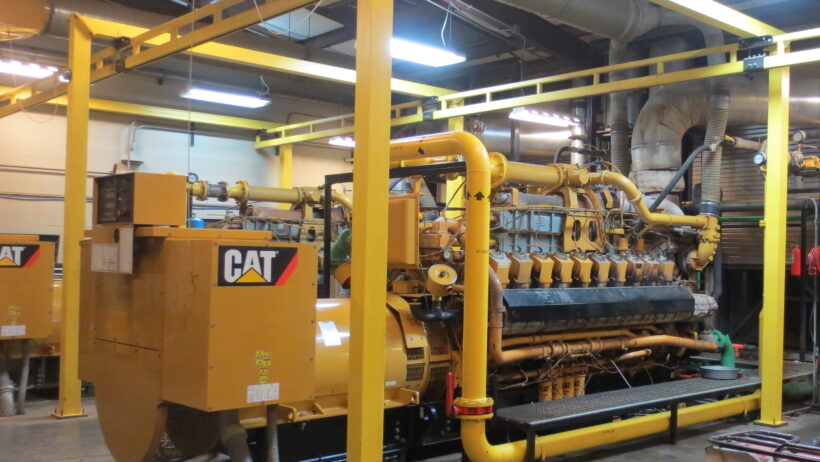
Cogeneration systems operate on a straightforward premise: they improve overall energy efficiency by simultaneously producing electricity and capturing the thermal energy usually lost in conventional power generation. Typically, a cogeneration setup combines a power generation unit, such as a gas turbine or reciprocating engine, with heat recovery mechanisms like heat exchangers or steam turbines.
When fuel is combusted to generate electricity, a significant amount of heat is produced. In traditional plants, this heat is often vented into the atmosphere, leading to energy loss. However, cogeneration captures this thermal output and repurposes it for heating water, space heating, industrial processes, or even district heating systems.
Cogeneration systems can be powered by various fuels including natural gas, biomass, or even waste-derived fuels. This versatility allows businesses across multiple sectors to adopt cogeneration tailored to their specific energy needs and environmental goals.
The Energy Efficiency Revolution: How Cogeneration Saves Energy
One of the primary motivations for adopting cogeneration technology is its remarkable efficiency. Traditional power plants usually operate at an efficiency of between 30% to 40%. By contrast, cogeneration systems can achieve efficiencies exceeding 80%. This significant improvement translates into a direct reduction in energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Reducing Energy Bills: The Economic Advantage
Implementing a cogeneration system can lead to substantial financial savings. Energy costs represent a significant expenditure for many businesses. With cogeneration, the ability to produce both power and heat on-site means lower reliance on grid electricity, minimizing energy bills in the process. Additionally, excess electricity generated can often be sold back to the grid, creating a potential revenue stream.
Cogeneration systems can also mitigate the impact of energy price volatility. By producing energy on-site, businesses can insulate themselves against fluctuating energy markets, further enhancing their financial stability.
Environmental Benefits: A Sustainable Approach
Beyond financial incentives, cogeneration implies a strong commitment to environmental stewardship. A substantial reduction in carbon emissions is one of the most significant advantages of adopting cogeneration technology. For each unit of energy produced, cogeneration emits fewer greenhouse gases compared to separate heat and power generation methods. This reduction contributes to the global efforts to combat climate change and promote sustainability.
Furthermore, the flexibility of cogeneration allows for the utilization of renewable energy sources. By leveraging biomass or biogas, cogeneration can effectively reduce the carbon footprint of energy production, aligning with a growing demand for greener alternatives in energy generation.
Applications of Cogeneration: Where Efficiency Meets Utility
Cogeneration is not limited to industrial applications; it has found success across several sectors, including commercial, institutional, and residential settings.
Industrial Use: Powering Production Processes
Industries with high thermal and electrical energy demands, such as food processing, chemical manufacturing, and pulp and paper, benefit greatly from cogeneration. The simultaneous production of heat and power supports various operational processes, such as steam generation, which is essential in many manufacturing workflows.
Commercial Deployment: Enhancing Buildings
In commercial buildings, cogeneration systems can significantly improve energy efficiency. Providing heating, cooling, and electricity on-site, these systems help businesses meet their energy needs while reducing operating costs. Hospitals, hotels, and office complexes are increasingly adopting cogeneration to enhance their energy profiles and ensure reliability.
Residential Applications: Bringing Efficiency Home
Though less common, residential cogeneration systems are gaining traction, particularly in areas where energy costs are high and grid reliability is uncertain. Homeowners can install micro-cogeneration units, providing electricity and heat for their households. This not only leads to reduced utility bills but also increases energy independence.
Challenges and Future of Cogeneration
While cogeneration technology offers numerous advantages, it is not without its challenges. The initial capital investment can be significant, which may deter some potential adopters. Additionally, regulatory hurdles and the need for adequate infrastructure can hinder widespread implementation.
However, as technology advances and the push for energy conservation becomes more pronounced, cogeneration is poised for growth. Innovative funding models, supportive policies, and increasing awareness of the environmental benefits are likely to pave the way for broader acceptance.
In conclusion, cogeneration represents a pivotal advancement in energy conservation. By producing electricity and capturing waste heat, it enhances energy efficiency, supports financial savings, and contributes to environmental sustainability. As society faces pressing energy challenges, embracing innovative solutions like cogeneration is not only beneficial but essential for a sustainable future.