The concept of energy conservation is foundational in the realm of physics, playing a pivotal role in understanding a myriad of natural phenomena. At its core, conservation of energy refers to the principle that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. This principle shapes the laws of physics and underpins various scientific disciplines, ranging from mechanics to thermodynamics and beyond.
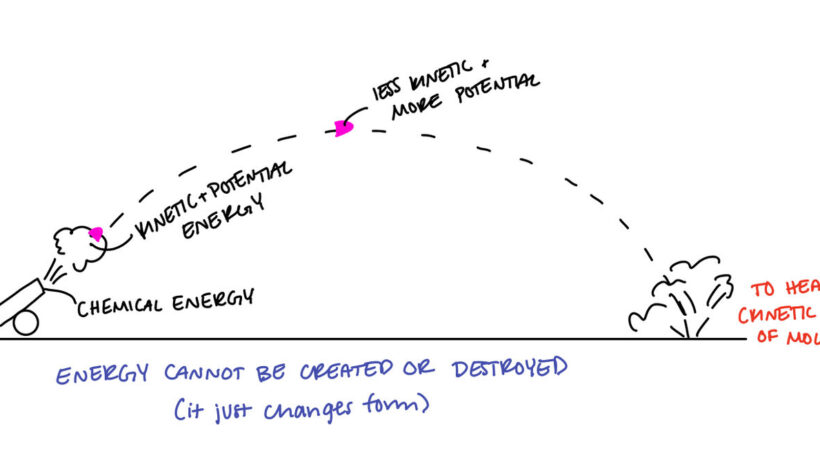
The principle of conservation of energy is often encapsulated in the first law of thermodynamics. This law states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant; energy can only change forms, such as potential energy converting to kinetic energy. For instance, when an archer draws back a bowstring, the energy expended by the archer is stored as potential energy in the bow. Upon release, this potential energy transitions into kinetic energy, launching the arrow forward. Such transformations are not merely commonplace; they provide a window into the very fabric of our universe, showcasing the elegance of physical laws at work.
Consider the example of a roller coaster. As the coaster climbs to the top of a hill, energy is stored in the form of gravitational potential energy. At the apex, the coaster possesses maximum potential energy and minimal kinetic energy. As it begins its descent, potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy, resulting in swift acceleration. The interplay of these energy forms occurs in a cycle, creating a thrilling experience while simultaneously obeying the laws of conservation.
This dynamic energy exchange is evident in everyday life, providing a tangible demonstration of conservation principles. For instance, when a car accelerates, chemical energy stored in fuel undergoes conversion, eventually manifesting as mechanical energy to propel the vehicle forward. However, what lies beneath these observable phenomena is a more profound consideration regarding the efficiency of energy transformations. Energy often dissipates as heat due to friction and other inefficiencies, presenting challenges in harnessing energy for desired purposes.
Understanding the mechanisms behind energy conservation illuminates its significance in environmental sustainability. The pressing need to conserve energy stems from finite resources and environmental implications associated with energy consumption. Fossil fuels, while rich in energy, release greenhouse gases upon combustion, contributing to climate change and ecological degradation. Therefore, it is imperative to explore sustainable alternatives that maximize the principles of conservation. Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, exemplify the transformative capacity of harnessing natural energy while aligning with conservation principles.
The fascination with energy conservation extends into theoretical realms, inviting inquiry into the fundamental nature of the universe. For example, physicists contemplate the conservation of energy within the context of quantum physics. At this minuscule scale, energy conservation behaves in unexpectedly nuanced ways, invoking principles like uncertainty. The notion of virtual particles fleetingly appearing and vanishing challenges traditional definitions, yet they obey energy conservation principles when considered across broader timescales. Such explorations tease out the convergence of conservation laws with the deepest aspects of physical reality, revealing an intricate tapestry underpinning existence.
Delving deeper, conservation of energy intertwines with concepts like entropy and the second law of thermodynamics, which posits that in an isolated system, entropy tends to increase. This increase signifies the dispersion of energy and heat, driving the arrow of time forward. While energy remains conserved, its usability diminishes over time, paving the way for larger discussions on energy quality and sustainability. Engineers, researchers, and policymakers alike grapple with the challenge of managing energy flows within this framework, striving to utilize resources efficiently while ensuring minimal ecological impact.
Moreover, the conservation of energy principle resonates broadly across applications in engineering and technology. Innovations in energy-efficient technologies—such as electric vehicles, energy-efficient appliances, and smart grid systems—underscore the practical implications of conservation. Each innovation encapsulates the spirit of adapting energy conservation principles to contemporary challenges, pointing towards a future that respects and employs these natural laws.
In educational contexts, conveying the importance of energy conservation adopts a foundational importance, shaping future generations’ understanding of physics and environmental stewardship. By emphasizing the concept of energy transformations, educators equip students to navigate the complexities surrounding energy use in modern society. This knowledge fosters a culture of responsibility, encouraging informed decisions about energy consumption that reflect an awareness of broader ecological implications.
Lastly, the engaging nature of energy conservation invites individuals to appreciate the interconnectedness of scientific principles and their manifestations in the world around them. It invites an acknowledgment of the cosmic dance wherein energy lies at the heart of existence. As one contemplates the various forms of energy—thermal, mechanical, chemical, and beyond—an appreciation arises for the cyclical resilient nature of energy, continuously reiterating the notion that while energy can change its guise, its essence remains fundamentally unchanged.
In conclusion, conservation of energy is not merely a scientific principle; it is a lens through which we observe the world, an imperative that pushes humanity towards more sustainable practices. The delicate balance of energy transformation encapsulates the essence of physics, revealing profound connections to the environment and our collective future. Addressing energy conservation hones a collective awareness of our actions and their consequences, shaping a world where responsible use of energy paves the way for a sustainable future.