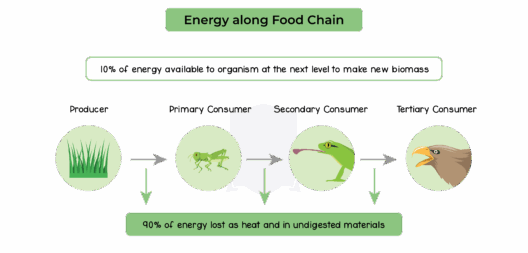
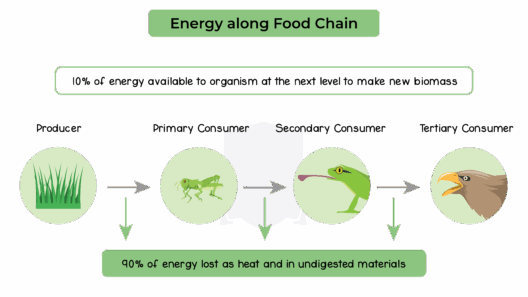
In an age marked by rapid industrialization and burgeoning urbanization, the conservation of energy resources emerges as an imperative endeavor. Its significance extends beyond mere utility management to encompass broader existential threats posed by climate change, resource depletion, and environmental degradation. The concept of conserving energy resources embodies a crucial synergy between environmental stewardship and economic rationality, seeking not only to optimize energy use but also to safeguard the planet’s natural reserves for future generations.
At its core, conservation of energy resources entails the prudent and judicious use of available energy sources while minimizing waste. This involves a deliberate approach to energy consumption and a commitment to enhancing energy efficiency across various sectors, including residential, commercial, and industrial domains. It is essential to recognize that energy resources are finite. Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, remain the predominant energy sources globally. Their extraction and combustion have a substantial ecological footprint, emitting greenhouse gases that exacerbate climate change. Therefore, transitioning to sustainable energy practices is paramount.
One of the most compelling motivations for energy conservation lies in the palpable phenomenon of climate change. The correlation between carbon emissions and rising global temperatures is irrefutable. Energy conservation plays a pivotal role in mitigating the adverse effects of climate change by reducing fossil fuel reliance and promoting cleaner energy alternatives. By implementing energy-efficient technologies and practices, we can collectively diminish our carbon footprint, thus contributing to a healthier atmosphere.
Moreover, energy conservation is intricately linked to economic viability. As populations grow and economies expand, the demand for energy is expected to soar. This surge in demand could potentially outpace supply, resulting in increased energy prices and economic instability. Consequently, cultivating a culture of energy conservation is not only environmentally responsible but also economically prudent. Investments in energy-efficient infrastructure and renewable energy sources can yield substantial long-term financial savings for both consumers and businesses alike.
The implementation of energy conservation strategies often begins at the grassroots level. Households can lead the charge by adopting energy-efficient appliances, utilizing smart technology, and incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels. Simple behavioral changes, like turning off lights when leaving a room or reducing thermostat settings during winter, can cumulatively result in significant energy savings. Educational programs aimed at raising awareness about energy conservation can empower individuals to adopt sustainable practices in their daily lives.
In commercial and industrial sectors, energy conservation takes on a multifaceted approach. Corporations can conduct energy audits to identify inefficiencies in their operations and subsequently implement measures to optimize consumption. This may involve transitioning to LED lighting, investing in energy-efficient HVAC systems, or utilizing energy management systems to monitor and control energy usage in real time. Adopting renewable energy sources can further amplify these efforts. Companies that prioritize energy conservation not only enhance their operational efficiency but also reinforce their corporate social responsibility, which can enhance their reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Furthermore, the role of government in promoting energy conservation is indispensable. Policymakers can incentivize conservation efforts through legislation, subsidies for renewable energy projects, and heightened regulations aimed at reducing energy consumption in various industries. Implementing energy efficiency standards for appliances, vehicles, and buildings can dramatically reduce energy demand on a macro scale. Government campaigns aimed at educating the populace on energy conservation practices can also facilitate a widespread cultural shift toward sustainability.
However, the pursuit of energy conservation is not without challenges. Resistance from industries reliant on fossil fuels and the inertia of established energy consumption habits often impede progress. To overcome these obstacles, a collaborative approach that involves stakeholders from all sectors—government, industry, and consumers—is essential. Strategies such as public-private partnerships can foster innovation and accelerate the transition to sustainable energy practices.
Another emerging trend in energy conservation is the concept of the circular economy. This model emphasizes reducing waste and reusing materials, thereby creating a closed-loop system that minimizes the demand for new resources. In the context of energy, this translates to utilizing waste energy from industrial processes or repurposing materials to generate energy, effectively lessening our reliance on virgin energy sources.
Innovation in technology also plays a crucial role in advancing energy conservation. The rise of smart grids, energy storage solutions, and advancements in renewable energy technologies exemplify the potential for smarter energy systems. These innovations not only enhance efficiency but also enable greater integration of renewable sources into the energy mix. With the proliferation of electric vehicles and energy-efficient technologies, the paradigm of energy consumption is shifting toward sustainability.
In conclusion, the conservation of energy resources is a multifaceted endeavor that intertwines environmental sustainability, economic rationality, and technological innovation. Addressing the urgent issues of climate change, resource depletion, and economic instability necessitates a collective commitment to energy conservation. By fostering a culture of conservation at all levels of society, from households to industries and governments, we pave the way for a sustainable and prosperous future. The journey toward responsible energy use requires concerted effort and collaboration, ensuring that both present and future generations can thrive within a balanced ecosystem.