Energy conservation within healthcare institutions stands as a pivotal yet often underestimated component of environmental stewardship. This principle, while predominantly associated with domestic and industrial domains, extends its reach unambiguously into the realm of healthcare, where the stakes are particularly high. Hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities consume vast amounts of energy, not only for lighting and heating but also for sophisticated medical equipment and technology. As a result, the significance of energy conservation in this sector cannot be overstated; it represents a crucial opportunity to mitigate environmental impact while simultaneously enhancing operational efficiency.
The essence of energy conservation lies in the deliberate and strategic reduction of energy consumption through measures that improve efficiency without detrimentally impacting service delivery. In healthcare, this translates into various interventions, ranging from facility management practices to the incorporation of cutting-edge technology. Indeed, embracing energy conservation not only fosters a sustainable environment but also liberates financial resources that can be repurposed for patient care and critical services.
First and foremost, the operational inefficiencies within healthcare systems expose a dire need for energy conservation strategies. Hospitals operate around the clock and employ complex systems for heating, cooling, and ventilation. Inadequate management can lead to excessive energy consumption, with studies indicating that healthcare facilities are responsible for approximately 8-10% of the total carbon footprint in the United States. This staggering statistic highlights a dual imperative: reducing energy use must become an integral part of healthcare management strategies.
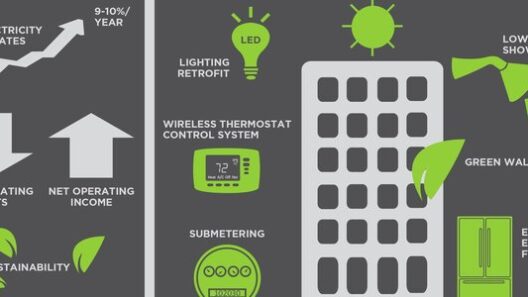
In examining energy conservation techniques in healthcare settings, one must acknowledge the role of infrastructure upgrades. Retrofitting older facilities with energy-efficient lighting systems, advanced HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) technologies, and enhanced building insulation represents a significant step towards greater energy efficiency. For instance, transitioning from traditional incandescent bulbs to LED lighting can result in energy savings upwards of 80%. These seemingly mundane upgrades usher in a transformative potential, not just for energy savings, but also for elevating the quality of the work environment for healthcare workers.
Moreover, the implementation of smart technologies has revolutionized energy conservation in healthcare. The Internet of Things (IoT) enables real-time monitoring and management of energy systems, ensuring that energy is consumed judiciously. Automated systems control lighting and climate based on occupancy, and sophisticated algorithms predict and respond to demand, thus optimizing energy use. By employing smart meters and energy management systems, healthcare facilities can analyze usage patterns and identify inefficiencies, further propelling their energy conservation efforts.
Additionally, fostering a culture of sustainability within healthcare organizations is paramount. Engaging staff in energy conservation initiatives can amplify overall impact. Training programs that emphasize energy awareness can empower employees to adopt energy-efficient practices in their daily responsibilities. Simple actions—such as turning off lights in unoccupied rooms or utilizing equipment only when necessary—can cumulatively generate substantial savings over time. This cultural shift not only propels operational efficiency but also galvanizes a collective commitment to environmental stewardship.
Innovations in medical technology also present avenues for energy conservation. The burgeoning field of telemedicine, for instance, allows for remote consultations, significantly reducing the need for facility-based services. This not only saves energy but also enhances patient accessibility. Furthermore, the development of energy-efficient medical devices, such as low-energy MRI machines and bionic prosthetics with optimized energy consumption, epitomizes the intersection of medical advancement and ecological responsibility.
Nevertheless, challenges remain. The upfront costs associated with implementing energy-efficient solutions can deter healthcare facilities from committing to such strategies. Convincing stakeholders to invest in energy conservation endeavors—despite the long-term benefits—requires a paradigm shift in healthcare financing models. Public and private incentives, including grants and tax credits for adopting green technologies, can ameliorate this barrier. Moreover, the fiscal arguments are compelling: with energy costs continuing to rise, facilitating a transition to a more energy-efficient landscape offers substantial cost-savings potential.
Moreover, as healthcare facilities increasingly integrate energy conservation into their strategic frameworks, they can drive broader systemic change. Collaborations between healthcare providers and energy agencies can yield innovative solutions tailored specifically for the unique demands of the healthcare sector. Such partnerships may involve shared resources, research initiatives, and the dissemination of best practices, ultimately fostering a holistic approach to sustainability in healthcare.
Crisis moments, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, have also illuminated vulnerabilities in current energy practices within healthcare. As telehealth options proliferate, healthcare facilities have experienced surges in energy demand due to increased reliance on technological infrastructures. This impetus emphasizes the necessity of adaptive energy management strategies that can respond efficiently to diverse and fluctuating operational demands.
In conclusion, energy conservation in healthcare is not merely a benefit—it’s an essential tenet of modern healthcare delivery. By fundamentally re-orienting practices towards energy efficiency, healthcare institutions can significantly reduce their environmental footprint while simultaneously enhancing service delivery and operational viability. Exploring diverse techniques, from infrastructure upgrades to smart technologies and cultural engagement, offers a multifaceted approach that promises substantive, sustainable results. As the healthcare sector embraces a greener future, energy conservation will transform from an obligation into an enduring commitment that benefits public health, the environment, and organizational resilience.