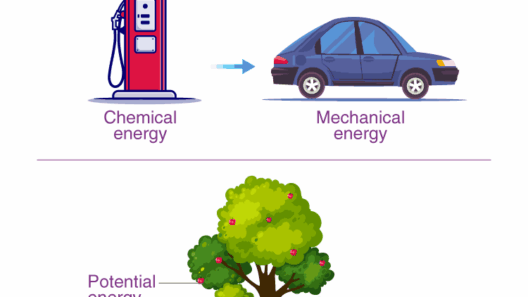
Energy conservation planning is an essential component of sustainable development. It encompasses a multifaceted approach to ensuring that energy resources are used judiciously and responsibly. This type of planning adopts strategies that aim not only to reduce energy consumption but also to promote renewable energy sources and improve energy efficiency across various sectors. In a world grappling with climate change and dwindling fossil fuel reserves, energy conservation planning emerges as a beacon of hope, illuminating pathways toward a sustainable future.
The crux of energy conservation planning lies in its ability to integrate various strategies—technological, behavioral, and policy-oriented—into a cohesive framework. This synthesis is critical for curtailing energy waste while enhancing economic productivity. It is imperative for stakeholders, including government bodies, businesses, and individuals, to understand the diverse strategies that contribute to energy conservation. Here, we delve into these strategies to underscore their significance in fostering a sustainable future.
One primary strategy within energy conservation planning is the implementation of energy efficiency measures. This involves the adoption of technologies and practices that allow for the same level of service or output but with reduced energy input. For instance, utilizing LED lighting instead of traditional incandescent bulbs can significantly lower electricity consumption. Similarly, upgrading heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to high-efficiency models can lead to substantial reductions in energy usage.
Beyond individual technologies, energy efficiency retrofitting in existing infrastructure is a transformative approach. Buildings are significant consumers of energy, and their retrofitting—an upgrade of existing structures to improve energy performance—can lead to dramatic decreases in energy demand. This not only includes insulation improvements but also the installation of energy-efficient windows and state-of-the-art energy management systems. The cumulative effect of such measures contributes substantially to energy conservation at the community and regional levels.
However, energy conservation extends beyond technological advancements. Behavior modification initiatives play a pivotal role in shaping energy consumption patterns. Education and awareness campaigns aimed at informing the public about energy-saving practices can significantly influence consumer behavior. Simple actions such as turning off lights when leaving a room or using public transportation instead of personal vehicles can collectively yield significant energy savings.
Moreover, the concept of demand-side management (DSM) represents a strategic approach aimed at modifying consumer demand for electricity. Through mechanisms such as time-of-use pricing, consumers are incentivized to adjust their electricity usage according to peak and off-peak hours, thus alleviating strain on the grid and promoting energy conservation. Such strategies highlight the importance of consumer engagement in energy conservation planning.
In the realm of policy, governmental initiatives and regulations are paramount. Sustainable energy policies are crafted to support energy conservation efforts through incentives, rebates, and tax credits for energy-efficient appliances, retrofitting, and renewable energy installations. Policies that mandate energy audits for large buildings or that promote the use of renewable energy sources—like solar and wind—are also crucial for fostering a culture of conservation.
Renewable energy integration forms a cornerstone of energy conservation planning. By transitioning away from fossil fuel dependency and toward sustainable alternatives, we can mitigate greenhouse gas emissions while promoting energy security. The implementation of solar panels, wind turbines, and biomass energy systems not only contributes to conservation efforts but also diversifies the energy portfolio, making it resilient to fluctuations in fossil fuel markets.
Another innovative strategy is the adoption of smart grid technologies, which leverage information and communication technologies to enhance the efficiency of electricity distribution. Smart grids enable real-time monitoring of energy usage, facilitate demand response initiatives, and improve the integration of renewable energy sources. This technological advancement fosters a dynamic relationship between energy producers and consumers, creating a more responsive energy ecosystem.
Furthermore, the concept of circular economy principles should be incorporated into energy conservation planning. This approach advocates for the reuse, recycling, and repurposing of materials, which can significantly reduce energy consumption associated with the manufacturing of new products. By focusing on lifecycle impacts and promoting sustainable consumption habits, businesses and consumers alike can become active participants in energy conservation efforts.
As communities worldwide grapple with the ramifications of climate change, energy conservation planning is indispensable in creating a sustainable future. It requires a holistic perspective that encompasses technological innovation, behavioral change, robust policymaking, and public engagement. There is no singular path to energy conservation; rather, it consists of an amalgamation of strategies that collectively drive us toward a more sustainable future.
Ultimately, the success of energy conservation planning hinges on collaboration and commitment from all sectors of society. Stakeholders must recognize the interdependence between energy, the economy, and the environment. As we forge ahead, the focus must remain on cultivating a culture of energy conservation that transcends individual actions and fosters communal responsibility. The importance of this initiative cannot be overstated, as it presents an opportunity to reshape our world and secure a sustainable legacy for future generations.